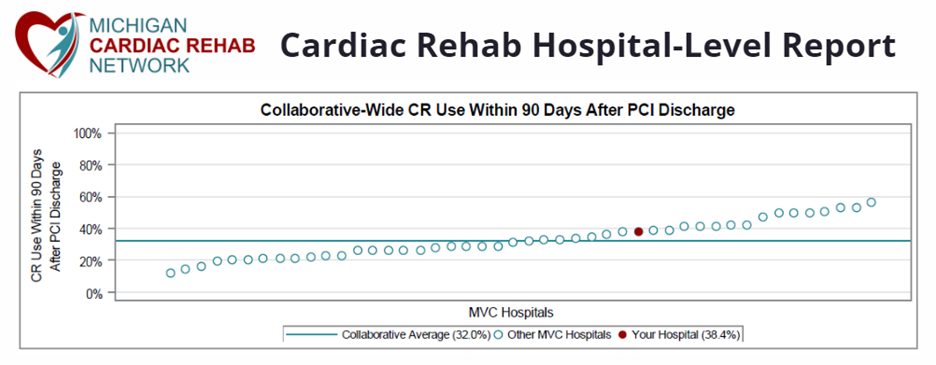
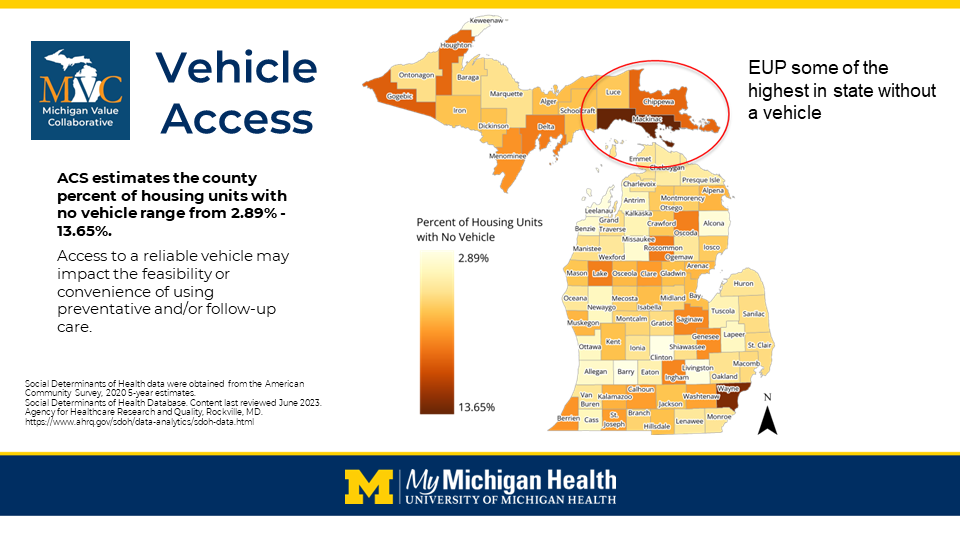
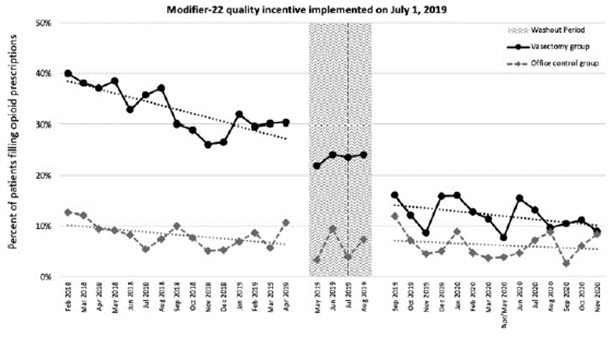
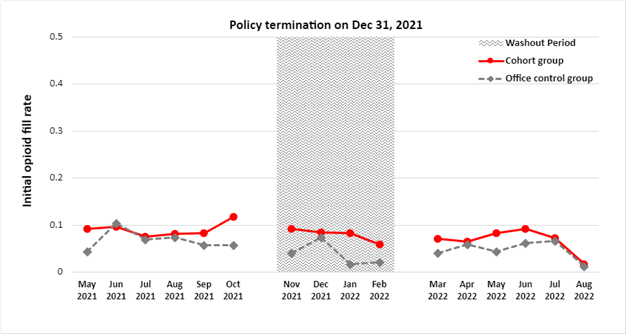
BMC2 (Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Cardiovascular Consortium) has been recognized with the prestigious John M. Eisenberg Patient Safety and Quality Award in the Local Level Innovation in Patient Safety and Quality category.
