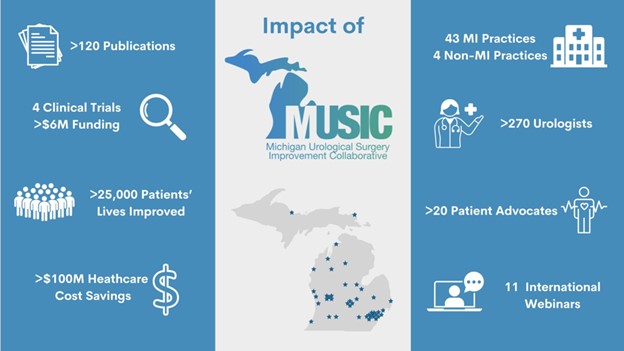
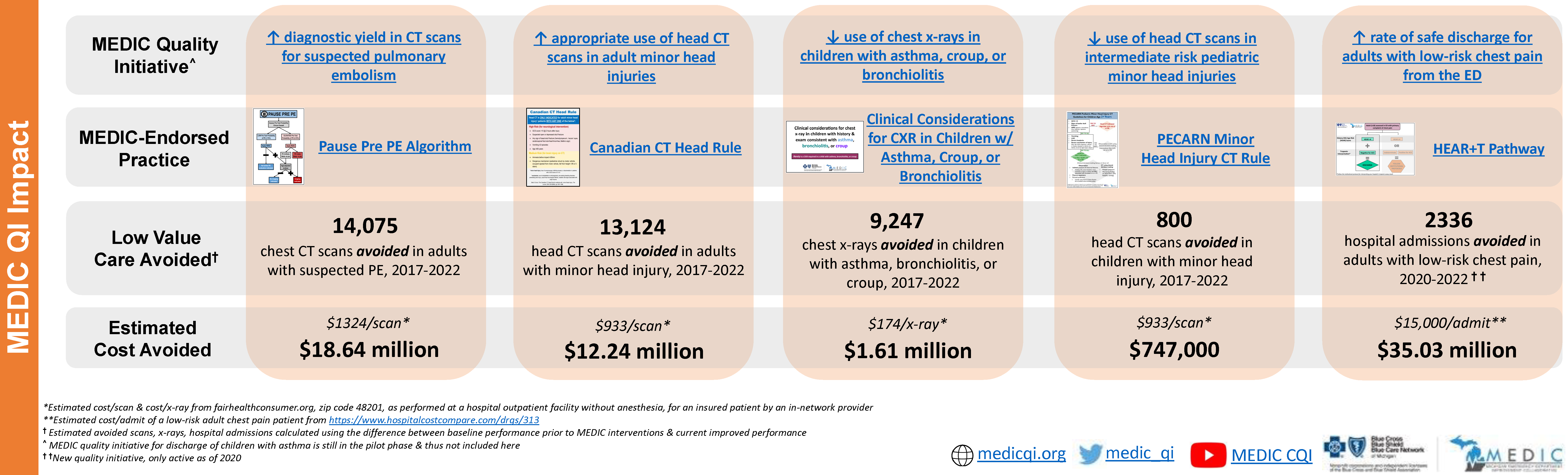
The Michigan Cardiac Rehab Network (MiCR) held its fourth annual in-person meeting at Corewell Health East in Troy, MI on Nov. 13, 2025. The full slide deck is now available [LINK]. Opening the meeting’s agenda was Mike Thompson, PhD, MPH, co-director of MiCR and senior advisor at MVC. He welcomed attendees to the Corewell Health Beaumont Troy campus, announced the finalization of MiCR’s two-year strategic plan (Figure 1), and shared that Henry Ford Hospital was receiving the final MiCR Cardiac Rehabilitation Utilization Award mini grant to support their QUASAR project, which pilots a hub-and-spoke telehealth model for cardiac rehabilitation (CR) delivery. He also highlighted renewed engagement of the MiCR Advisory Council and ongoing collaboration with the Healthy Behavior Optimization for Michigan (HBOM) team to collect patient stories.
