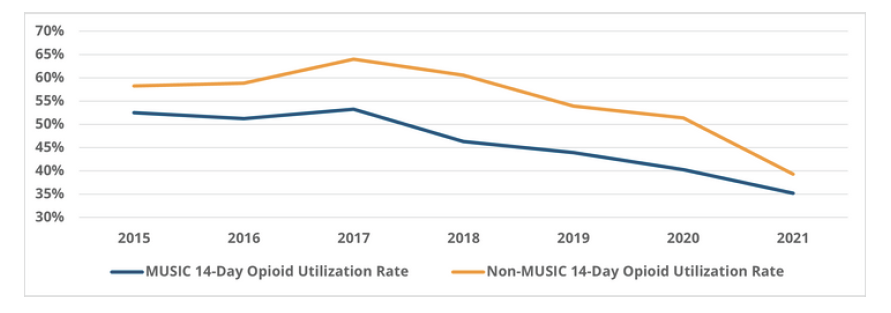
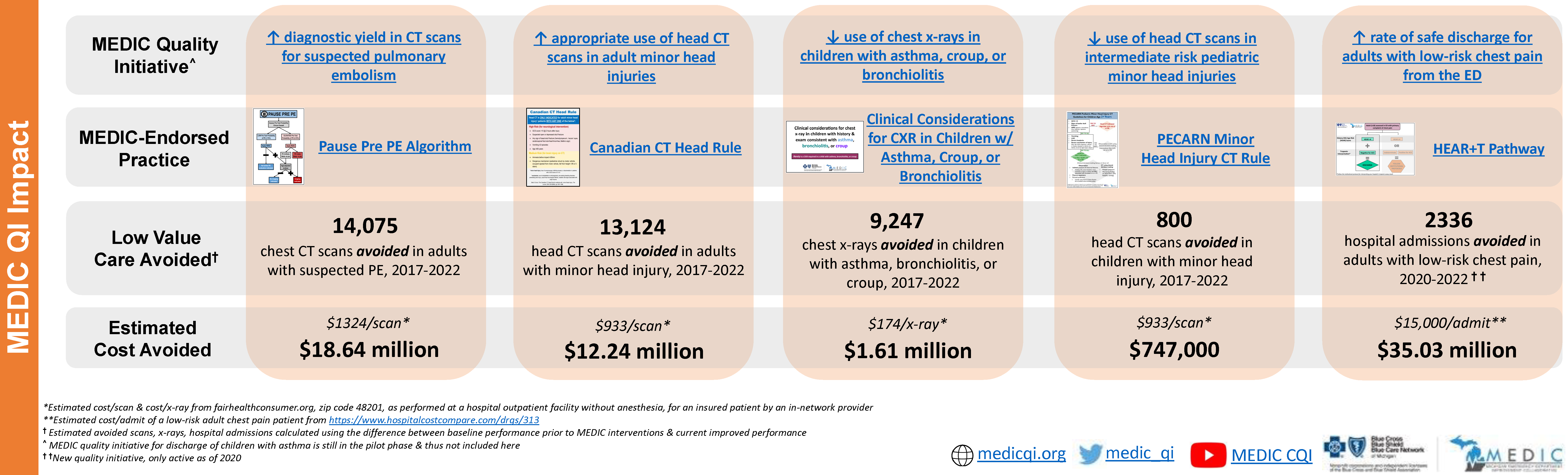
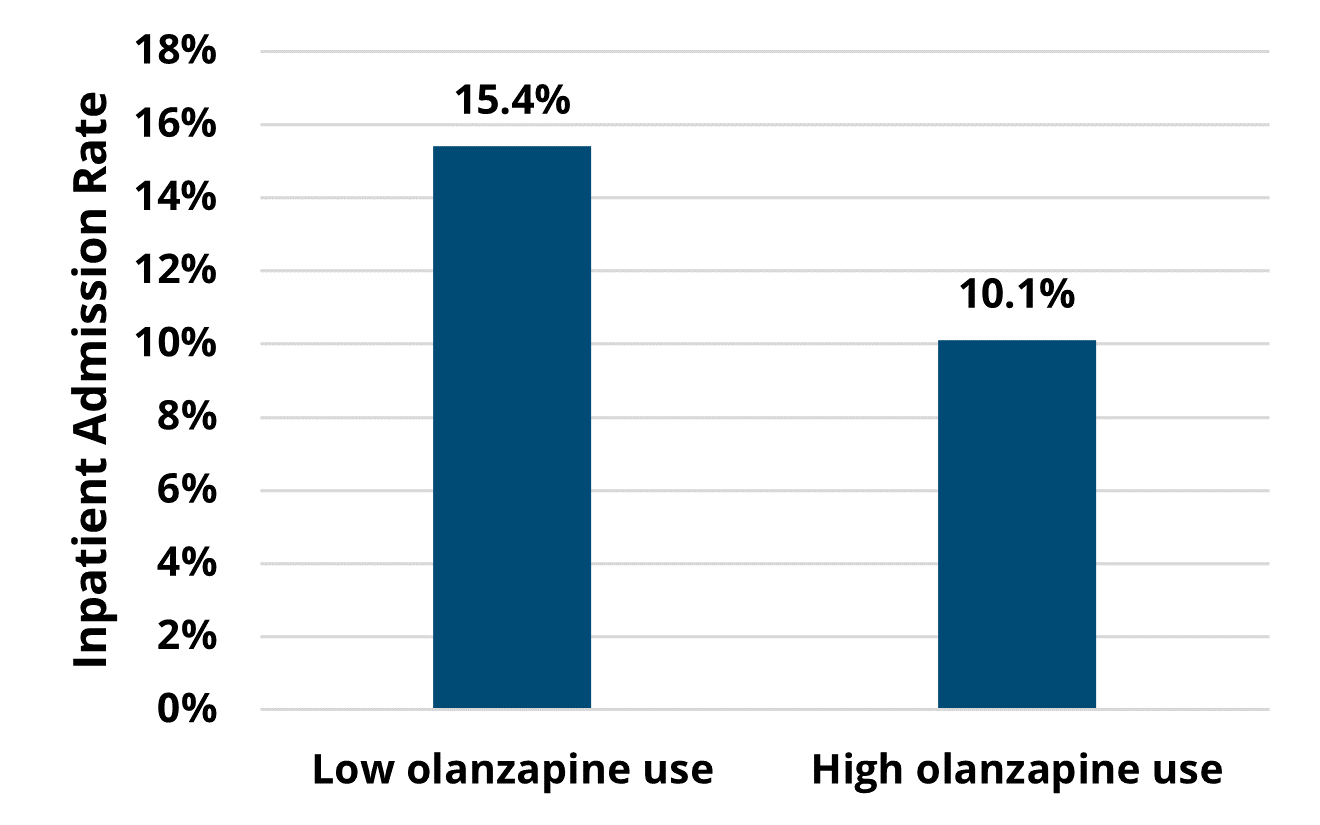
Surgical quality improvement is essential for enhancing patient outcomes, ensuring safety, optimizing healthcare costs, and strengthening overall healthcare system performance. To build patient trust, reduce disparities, and drive continuous advancements in surgical practices, the Michigan Surgical Quality Collaborative (MSQC) was established in 2005. Originally created through a partnership between Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan (BCBSM), Blue Care Network (BCN), the American College of Surgeons, and 17 participating hospitals, MSQC aimed to foster collaboration in advancing surgical quality. Today, the collaborative includes 70 Michigan hospitals, all committed to improving care delivery through the promotion of evidence-based, best practices in general surgery.
MSQC Achievements
Over the past two decades, MSQC has made a profound and lasting impact on surgical quality, achieving milestones that have significantly advanced the field. The following are highlights of those success stories.
