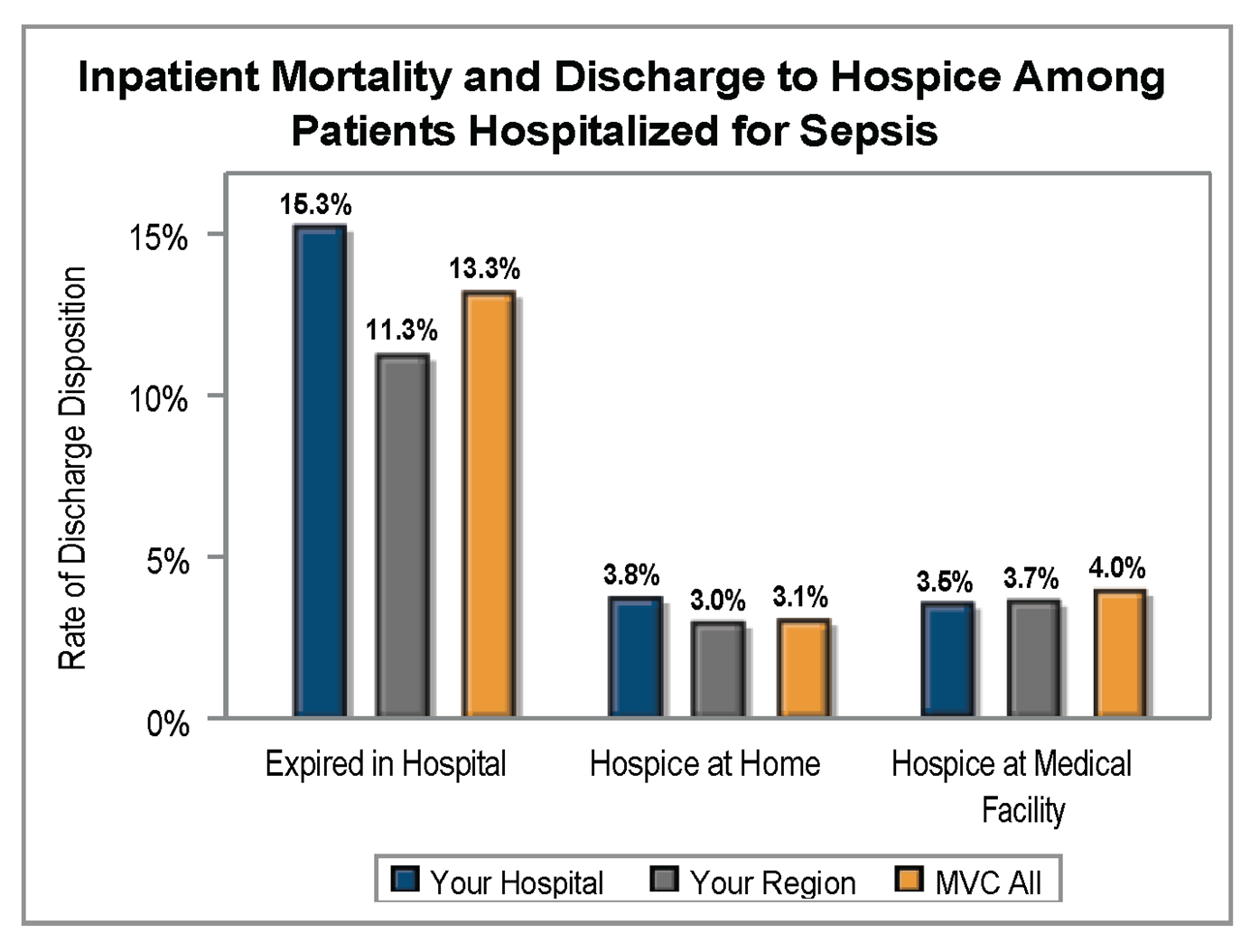
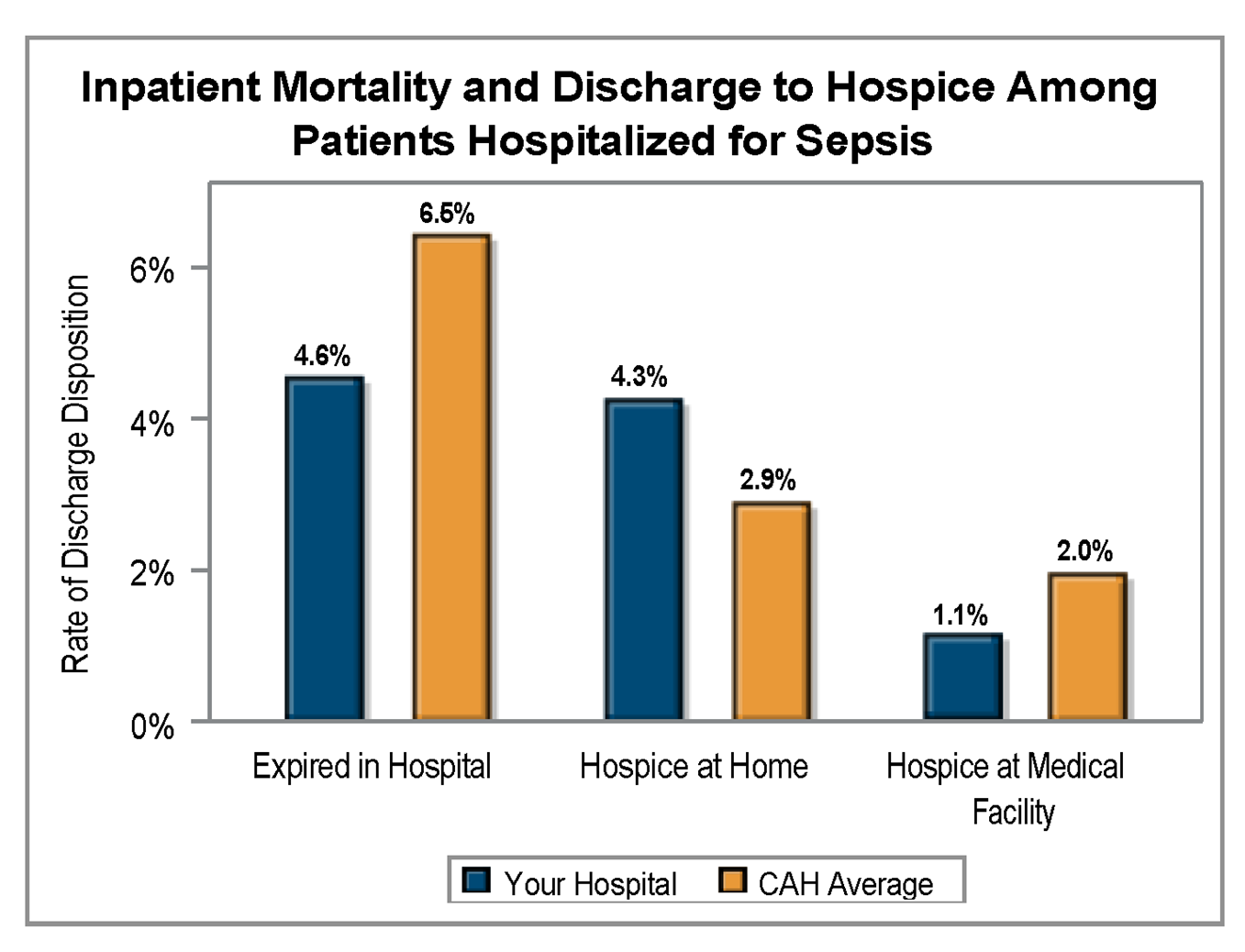
The MVC Coordinating Center distributed refreshed hospital-level versions of its push report utilizing emergency department-based episodes (“ED-based episodes”) in April, preparing versions for acute care hospitals and Critical Access Hospitals to include different comparison groups. The report leverages data focused specifically on patient episodes first initiated by a visit to the emergency department and follows those episodes to determine common metrics such as episode payments, post-ED care utilization, and outpatient service rates.
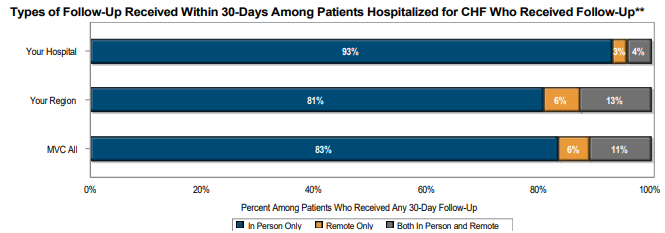
