Emphasizing health equity in Michigan is a key strategic initiative for the Michigan Value Collaborative. MVC kicked off this strategic initiative at its October 2021 semi-annual meeting with the theme of “The Social Risk and Health Equity Dilemma.” Since then, MVC has expanded its access to data sets related to health equity, developed hospital health equity reports, and regularly convened stakeholders from around the state via a health equity workgroup series that launched in January 2022. MVC is eager to find new and exciting ways to utilize data and collaborate with members on health equity topics in Michigan.
One of the more recent enhancements to MVC’s capacity was the addition of more granular data on social determinants of health. MVC secured access to Distressed Community Index (DCI) data, a tool for measuring the comparative economic well-being of US communities. DCI data was first integrated into MVC reporting in August with the distribution of a new push report on emergency department and post-acute care use. It was also incorporated in MVC’s newest physician organization report on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which was distributed to PO members last month.
The DCI data are developed by the Economic Innovation Group and derived from the US Census Bureau’s Business Patterns and American Community Survey Five-Year Estimates (2016-2020). The DCI is a composite measure of ZIP-code level socioeconomic distress comprised of seven key indicators, including education, housing, unemployment, poverty, income, employment changes, and business (see Figure 1).
Figure 1.

The resulting DCI composite measure assigns individual five-digit ZIP codes a number from 0 to 100 with 0 representing the least distressed communities and 100 representing the most distressed communities. The DCI is then grouped into five ordered categories for ease of comparison: distressed, at risk, mid-tier, comfortable, and prosperous. The data include details on 874 ZIP codes in Michigan that have at least 500 residents, of which 192 (22%) are prosperous communities and 120 (14%) are distressed communities. The map below (see Figure 2) highlights the distribution of community-level distress categories across the state of Michigan, with the blue areas representing more prosperous communities and the red areas representing more distressed communities.
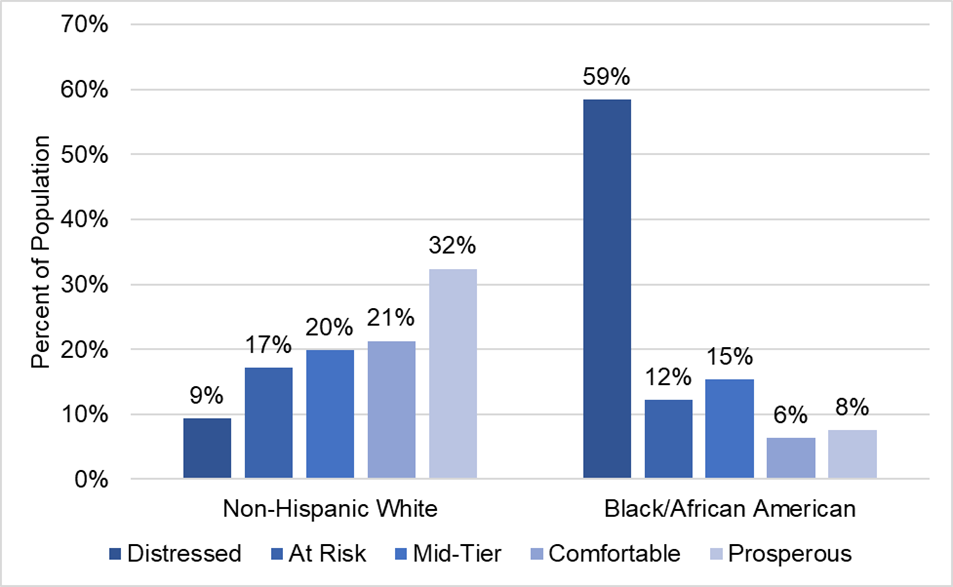
The data also reveal staggering racial/ethnic disparities in Michigan. As seen in Figure 3 below, Black/African American Michiganders are far more likely to live in distressed communities relative to non-Hispanic whites. This information is further evidence of the need for broad efforts to reduce disparities according to race/ethnicity and local community distress.
Figure 3.
Incorporating the DCI into MVC data analytics will offer new opportunities to better understand health equity challenges in Michigan. The MVC Coordinating Center looks forward to using these data in collaboration with its members and is eager to discuss how best to leverage such data sets to identify inequity in Michigan healthcare. Please contact MVC to learn more or request custom analytics.