Postoperative Opioid Prescribing Recommendations
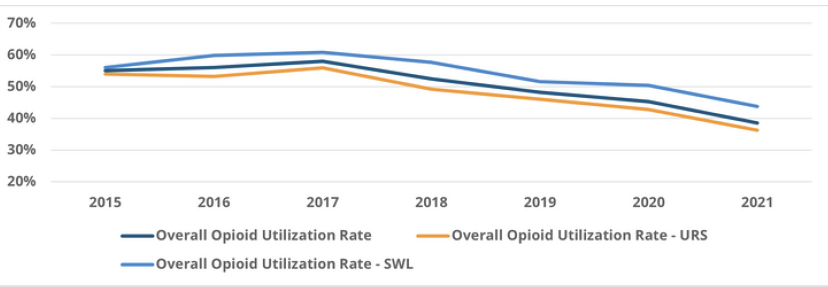
Post-procedural pain management is a crucial component of surgical care, and yet the ongoing opioid epidemic posed a pressing question: How much prescription pain medication should be prescribed after surgery? Recognizing the absence of a standardized, evidence-based approach to opioid prescribing, MSQC partnered with Michigan Overdose Prevention Engagement Network (OPEN) in 2016 to develop and implement new guidelines for general surgery and hysterectomy patients. A range of quantitative measures were employed to inform these recommendations, including the number of pills prescribed, patient-reported outcomes on pill usage, and pain levels post-surgery.
Since the guidelines were introduced, opioid prescriptions across Michigan have dropped by 50% over the course of a few years. Follow-up data showed that patients did not report higher pain levels, reductions in satisfaction with their care, or the need for additional prescriptions. This initiative has had a significant impact on public health in Michigan, helping to reduce the availability of unused opioids in the community and mitigate their potential for misuse.
MSQC Care Pathways
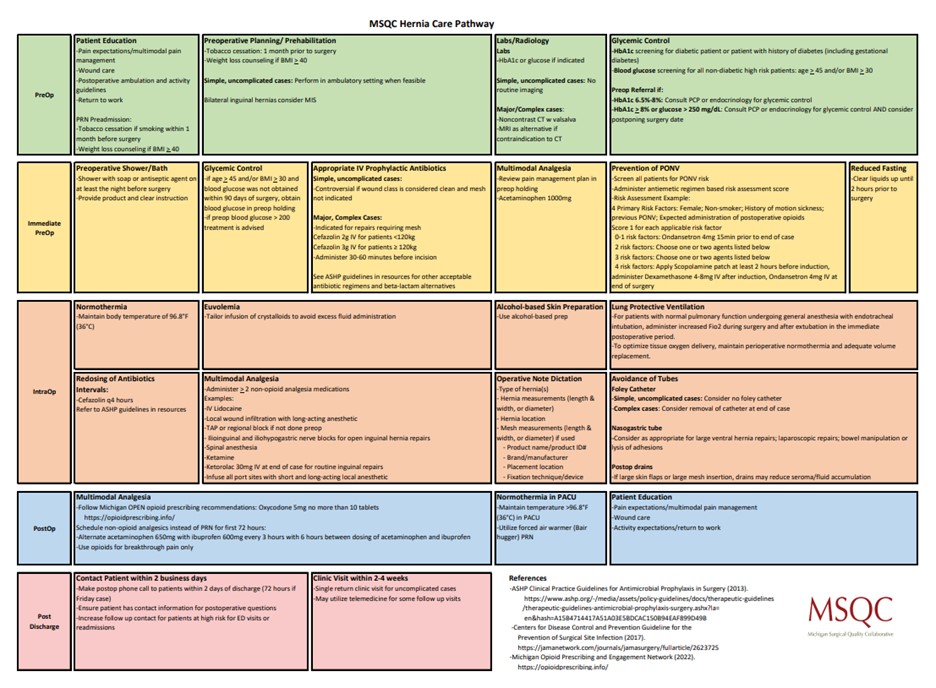
In the surgical field, the absence of standardized procedures often results in variation in practice, as demonstrated by the previously mentioned lack of opioid prescribing guidelines. MSQC is dedicated to fostering consistency by standardizing approaches and ensuring the adoption of evidence-based practices. Through collaboration with multidisciplinary teams across member hospitals statewide, MSQC developed the MSQC Care Pathways (Figure 1). These standardized care pathways, which cover surgeries such as colon surgery, hernia repair, laparoscopic cholecystectomy, hysterectomy, Whipple procedures, and outpatient mastectomies, are helping to improve patient outcomes and reduce care variation across Michigan.