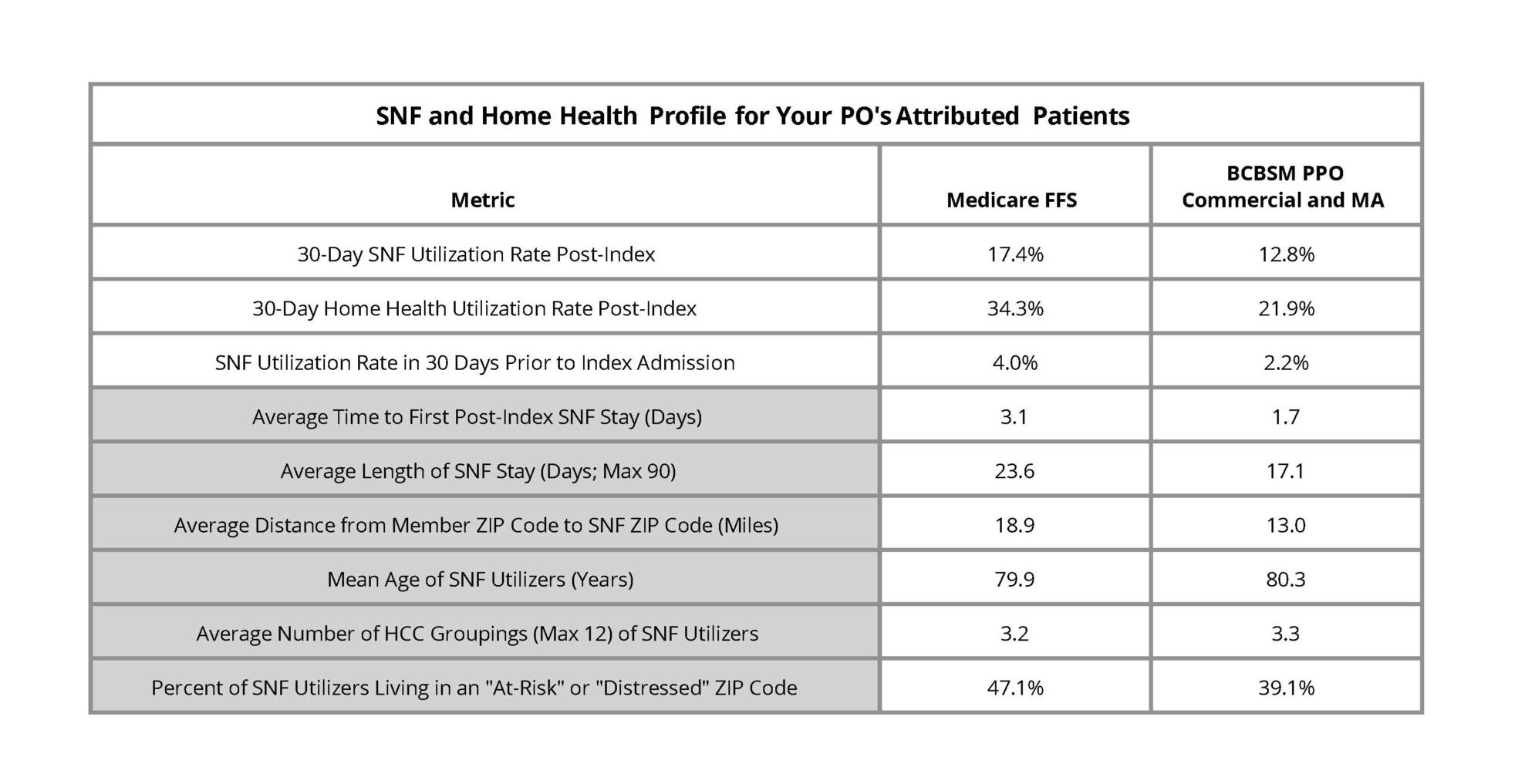
In addition to reflecting more recent data across all included payers, these refreshed hospital-level reports provide additional social risk data than was offered previously with the addition of several metrics based on patient Zip code to the patient population snapshot table. This allows hospitals to better understand the patients represented in various service line cohorts presented within the ED-based episodes report and the types of social risk factors that may be present, such as low median household income, SNAP usage, vehicle ownership, and homeownership.
Each page of the report is dedicated to a specific condition with mostly the same metrics throughout, such as risk-adjusted, price-standardized 30-day total episode spending, inpatient admission rates, and rates of post-ED utilization. Reports feature each hospital’s own attributed ED-based episode data for eight high-volume ED conditions: abdominal pain, cellulitis, chest pain (nonspecific), congestive heart failure (CHF), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), diabetes with long-term complications (including renal, eye, neurological, or circulatory), diabetes with short-term complications (including ketoacidosis, hyperosmolarity, or coma), and urinary tract infection (UTI).