Figure 1. 2025-2027 MiCR Operational and Strategic Framework

Dr. Thompson described MiCR’s strategic initiatives in two key areas: telehealth and medication management. For telehealth, MiCR is employing a multi-pronged approach that includes surveys, qualitative interviews, and stakeholder outreach to understand the current state, implementation plans, and barriers to telehealth CR implementation in Michigan. This effort will also include an evaluation of the value and utilization of existing resources that support telehealth CR. In the realm of medication management, MiCR is using claims data to assess variability in medication adherence among CR participants and applying surveys, interviews, and outreach to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement. These efforts will lead to actionable plans designed to help stakeholders implement initiatives that elevate CR services across the state.
MiCR/HBOM Heart-to Heart Collaboration Update
Larrea Young, MDes, a human-centered design project manager at HBOM, announced the launch of Heart-to-Heart, a new initiative designed to inspire both patients and providers by collecting and sharing diverse stories of patient experiences with CR. The goal of this effort is to foster broader conversations about the life-changing impact of CR and encourage patient enrollment by providing strong peer endorsements. The HBOM and MiCR teams are gathering first-person accounts in video, audio, and photo formats to create an engaging, free, and reusable story library for CR advocates across Michigan and beyond. Progress so far includes 10 patient interviews at two sites, representing a wide range of demographics and experiences. HBOM previewed a clip from a patient interview at the meeting. Clinicians were also encouraged to contribute to the effort by sharing voice messages about cardiac rehabilitation through Speakpipe.
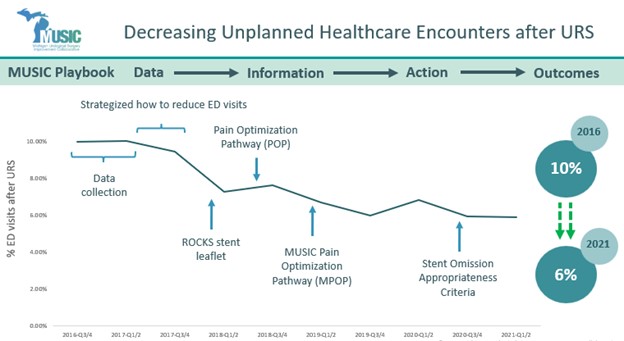
Leveraging National CR Quality Improvement (QI): Efforts, Updates, and Next Steps
Megan Gross, MPH, CHES, ACSM-CEP, EIM, clinical exercise physiologist at Holland Hospital and board director of the Michigan Society for Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation (MSCVPR), shared a summary of national CR QI efforts and discussed how her organization has leveraged these initiatives to advance local QI projects. She identified tools and resources, advocacy, and QI champions as the core “pillars” of quality improvement, all supported by a foundation of data. Gross highlighted nationally available resources such as the Million Hearts/American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation (AACVPR) Cardiac Rehab Change Package and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s (AHRQ) TAKEheart initiative, as well as ongoing advocacy, research, and publications. Encouraging all CR program staff to view themselves as champions, she transitioned to describe how Holland Hospital has applied these tools in their own QI efforts, concluding with a description of their project to implement an inpatient liaison model aimed at increasing CR participation.
Understanding the Physiologic and Clinical Significance of Metabolic Equivalents (METS)
Barry Franklin, PhD, a director emeritus of preventive cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at Corewell Health East, gave a presentation explaining the physiological and clinical significance of metabolic equivalents (METs). Dr. Franklin summarized key lessons from his 50-year career in clinical exercise physiology, highlighting topics such as energy systems for exercise, acute cardiorespiratory responses (VO2 max), METs, anaerobic (ventilatory) threshold, fitness and mortality, fitness in relation to surgical outcomes and health care costs, and clinical considerations for prescribing exercise intensity. Dr. Franklin’s key take home message related to his guidelines and recommendations for moving patients from achievement of lower to higher METs through CR participation.
