The emergency department (ED) is a unique and critical component of the healthcare system in the U.S., treating acute injuries or illnesses and acting as a safety net for patients who are uninsured or low income. ED visits are also very expensive, and that spending is growing according to a recent retrospective study of ED trends. This week the Michigan Value Collaborative (MVC) is distributing its newest push report on ED and post-acute care (PAC) utilization to support members' efforts in this space.
Since the ED serves as a safety net for patients experiencing barriers to healthcare access, the Coordinating Center report purposefully integrates measures tied to social determinants of health and health equity. Reports contain a patient population snapshot table showcasing several patient characteristics by payer (see Figure 1), including age, race, comorbidities, zip code, dual-eligibility status, and economic distress scores. Dual-eligible patients are those who qualify for both Medicaid and Medicare; these patients tend to have a higher prevalence rate for chronic conditions, disabilities, and other care needs that substantially increase healthcare utilization.
Figure 1.
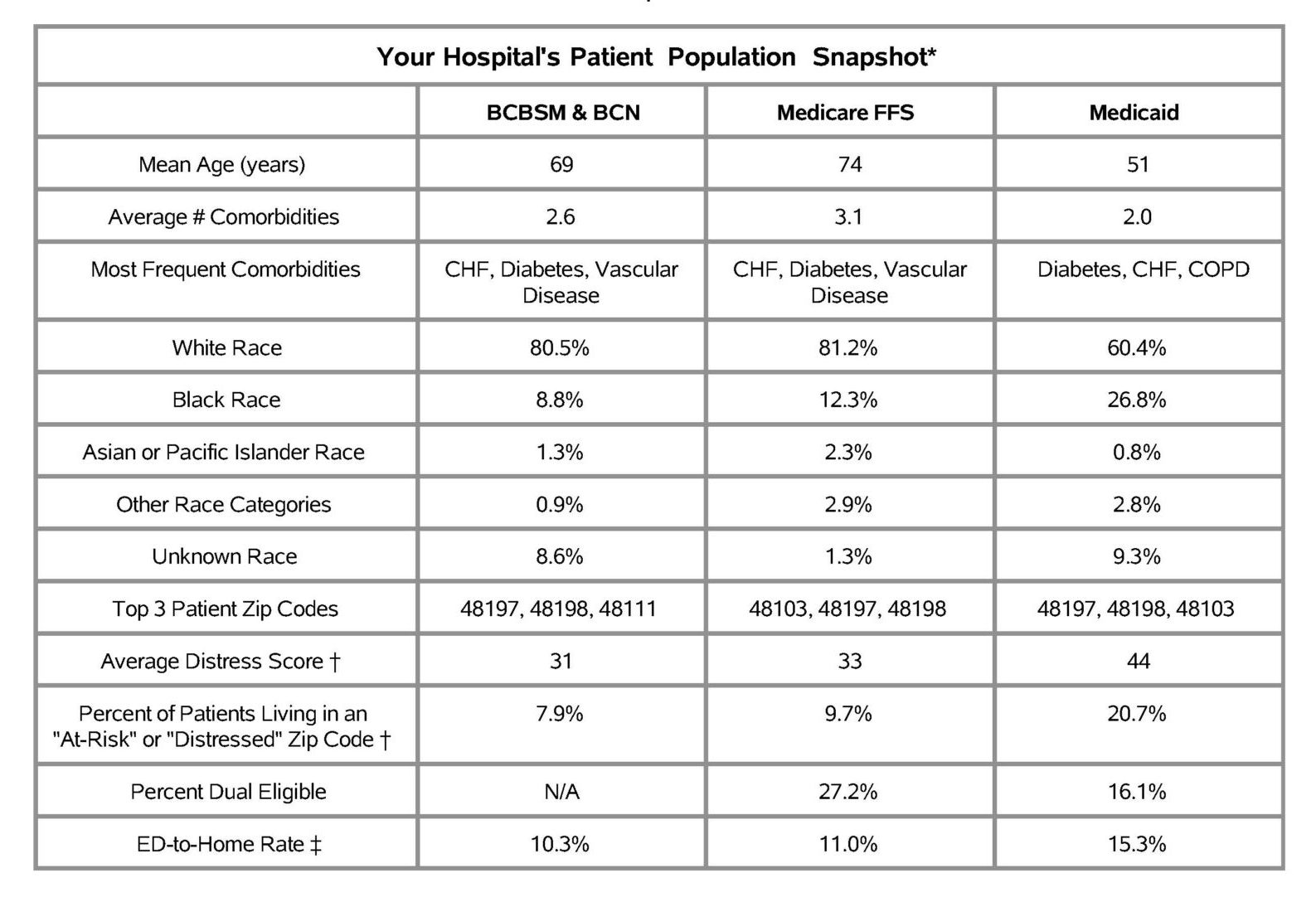
Economic distress scores range from 0-100 with a higher score indicating greater economic distress. These scores come from the Economic Innovation Group’s Distressed Communities Index (DCI), which is derived from the U.S. Census Bureau’s Business Patterns and American Community Survey. The DCI combines seven complementary economic indicators (see Figure 2) to provide a single, holistic, and comparative measure of economic well-being across communities in the U.S. In MVC’s report, there is a proportion of patients living in an “at-risk” or “distressed” zip code across all payers, as classified by the DCI. However, as the literature often indicates, the Medicaid population has the highest average distress score and a larger proportion of patients living in an “at-risk” or “distressed” zip code.