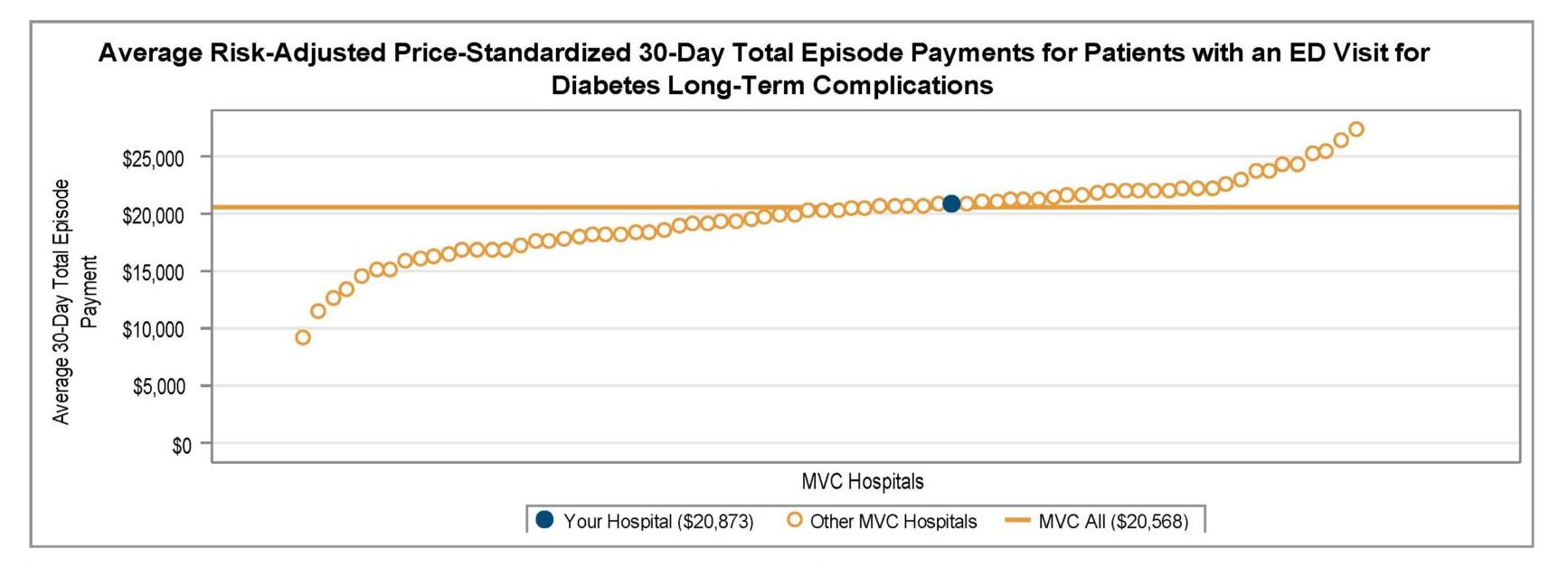
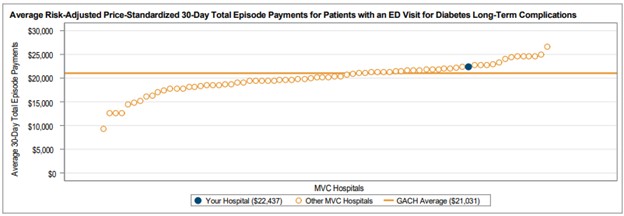
Among general acute care hospitals receiving a report, the average risk-adjusted, price-standardized 30-day total episode payment (Figure 1) for the reported conditions is highest for diabetes with long-term complications ($21,031), followed by CHF ($18,363), diabetes with short-term complications ($12,571), and COPD ($11,145). The collaborative-wide average total episode payment is lowest for chest pain ($3,327) and abdominal pain ($3,405). These rankings are consistent with the 2024 ED-based episode reports.
Figure 1.
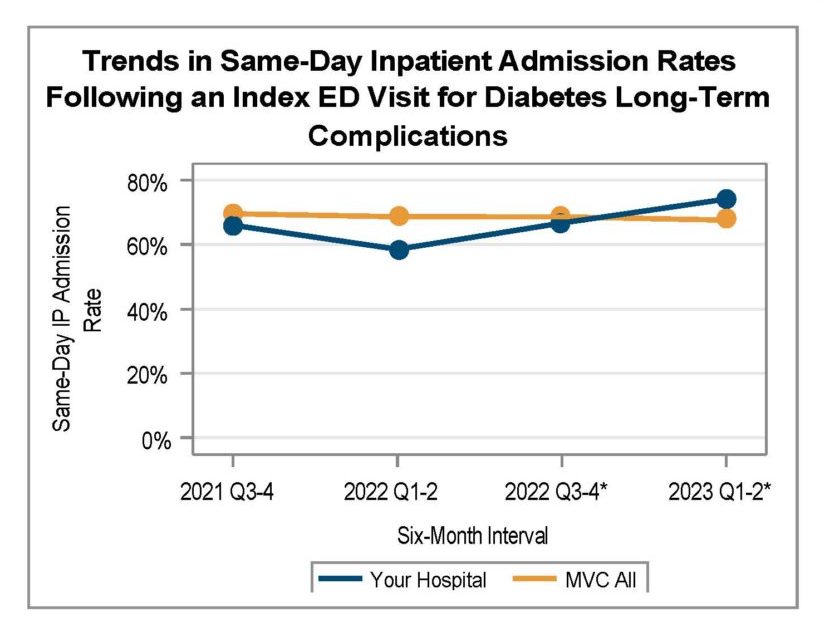
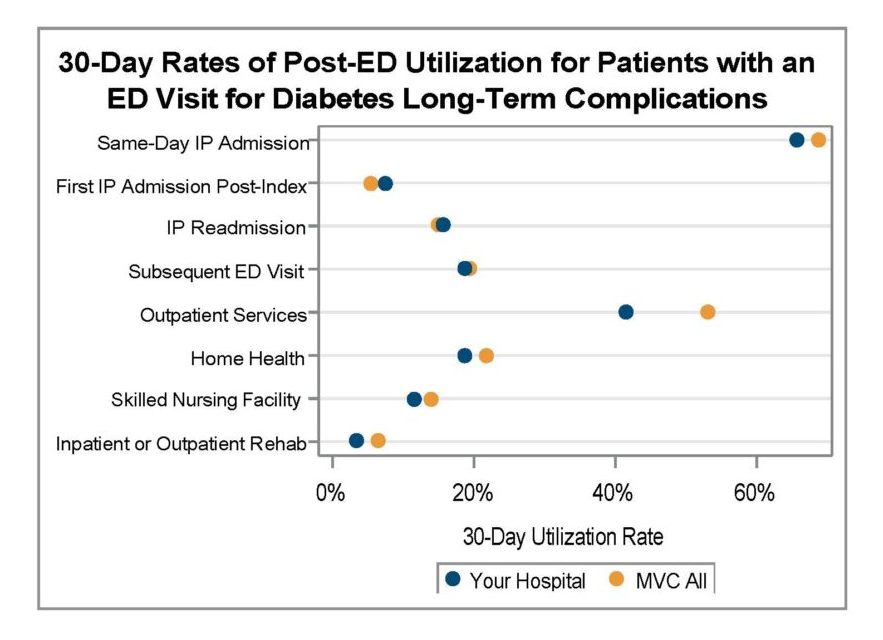
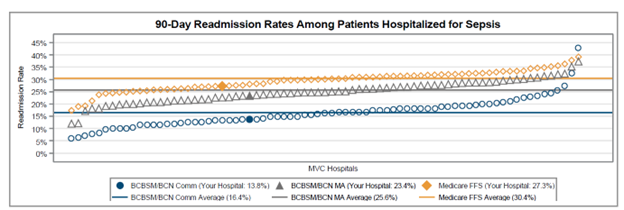
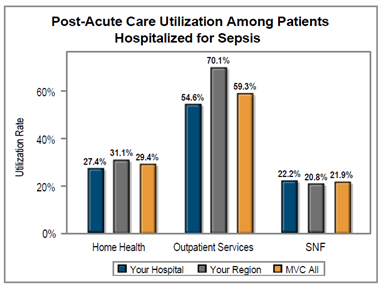