Figure 1. MSQC Hernia Care Pathways
Current Initiatives
Building on its past successes, MSQC is advancing several key initiatives to further enhance surgical care. This includes focuses on surgical quality measures for specific procedures, including colorectal cancer, abdominal hernia, and breast surgery, for which MSQC intends to improve both short- and long-term outcomes. Additionally, MSQC is working to identify patient frailty before surgery and implement targeted interventions to enhance overall surgical experiences and outcomes.
In collaboration with ASPIRE/MPOG, MVC, and MPrOVE, MSQC is also supporting the de-implementation of unnecessary preoperative testing before low-risk surgery. As such, MSQC offered metrics in 2023 and 2024, with 33 MSQC hospitals participating in the initiative and observing a 20% reduction in testing. MSQC continues this partnership via the RIght-Sizing Testing before Elective Surgery (RITE-Size) grant, which aims to support hospitals across Michigan in reducing unnecessary testing via a multi-component intervention first piloted at Michigan Medicine. Several of the resources used in the RITE-Size program (Figure 2) were developed in partnership with MSQC and its hospital abstractors, such as the decision aid, sample testing protocol, and engagement package for primary care physician partners.
Figure 2. RITE-Size Resources

A recent survey of surgeons identified postoperative urinary retention as one of the most common challenges in their practices. In response, MSQC has partnered with the Surgical Urinary Catheter Care Enhancement Safety Study (SUCCESS) team to develop a comprehensive toolkit. Created and tested in collaboration with a pilot group of MSQC hospitals, surgeons, and nurses, the toolkit aims to reduce inappropriate perioperative urinary catheter use, prevent complications such as infections and trauma, and improve the management of postoperative urinary retention. By 2024, over 35 MSQC hospitals had implemented these tools, significantly enhancing patient safety, particularly for the most vulnerable populations.
Services and Benefits for MSQC Members
MSQC offers a unique opportunity for hospitals and surgeons to improve surgical care through reliable, real-time, risk- and reliability-adjusted data. By leveraging data collected from trained nurse data abstractors, MSQC helps hospitals statewide with benchmarking, meeting quality standards, and driving continuous improvement in surgical care. In collaboration with surgeon leaders across Michigan, MSQC develops robust variables not captured by other organizations, offering valuable insights into a variety of surgical procedures. Additionally, MSQC provides participating surgeons with personalized reports, empowering them to assess their own performance and identify opportunities for improvement at the individual level. When asked what makes MSQC’s work within the CQI community unique, Dr. Michael Englesbe, MD, FACS, MSQC Program Director explained, “What makes us unique is the quality of clinical data that we have access to. Issues that matter the most to patients such as ‘Did I get the right cancer care’ or ‘Will this hernia repair last me a long time’ are the focus of the MSQC. Again, the high-quality clinical data enables high-quality and impactful efforts to transform care in Michigan.”

MVC is proud to partner with MSQC in advancing surgical quality improvement across Michigan. The BCBSM-funded CQIs play a crucial role in driving healthcare quality improvement, and MVC is excited to continue showcasing the innovative contributions of individual CQIs and the ways in which MVC’s data analytics are supporting high-value care initiatives across the portfolio. Please reach out to us by email if you are interested in learning more about MVC data and collaboration offerings.