Figure 2.

The bulk of MVC’s latest report aims to provide its members with more granular insights into PAC utilization in the 30-day post-discharge period than is available on the MVC registry. Using index admissions for medical conditions from 1/1/18 through 12/31/20, the report focuses predominantly on ED utilization, which is categorized as either “ED to Home” or “ED to Readmission.” ED to Home represents ED visits that do not occur on the same day as readmission, and ED to Readmission refers to those visits occurring on the same day as readmission.
The report includes figures illustrating trends in 30-day ED to Home rates between 2018 and 2020, top reasons for ED visits at a given hospital, the number of ED to Home visits within 30 days post-discharge, the number of days until the first ED visit post-discharge, the ED to Home rate and the breakdown of total PAC spending for a hospital’s three highest-volume conditions, and the average ED facility payment. MVC included the following payers in this report: Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan (BCBSM) PPO Commercial, BCBSM Medicare Advantage (MA), Blue Care Network (BCN) HMO Commercial, BCN MA, Medicare Fee-for-Service, and Medicaid.
Overall, the MVC report confirms published findings that Medicaid patients utilize the ED at a higher rate than patients insured by other payers. The Coordinating Center also finds that ED use differs between types of providers. For acute care hospitals, for example, over half of ED visits occur on the same day as readmission, whereas these visits account for 40% at Critical Access Hospitals (CAHs).
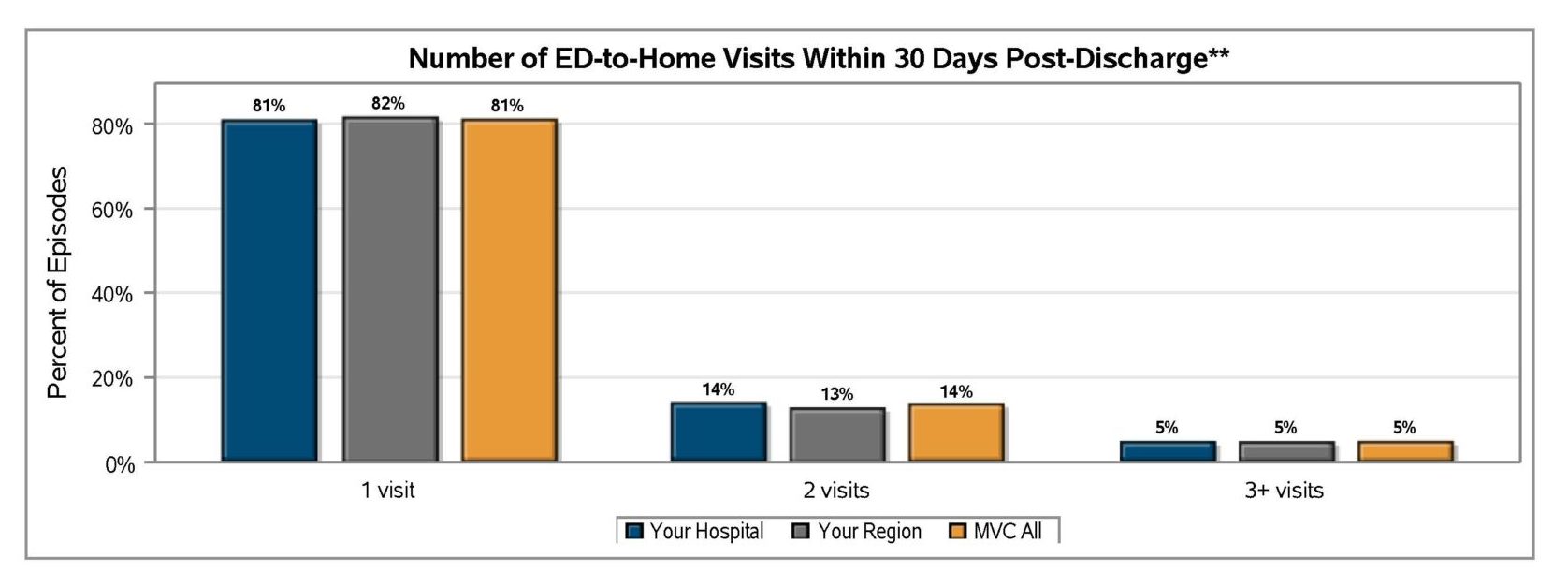
MVC also finds that ED to Home visits most often occur once in the 30 days following discharge for most of the collaborative (see Figure 3). There are some members, however, with three or more ED to Home visits within the 30-day post-discharge period.
Figure 3.
The Coordinating Center envisions this report being of particular importance to its CAH members, whose structures, services, and patient populations make the ED and PAC a top priority. As such, MVC prepared versions of this report for both CAHs and acute care hospitals using their respective comparison groups throughout. In other words, the CAH version of the report includes comparison points for all other CAHs in the collaborative. Acute care hospitals can see their traditional collaborative-wide and regional comparison data, not including hospitals with a CAH designation.
As members review and discuss the findings in their report(s), MVC encourages providers to utilize the Michigan Emergency Department Improvement Collaborative (MEDIC), which is dedicated to improving the quality of ED care across the state of Michigan. In addition, if members wish to discuss additional custom analyses on ED and PAC utilization, please contact the MVC Coordinating Center at michiganvaluecollaborative@gmail.com.