Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting (CINV) is among the most feared side effects of chemotherapy among cancer patients. It impairs the patient's quality of life and also adds to the morbidity and cost of therapy. That is why the Michigan Oncology Quality Consortium (MOQC)—a physician-led, voluntary collaborative of medical and gynecologic oncologists who work to improve the quality and value of cancer care in Michigan—initiated its Antiemetic Initiative. Through this initiative, MOQC supports participating oncology practices in aligning with current guidelines for use of prophylactic antiemetics, including olanzapine, in patients receiving chemotherapy. The Michigan Value Collaborative (MVC) recently partnered with MOQC to evaluate the impact of this initiative and estimated a cost savings of $334,095 across the course of chemotherapy from the increased use of olanzapine and decreased inpatient admissions in this cohort of patients.
Olanzapine is underused in patients receiving high-emetic-risk chemotherapy, despite evidence of efficacy and good patient tolerance (Navari et al., 2016). Olanzapine is a long-used medication (originally in higher doses for the treatment of psychosis) that is highly effective at decreasing nausea and vomiting. Uptake of olanzapine has been low, however, in part due to oncologists' lack of familiarity with the medication, lack of awareness or agreement with the guidelines, and lack of olanzapine inclusion on prepopulated order sets. The current labeling of olanzapine as an antipsychotic poses an additional barrier since this labeling generates additional concerns about stigma and side effects among patients. A benefit to this medication, in addition to its effect on nausea and vomiting, is its low cost compared with other medicines used to prevent the side effects of chemotherapy; the cost for each pill is about 25 cents.
Practices participating in MOQC’s Antiemetic Initiative receive performance data and baseline assessments in the area of CINV guideline adherence, support in identifying gaps in care and quality improvement measures, and resources for provider and patient education. To help evaluate the impact of this work on guideline-concordant olanzapine use, MOQC first reached out to MVC in 2022 to leverage its robust claims-based data. MOQC hypothesized that patients treated in medical oncology practices with low rates of olanzapine prescribing would have higher rates of healthcare utilization, including hospitalizations, emergency department (ED) visits, and unplanned outpatient visits between treatment cycles. The goal of this analysis was to estimate the initiative's overall impact on healthcare utilization for breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy as well as any related cost savings that improved the value of care delivery.
Methodology
The cohort for this analysis was comprised of female patients with a 90-day claims-based MVC episode of care for lumpectomy or mastectomy in 2016-2021 who received combination chemotherapy with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide as either neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy. The cohort included patients covered by Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan (BCBSM) PPO Commercial, BCBSM PPO Medicare Advantage (MA), Blue Care Network (BCN) HMO Commercial, BCN HMO MA, and Medicare Fee-For-Service. The resulting MVC analysis included episodes for 1,891 patients who had a breast cancer resection, received both chemotherapy drugs on the same day, and were attributed to a MOQC provider/practice. Patients were attributed to 45 of MOQC's participating practices.
Practice-level olanzapine data collected by MOQC was then used to assess whether each patient's first chemotherapy receipt was during a time when their attributed practice had high or low prescribing rates of olanzapine. The threshold for high versus low prescribing at a particular practice was set at a 25% prescribing rate. Once a practice reached 25% prescribing rates of olanzapine in MOQC's data, that practice was considered to have "high" olanzapine prescribing rates in all subsequent months for this analysis. Using that distinction of whether the practice was a high or low prescriber during the course of the patient's chemotherapy regimen, MVC compared post-chemotherapy healthcare utilization among patients treated by high- versus low-prescriber practices. Sub-analyses further restricted the cohort to patients attributed to a practice that ever became categorized as having high olanzapine prescribing rates. When limiting the analysis to practices that became high prescribers at any point, the cohort was narrowed down to patients attributed to 15 MOQC practices.
Limitations
The nature of claims data limited MVC's ability to identify patients attributed to participating oncologists at MOQC practices; the requirement of each patient in the cohort having a MOQC provider NPI on one of their claims reduced the analytic cohort to a smaller size than what would be seen in clinical data. Another limitation is that the findings may include period effects not controlled for in this analysis. Practice behavior and availability of inpatient beds may have differed between when a practice was a low olanzapine prescriber compared to when they began prescribing olanzapine at a higher rate. Finally, payment calculations included in this analysis are limited to dollars saved among the attributed claims-based population and, therefore, do not reflect savings that may be attributed to olanzapine use among the broader population of interest.
