On Monday, organizations large and small will honor the work and legacy of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. His work has continued to inspire the country on issues such as equality, discrimination, and systemic racism. As the MVC Coordinating Center approaches this national holiday, we reflect on the continued relevance of one of Dr. King’s famous quotations about healthcare injustices: "Of all the forms of inequality, injustice in health is the most shocking and inhuman.” Dr. King made this comment and others about healthcare discrimination in 1955, and yet almost 70 years later our healthcare system continues to grapple with issues of inequity, discrimination, and racism.
As a result, health equity is currently a priority across most major healthcare and government agencies. The MVC Coordinating Center has similarly identified health equity as a strategic priority in recent years and in its newest strategy refresh. This means that a variety of health equity conversations, reporting, and learning opportunities will be offered to MVC members throughout the year. In discussions with members to date, it has been evident that many are still in an information-gathering phase and desire advice around best practices. Therefore, MVC will seek to identify differing approaches to health equity across the collaborative through a health equity survey, which will be shared with members at the end of January. Members will have until mid-April to complete this survey, after which MVC will report aggregate results and facilitate connections between members.
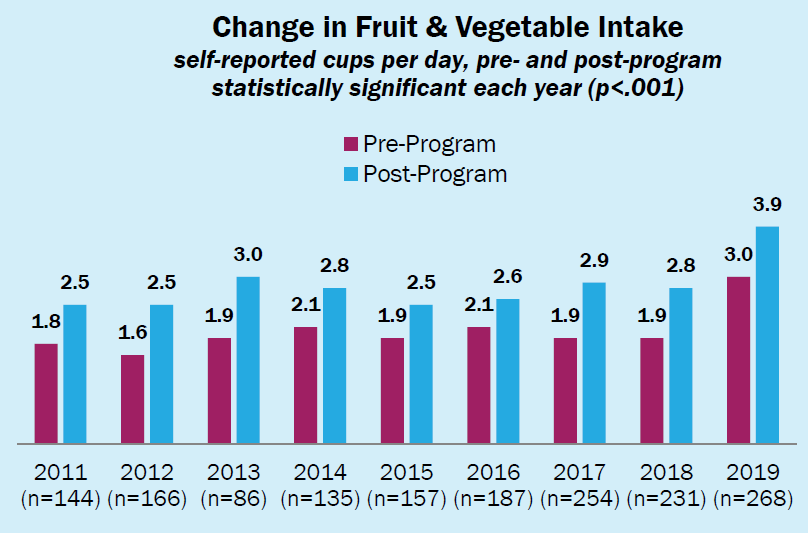
MVC also plans to continue integrating health equity into its workgroup offerings, with each workgroup series (e.g., cardiac rehab, preoperative testing, post-discharge follow-up, rural health, sepsis, health in action) offering at least one session focused on equity. In addition, MVC is planning to offer a reimagined health equity report informed by the results of the survey that integrates supplemental data sets tied to social determinants of health.
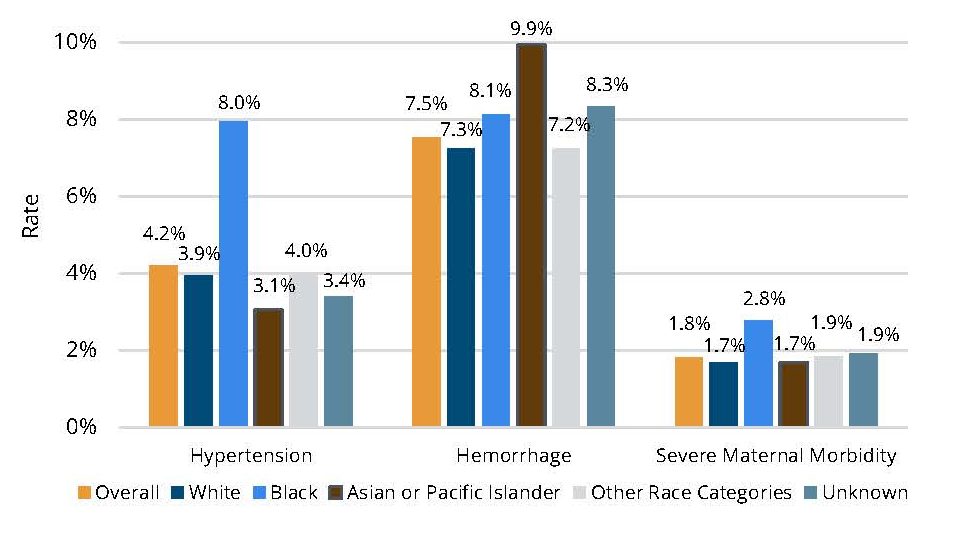
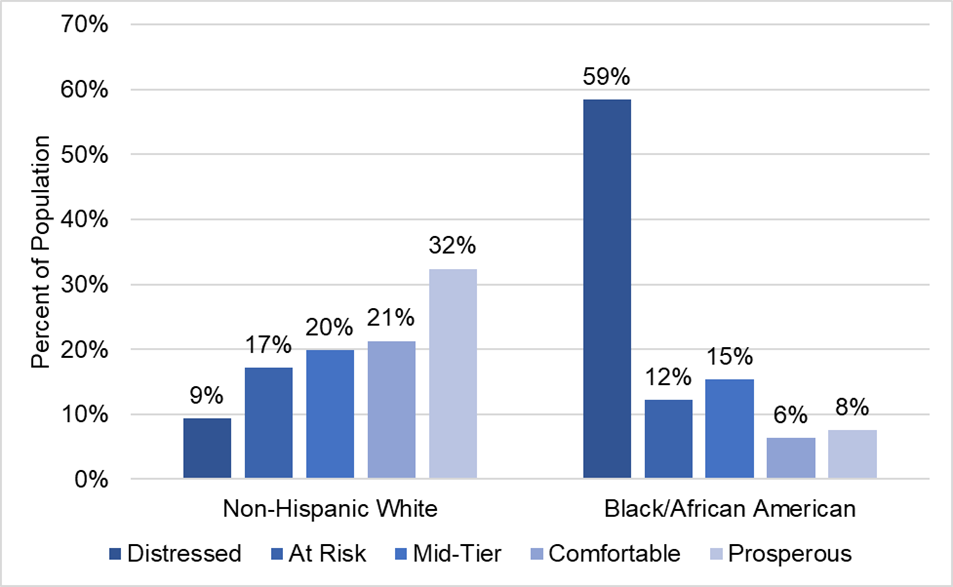
MVC’s equity activities this year come on the heels of MVC’s fall collaborative-wide meeting, which focused on how interdisciplinary collaboration can support efforts to reduce disparities and provide equitable healthcare. The agenda incorporated the voices of key leaders and community-based organizations working to improve equity in care delivery, including keynote speaker Renée Branch Canady, PhD, MPA, who serves as CEO of the Michigan Public Health Institute (MPHI) and is a recognized national thought leader in the areas of health inequities and disparities, cultural competence, and social justice. Key takeaways and links to slides from Dr. Canady and other guests are available in MVC’s meeting summary. The session also included roundtable speakers from community-based organizations, which helped to facilitate collaboration and networking to support direct patient support services. MVC will strive to offer similar networking and collaboration opportunities at future collaborative-wide meetings.
The MVC Coordinating Center wishes its members and partners well as they celebrate MLK Day in their way. We are grateful for your continued engagement and partnership on important issues as we collectively strive to provide high-quality care for all.