BMC2 has been honored for its remarkable improvements in the documentation of radiation use, a decrease in high-dose radiation exposure, and reduction in opioid pill prescribing rates. BMC2 is a statewide quality improvement collaborative that develops and administers a portfolio of quality improvement interventions for patients who undergo heart stenting, vascular surgical procedures, and transcatheter valve procedures in Michigan. The consortium is one of 22 Collaborative Quality Initiatives sponsored by Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network as part of the BCBSM Value Partnerships program.
The Eisenberg Awards honor the late John M. Eisenberg, MD, MBA, and bring together the quality community to recognize groundbreaking initiatives in healthcare that are consistent with the aims of the National Quality Strategy: better care, healthy people and communities, and smarter spending. Dr. Eisenberg was the former administrator of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and an impassioned advocate for healthcare quality improvement. The award, presented annually by The Joint Commission and the National Quality Forum (NQF), recognizes major individual, local, and national achievements in healthcare that improve patient safety and healthcare quality.
“BMC2’s work impacts 30,000 patients treated by hundreds of physicians from more than 100 hospital teams each year,” shares Dr. Hitinder Gurm, Director of BMC2. “We are fortunate to have this unique partnership between providers, hospitals, and payers, that is focused solely on improving safety, quality, and appropriateness of care. The collaborative creates data-driven quality improvement goals and initiatives, shares best practices, and distributes reports benchmarked to statewide performance, all focused on improving cardiovascular care throughout Michigan.”
In Michigan, documentation of radiation use improved from 73.1% in 2019 to 85.5% in 2021, and BMC2 sites are outperforming national rates, which were 57.5% in 2019 and 74.3% in 2021. BMC2 sites achieved an overall 43% decrease in cases with high-dose radiation exposure (2.8% in 2018 to 1.2% in 2021), affecting hundreds of patients and care teams. BMC2 also reduced opioid pill prescribing; data showed improvement in the rate of patients with a prescription of less than 10 opioid pills by approximately 30% between 2018 (62%) and 2021 (91%). In addition, BMC2 has been exploring strategies to address healthcare disparities and partners with a patient advisory council to create resources for patients and providers.
The Eisenberg Award panel was impressed by BMC2’s dissemination of its work. BMC2 data has supported more than 100 publications in peer-reviewed medical journals and more than 100 presentations at national and international conferences. The panel noted that this kind of collaborative, best-practice approach improved outcomes, reduced costs, and could be replicated by other states. The panel was inspired by BMC2’s inclusive scope across so many clinicians, physicians, teams, and sites, acknowledging the collaborative is “working to improve care, at every institution, and for every patient. It's remarkable.”
--
BMC2 is a collaborative consortium of health care providers in the State of Michigan comprised of three statewide quality improvement projects addressing percutaneous coronary interventions (BMC2 PCI), vascular and carotid interventions (BMC2 Vascular Surgery), and transcatheter aortic and mitral valve procedures (MISHC) in collaboration with the Michigan Society of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgeons. Learn more about BMC2’s activities and achievements in their 2023 Annual Report.
Like MVC, support for BMC2 is provided by Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network as part of the BCBSM Value Partnerships program.