Impact & Next Steps
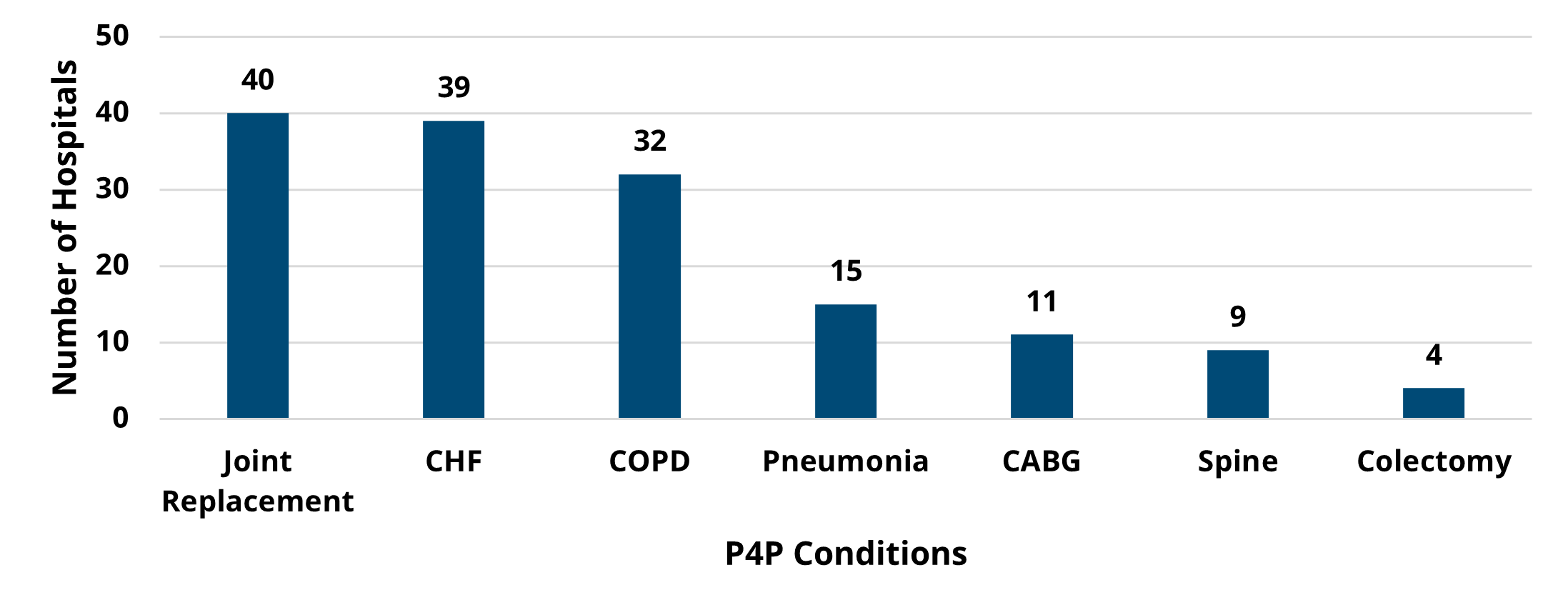
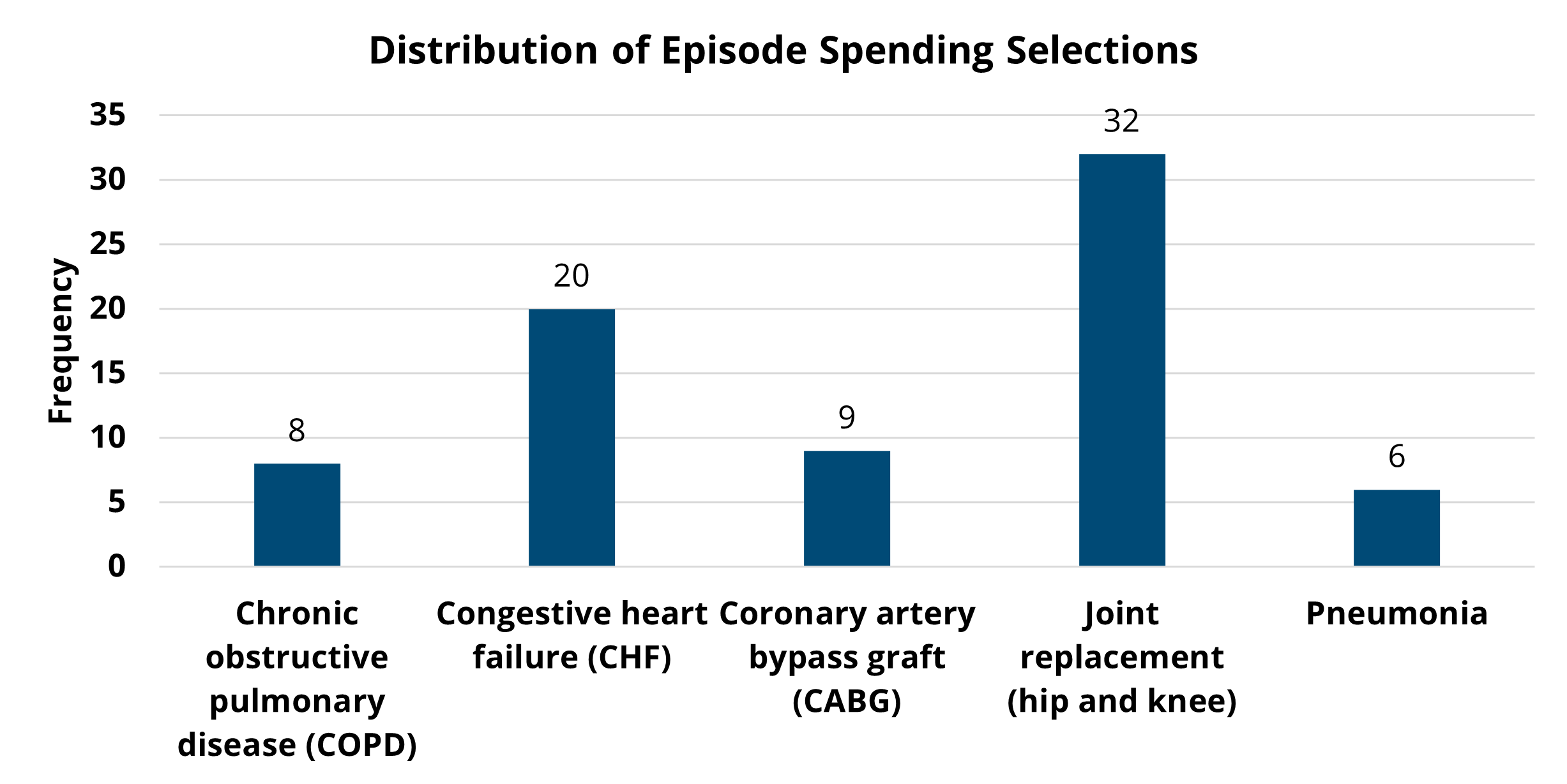
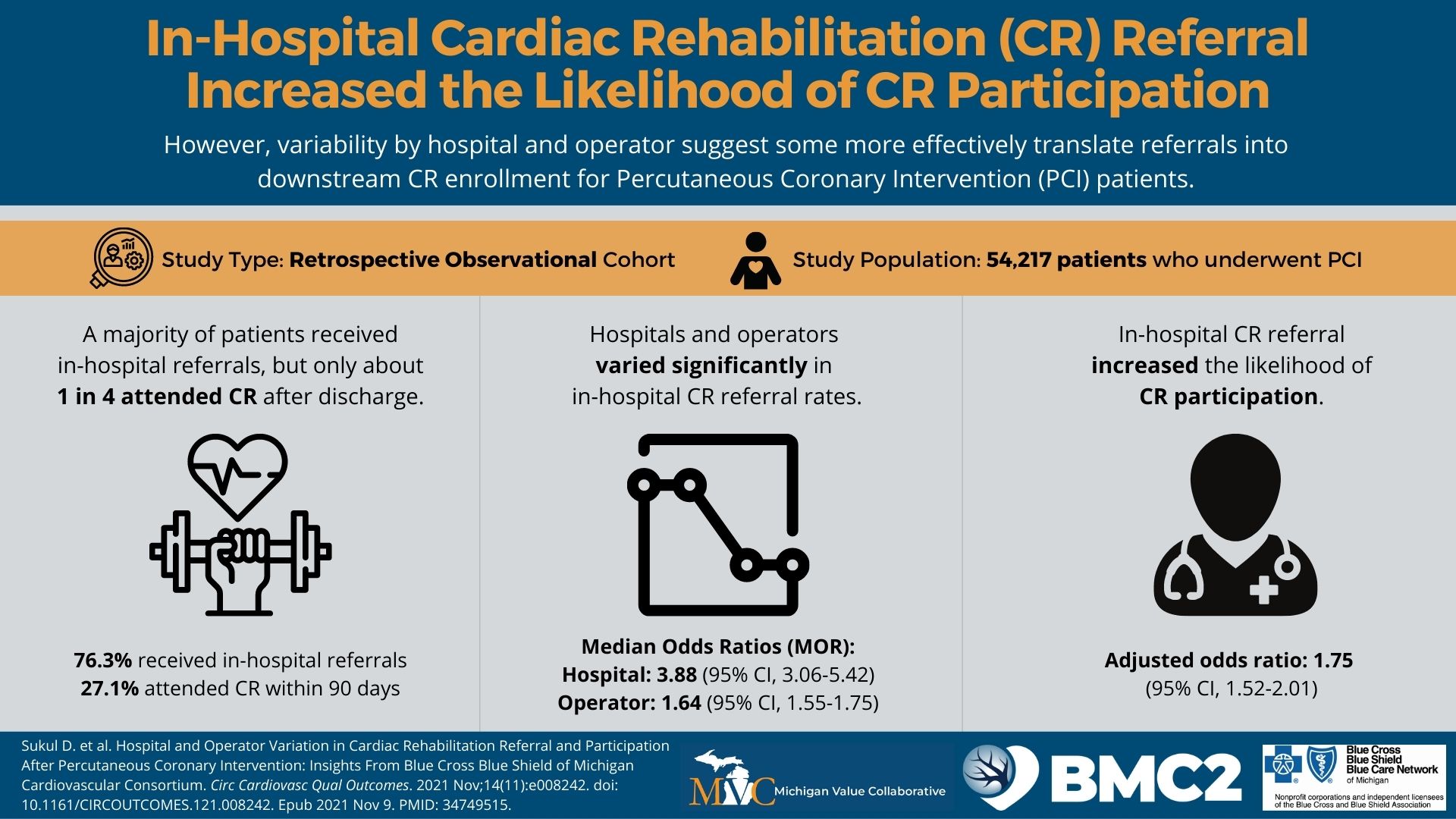
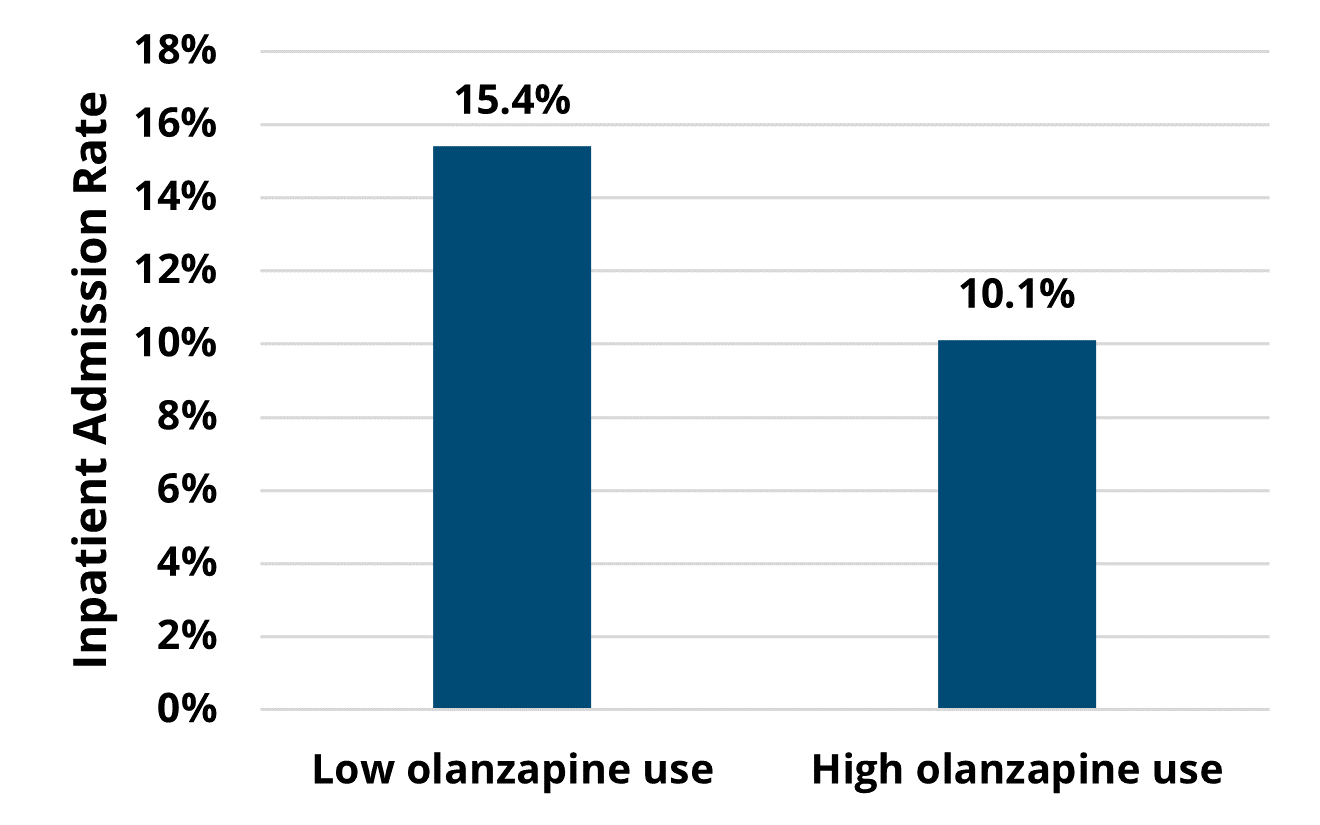
A key finding in the analysis included a significant difference in healthcare utilization across the course of chemotherapy among patients treated by high olanzapine prescribing MOQC practices compared to when they had low olanzapine utilization. Among the patients with cancer who received their first cycle of chemotherapy when their provider's practice had a high prescribing rate (≥25%), 10% were hospitalized (Figure 1). This inpatient admission rate was significantly lower than for those patients undergoing chemotherapy regimens at practices with low olanzapine prescribing rates, 15% of whom were hospitalized (p=0.02). This finding was based on a subset of patients attributed to practices who eventually became high olanzapine prescribers during the study period (922 patients at 15 practices).
