Since its founding, a core component of MVC’s strategy has been organizing opportunities to collaborate with and learn from peers, leading to the ongoing facilitation of MVC workgroups. MVC has hosted workgroup presentations twice per month in recent years, and this year’s workgroups are focused on six topic areas: post-discharge follow-up, sepsis, cardiac rehabilitation, rural health, preoperative testing, and health in action. Going forward, MVC will publish a monthly blog to highlight key takeaways and shared resources from the prior month’s presentations. In doing so, all MVC members and partners may utilize and benefit from the content regardless of their live participation.
September Post-Discharge Follow-Up Workgroup
MVC hosted a post-discharge follow-up workgroup on Sept. 10 featuring a presentation by Brian Leideker, RRT, COPD Navigator for Trinity Health Oakland Hospital. Leideker’s presentation summarized Trinity Heath Oakland Hospital’s progress since initiating an A3 COPD readmission committee in June 2021, including the key interventions their team has implemented to date.
One initial intervention was the hiring of a COPD navigator. Leideker described how his unique role as a respiratory therapist involved in case management has allowed him to be “a middleman between respiratory physicians and other entities trying to deliver and support services” for COPD patients.
Following several root cause analyses, the COPD committee identified that nearly 90% of patients readmitted for COPD at Trinity Health Oakland Hospital had an interruption in intended continuation of pharmacotherapy and/or non-pharmacotherapy treatments. This finding encouraged Leideker’s team to work to improve the education of patients, providers, and the greater healthcare community on ambulatory treatment for COPD as well as reviewing the testing and documentation needed to ensure coverage of durable medical equipment (DME) post-discharge.
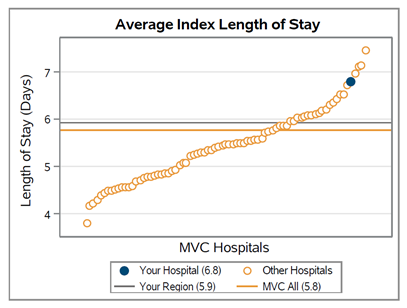
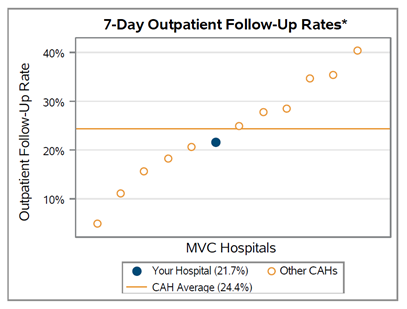
With the help of an MVC custom analytic report, Leideker was able to trend DME utilization rates for patients hospitalized with COPD since the initiation of these interventions, as seen in Figure 1.
Generally, the utilization rate of post-discharge non-bi-level home ventilators (E0466) was found to increase over time, while bi-level home ventilator (E0470) utilization has decreased. Leideker noted that this was somewhat expected since patients routinely report difficulty with the utilization of bi-level home ventilators (BiPAP) and often move on to non-bi-level home ventilators (CPAP). Additionally, based on Trinity Health Oakland’s internal analyses as of May 2024, their COPD three-day readmission rates have been reduced to <18% for all payers.
Sept. 10 Post-Discharge Follow-Up Workgroup
September Rural Health Workgroup
MVC hosted a rural health workgroup on Sept. 26 featuring a presentation by Brent Mikkola, MBA, PMP, Manager of Community Health at MyMichigan Health. Mikkola’s presentation summarized MyMichigan Health’s approach to developing a strategic plan for health equity and an overview of some specific community programs currently in place. MyMichigan Health’s phased approach to integrating health equity is currently focused on evaluating social determinant of health (SDoH) opportunities in an “assess, analyze, and address” model.
Some unique community partnerships that resulted from this process include:
- Gratiot County Public Transit voucher program
- Rx 4 Health – partnership with Michigan State Extension and specific grocery suppliers including SpartanNash, SaveALot, and Meijer
- Food Pharmacies & Weekend Kits - partnership with the Greater Lansing Food Bank and the Food Bank of Eastern Michigan
- Bridge to Belonging - virtual series on loneliness and social connection
- Continuing Care Clinic Pilot with Community Health Workers (CHWs)
- Intervention for Nicotine Dependence: Education, Prevention, Tobacco and Health (INDEPTH) Suspension Diversion Program
In addition to developing a strategic framework for reporting and developing objectives around health equity, Mikkola described how MyMichigan Health delved into the data collection, analysis, and quality improvement work surrounding health equity. For example, after initially integrating CHWs into community practices and inpatient services, MyMichigan Health further integrated CHWs following the WHO’s CHW Lifecycle Approach, as seen in Figure 2.
CHWs have become instrumental to MyMichigan’s assessment of SDoH as required by CMS and JCAHO mandates by filling gaps in system workflows and in the expansion of the Continuing Care Clinic Pilot. To date, nearly 500 well visit appointments have been completed by CHWs at MyMichigan. Of those patients, 34% were identified as having SDoH needs and 50% of those needs have now reportedly been met through connections to community support services.
Sept. 26 Rural Health Workgroup
To learn more about the efforts showcased by Trinity Health Oakland and MyMichigan Health, or to view past workgroup presentations, visit MVC’s YouTube channel here.
October’s workgroups will include a health in action presentation on Oct. 8 about the University of Michigan’s Hospital Care at Home program, as well as a sepsis presentation on Oct. 17 by Garden City Hospital. You can view the complete 2024 calendar of events and register for workgroups here. To learn more about MVC workgroups or other presentation opportunities, contact the MVC Coordinating Center by emailing us here.