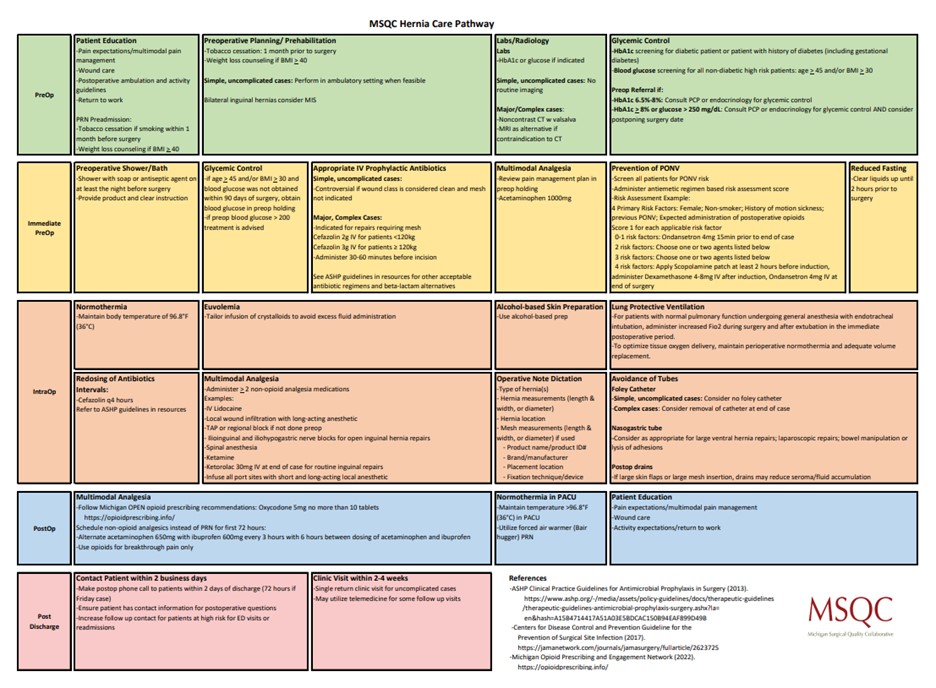
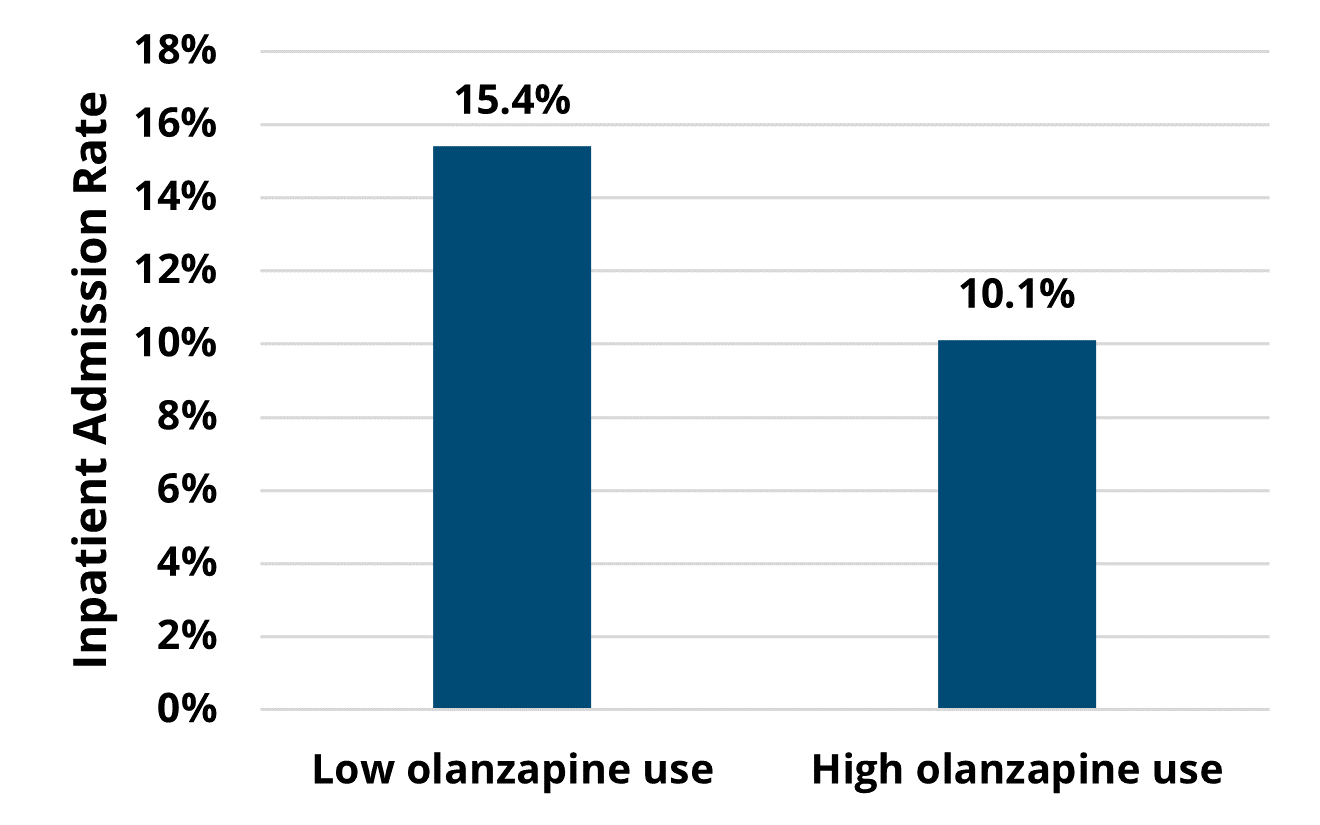
Sustaining Cardiac Rehab Through Health System Integration
Brett Reynolds, MPH, ACSM-CEP, and Cindy Haskin-Popp, MS, ACSM-CEP, of Corewell Health East shared their multi-year journey to build a fully integrated CR service line after the Corewell Health merger. They detailed key phases from planning and collaboration, such as forming committees, aligning workflows, and engaging stakeholders, to implementation, which involved developing communication channels, Epic workflow training, and designating super users for consistency. Post-integration successes included cross-training, improved communication, standardized competencies, and better patient care (Figure 2), while ongoing challenges remain in areas like documentation and order set variation. Looking forward, the team aims to pursue AACVPR accreditation, standardize patient education, and create a centralized referral process to further improve care quality and patient experience.
Figure 2. Corewell Health System CR Post-Integration Outcomes

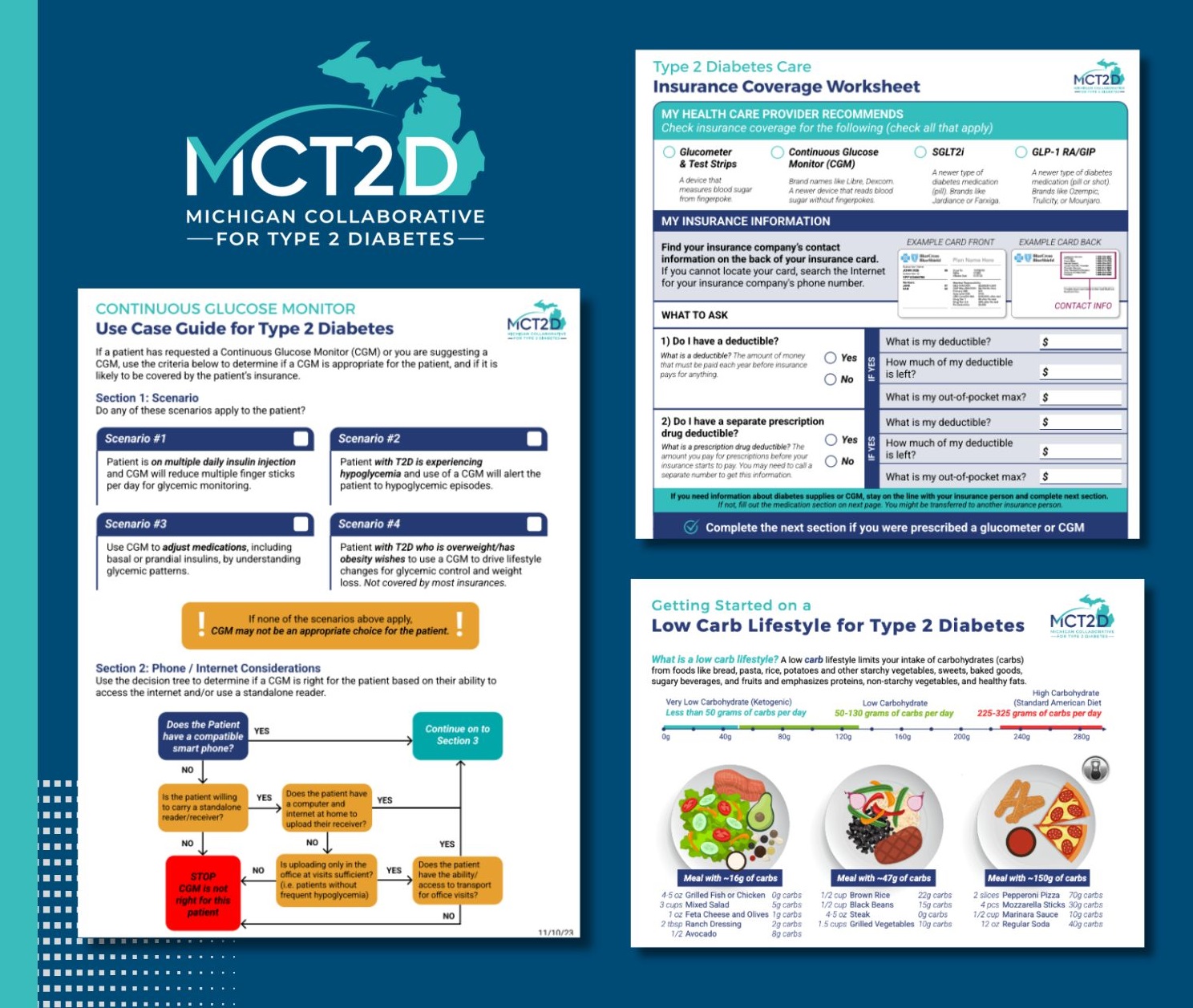
Medication Management Breakout Session
Following lunch, MVC Project Manager Emily Woltmann, PhD, MSW, led attendees through an interactive breakout session that explored roles, responsibilities, and strategies related to medication management in CR. Participants met in small groups to discuss strategies and barriers to addressing medication management issues with their CR patients (Figure 3). The information gathered will be used by the MiCR team to help drive forward the MiCR medication management strategic initiative.