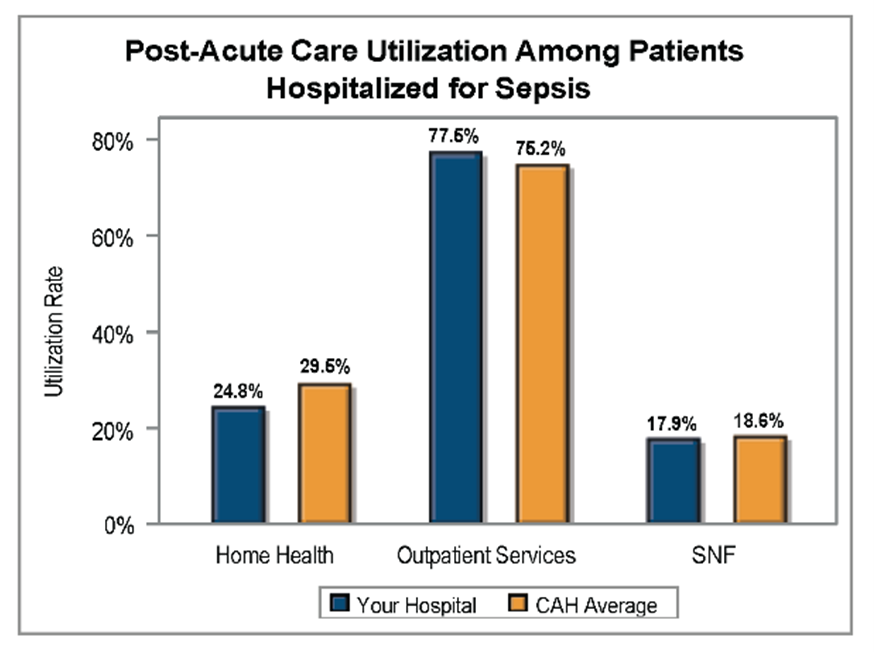
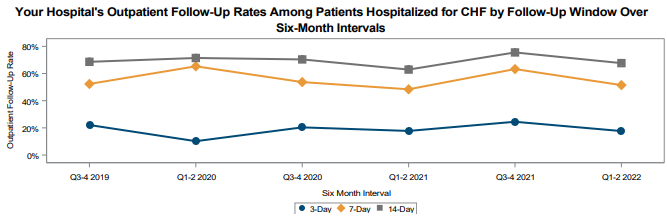
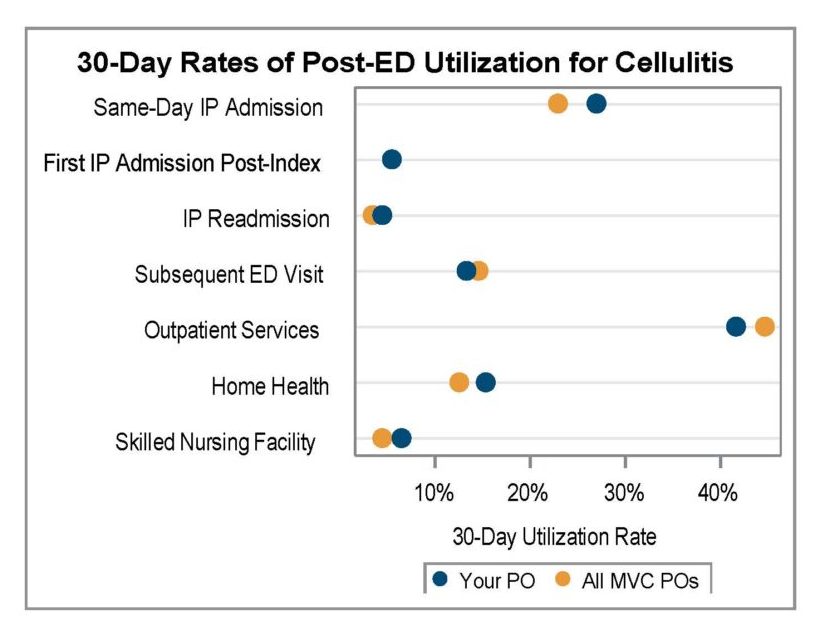
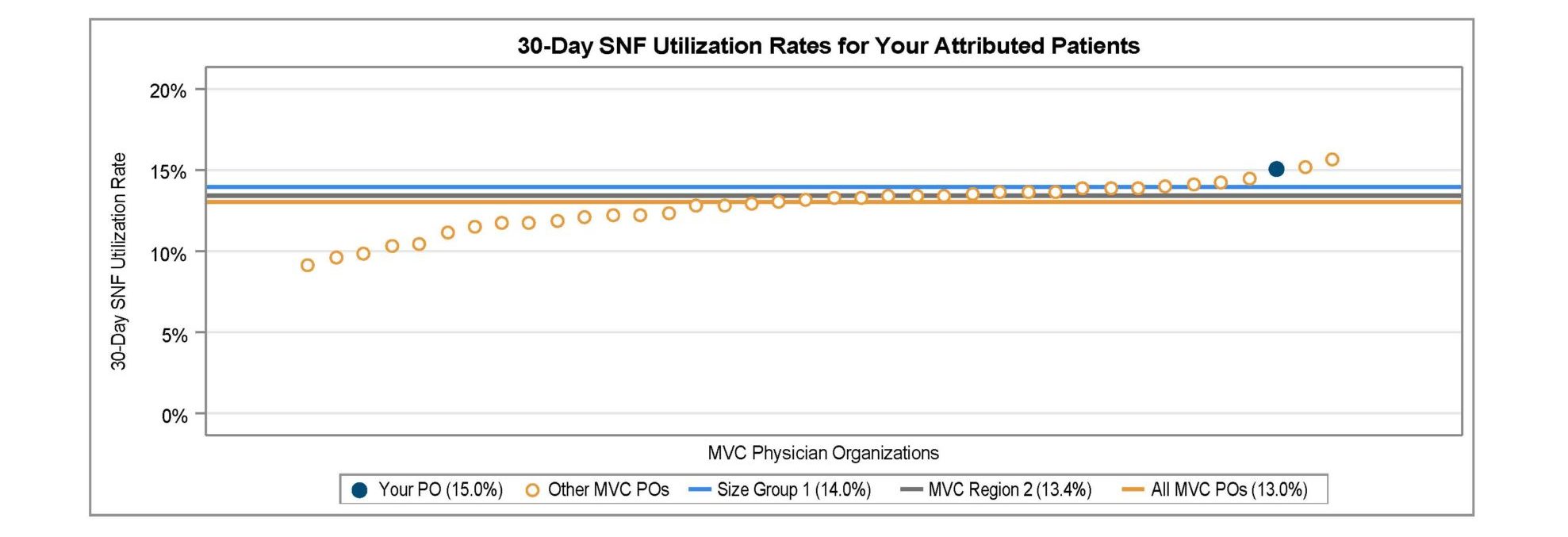
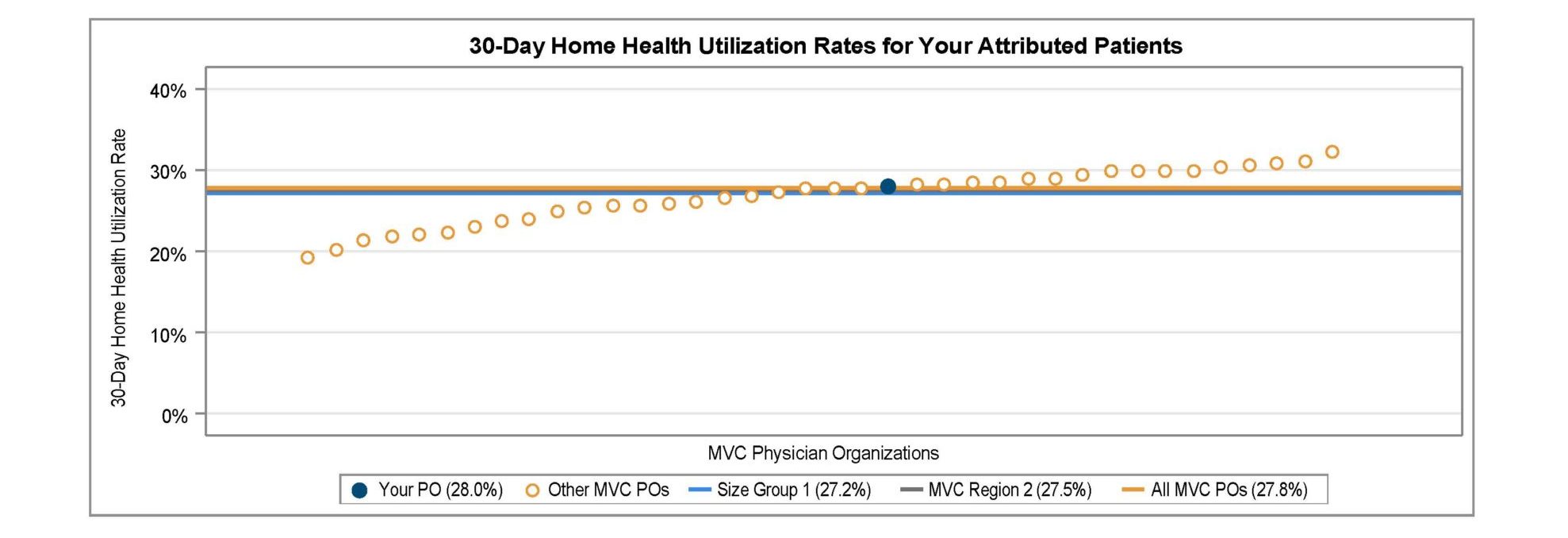
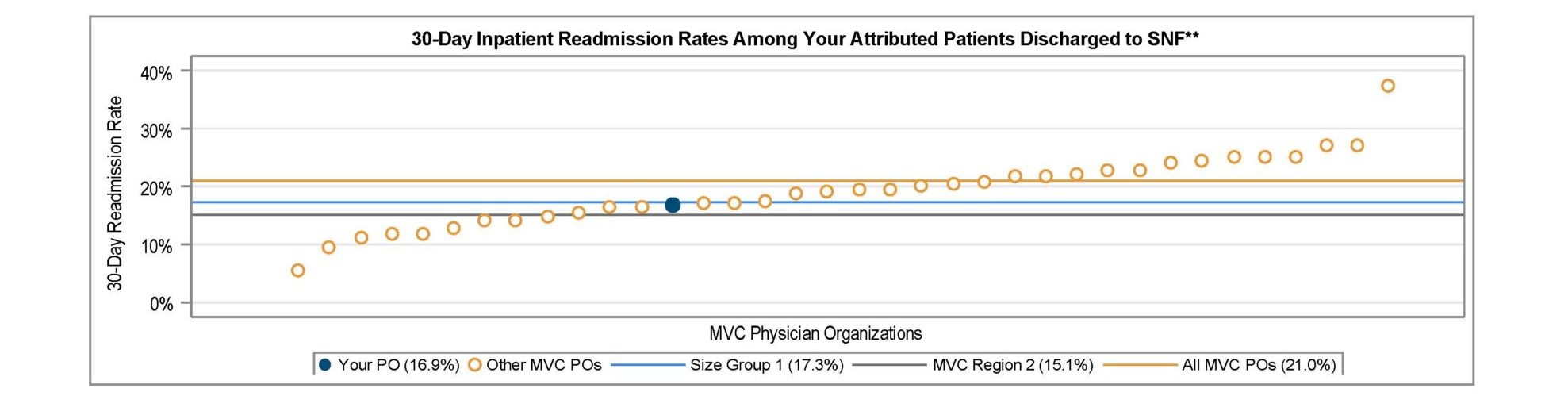
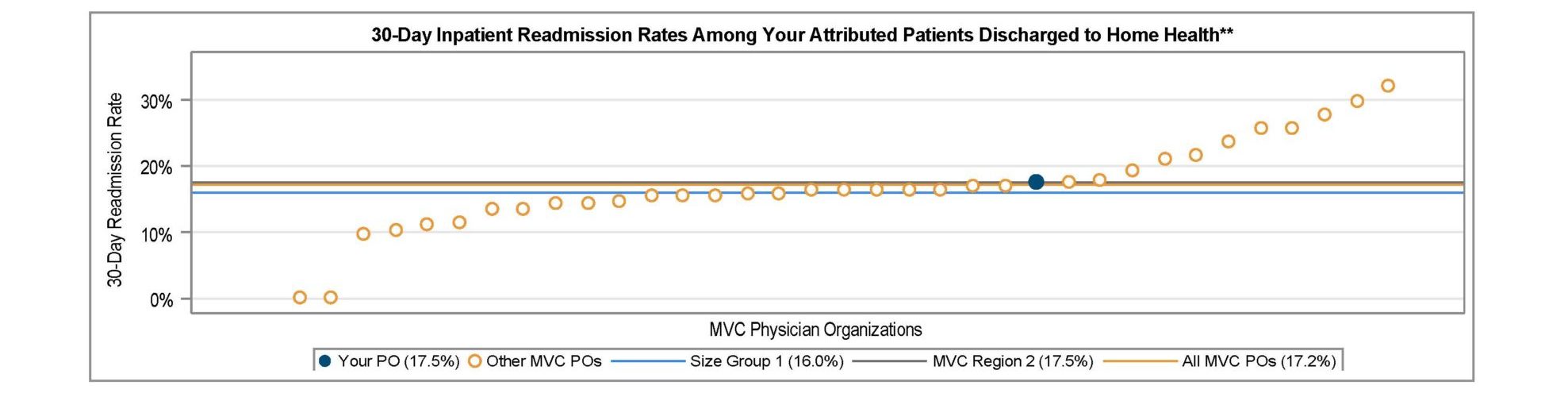
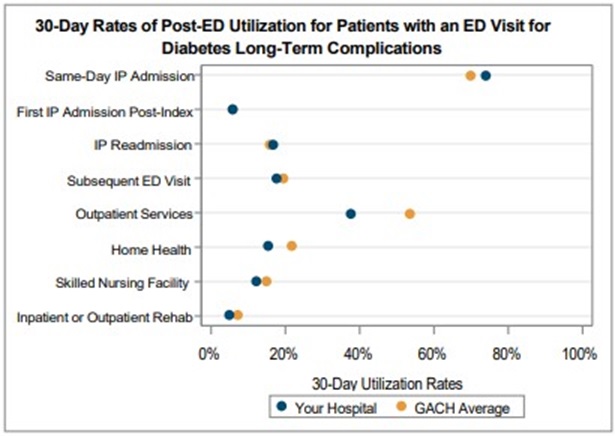
A key goal of these reports is to provide insights into healthcare utilization following index ED events; therefore, the latest reports continue to include a dot plot (Figure 2) comparing patient post-ED utilization at a member hospital against their peer comparison group. Dot plots provide information on what percent of episodes had a same-day inpatient admission, what percent did not have a same-day