Figure 1. Rates of Inpatient Admission Across Patients' Course of Chemotherapy, by Practice's Utilization Rate of Antiemetics at the Start of Chemotherapy (N=922)
This analysis further discovered a significant difference in the percentage of patients who had either an ED visit or inpatient admission. Of the patients receiving chemotherapy at MOQC practices, fewer patients at high-prescribing practices had either an ED visit or inpatient admission (19%) across the course of their treatment compared to patients receiving care at low-prescribing practices (26%).
MVC estimated a cost savings of $334,095 across the course of chemotherapy from the increased use of olanzapine and decreased inpatient admissions in this cohort of patients. Dollars saved were calculated by taking the number of patients whose chemotherapy began when their practice was a high prescriber (525), multiplied by the difference in the percentage of patients with an inpatient admission across the course of chemotherapy attributed to practice antiemetic prescribing rate (5.3%), multiplied by the average price-standardized payment for an inpatient admission during a 90-day episode of care among breast cancer resection episodes for the included payers ($12,007).
This analysis demonstrated further evidence that the use of prophylactic olanzapine is an effective strategy for managing CINV-related ED visits or hospitalizations. It furthermore identified tangible CQI impact in the form of patients who underwent breast cancer treatment being less likely to visit the ED or be hospitalized over the course of their chemotherapy regimen, as well as in the form of dollars saved on facility inpatient costs across the course of chemotherapy. Ongoing work will continue to support practices to make changes in the use of olanzapine, not only in patients receiving combination therapy with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide but also in other high-emetic-risk regimens.
MVC’s expertise and data frequently result in partner projects like this; MVC completed a number of CQI impact assessments last year, as well as several more so far in 2023. MVC also participates in collaborative activities with peer CQIs through new condition and report development, data analysis and metric consultation, and data matching exercises that pair clinical and claims-based data. To request a copy of any of MVC’s completed CQI impact assessments, please contact the MVC Coordinating Center.