Figure 3. MiCR Co-Director Mike Thompson facilitating a medication management breakout discussion

Data Presentation and Panel Discussion on CR Completion Rates
Dr. Thompson led a session utilizing MVC claims data, which shared aggregate and unblinded data on CR completion rates across Michigan. This included a summary of the proportion of participating patients who finished the widely recommended 36 sessions, as well as those who completed at least 12 or 24 sessions. The findings revealed substantial variability among cardiac rehabilitation programs based on both metrics, with completion rates for the full 36 sessions ranging from 0% to 50% at CR programs across Michigan.
A subsequent panel discussion moderated by Dr. Thompson included Amy Poindexter, BS, CEP, CR manager at Trinity Health Ann Arbor and Livingston Hospitals, Amber Steele, BS, ACSM-CEP, CR lead at McLaren Bay Region Hospital, and David Running, BS, ACSM-CEP, CEPA, supervisor of CR at University of Michigan Health-West. Both the panel and the audience voiced a variety of strategies they use to increase session attendance in CR, such as developing supportive relationships with patients, watching for plateaus in progress, and having completion rituals and celebrations when a patient graduates from CR. The most frequently cited challenges to patients completing an adequate number of sessions were barriers related to the travel distance to CR programs and medical insurance copays.
AACVPR President Stacey Greenway Presents Keynote on AACVPR Strategic Plan