inpatient admission but did see the patient admitted in the 1 to 30 days following the index ED visit, and the percent of patients who had two or more inpatient admissions (thus, at least one readmission) during the episode of care. Rates of subsequent ED visits, outpatient services, home health, skilled nursing facility care, and inpatient or outpatient rehab are also provided.
Figure 2.
MVC uses its most recent medical insurance claims data from Medicare FFS, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan PPO Commercial and Medicare Advantage plans, Blue Care Network HMO Commercial and Medicare Advantage plans, and Michigan Medicaid to build these ED-based episodes reports.
MVC recently presented data on the incidence of behavioral health co-diagnoses on ED-based episodes at its May collaborative-wide meeting. This presentation highlighted the presence of behavioral health ICD-10 codes on index ED visits for patients with a primary diagnosis code matching one of MVC’s ED conditions. MVC reported 13% of ED index events statewide contained a behavioral health code. The most common codes observed were for anxiety disorder (36.7%), major depressive disorder (10.6%), and dementia (8.7%). The recent ED-based episode reports include a row for “most frequent comorbidities” by condition, which will help members determine service lines where psychological disorders or substance abuse disorders are a common consideration for specific service lines at their hospital.
MVC’s ED-based episode structure was developed in collaboration with the Michigan Emergency Department Improvement Collaborative (MEDIC), a BCBSM-funded Collaborative Quality Initiative with the goal of improving care and patient outcomes in Michigan emergency departments. MVC and MEDIC team members worked closely to develop 30-day episodes of care initialized by a patient’s visit to the ED and including all claims-documented care received in the 30 days following a patient’s index ED visit.
Please share your feedback with the MVC team if certain report measures are helpful or if you wish to see additional ED-based episode reporting for certain conditions and metrics. MVC is now also accepting custom report requests using its ED-based data. Contact MVC to learn more.