Stacey Greenway, MA, MPH, MAACVPR, ACSM-CEP, the newly elected president of AACVPR, delivered the meeting keynote, highlighting AACVPR’s growing multidisciplinary membership, widely recognized training and certification programs, and enhanced data registry resources for cardiac and pulmonary rehabilitation professionals. She outlined the 2026–2028 strategic plan focused on increasing awareness and engagement, advancing innovative delivery models like telehealth, and strengthening research and outcomes through a national network. Greenway encouraged MiCR members to participate nationally via opportunities such as the AACVPR quality improvement cohort, day on the hill, and legislative advocacy, and she invited involvement in content submission and session proposals for the 2026 Annual Meeting in San Antonio, TX.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Dr. Jessica Golbus, MD, MS, Co-Director of MiCR, wrapped up the meeting with a summary of the day’s key points and next steps. She shared that a follow-up email will be sent in the coming weeks and announced the dates for MVC cardiac rehabilitation virtual workgroups scheduled for 12 p.m. on Feb. 10, June 9, and Oct. 20 in 2026. The date for MiCR’s spring webinar will be announced soon.
MiCR is a partnership between BMC2 and MVC, the purpose of which is to improve access to, utilization of, and delivery of cardiac rehabilitation services across the state of Michigan. MVC is proud to partner with providers, hospitals, and fellow CQIs in advancing quality initiatives that benefit patients in Michigan. If you have questions about any of the topics discussed at the MiCR annual meeting or are interested in following up for more details on other initiatives, email the MiCR leadership team [EMAIL] or the MVC Coordinating Center [EMAIL].