The Michigan Value Collaborative (MVC) held its spring 2024 collaborative-wide meeting on Friday, May 10, in Midland. A total of 114 attendees representing 69 hospitals, 10 physician organizations, 4 Collaborative Quality Initiatives (CQIs), and 10 healthcare systems from across the state of Michigan came together to discuss new strategies for coordinating care across the continuum. The theme of this meeting was chosen in response to questions echoed by many attendees at the fall 2023 meeting about how to improve care coordination for our patients and families. Looking to the success stories of members and other stakeholders across the state, the MVC Coordinating Center recognized care coordination as a key strategy to high-value healthcare delivery.
MVC Director Hari Nathan, MD, PhD, kicked off Friday’s meeting with an update from the MVC Coordinating Center (see slides). He welcomed MVC’s newest team members - Site Engagement Coordinator Emily Bair and Senior Advisor Nora Becker – and expressed recognition and gratitude for Mike Thompson’s contributions as MVC’s Co-Director as he transitions to the role of senior advisor. Additionally, Dr. Nathan highlighted the successes delivered by the Coordinating Center since October’s collaborative-wide meeting, including co-hosting the Michigan Cardiac Rehab network (MiCR) meeting and launching a preoperative testing trial. MVC’s new multi-payer cardiac rehab registry reports were also introduced. Dr. Nathan then provided an overview of MVC’s refreshed strategic framework, which will serve to guide the Coordinating Center’s strategic direction over the coming years. Key components of MVC’s refreshed framework (Figure 1) include augmenting existing data to enhance and enrich MVC data sources, methods, and outputs; extending membership reach to broaden MVC’s membership base and refresh engagement approaches; and emphasizing equity to increase focus on health equity and social risk to improve the health of all groups.
Figure 1.

Following the MVC’s updates, Dr. Nathan introduced Kim Fox, MPH, Senior Data Analyst with MVC, who led a presentation on exploring organizational and system-level insights through MVC custom analytics (see slides). In collaboration with McLaren Macomb, the session highlighted MVC’s custom analytic process, the value and impact of customized reports (Figure 2), and findings from a recent report prepared for McLaren Macomb.
Figure 2.
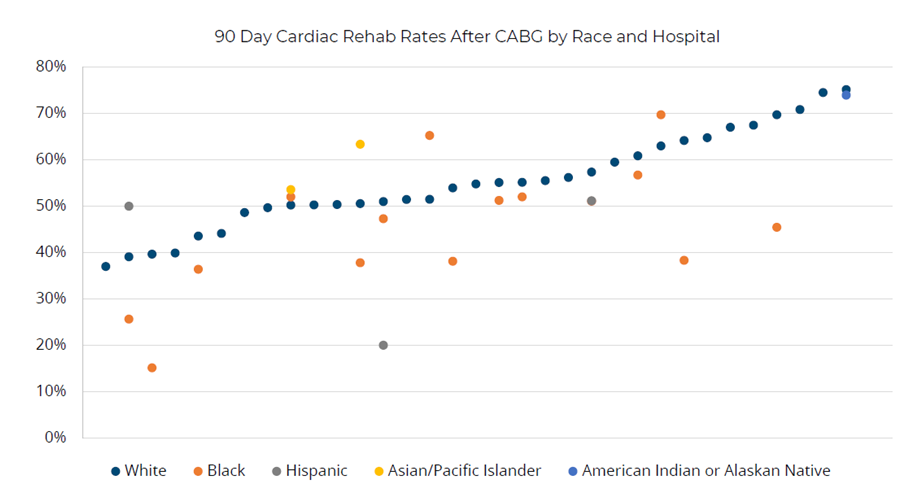
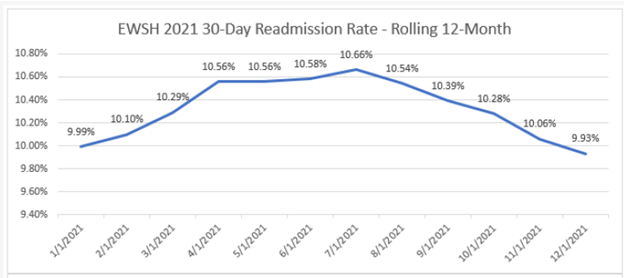
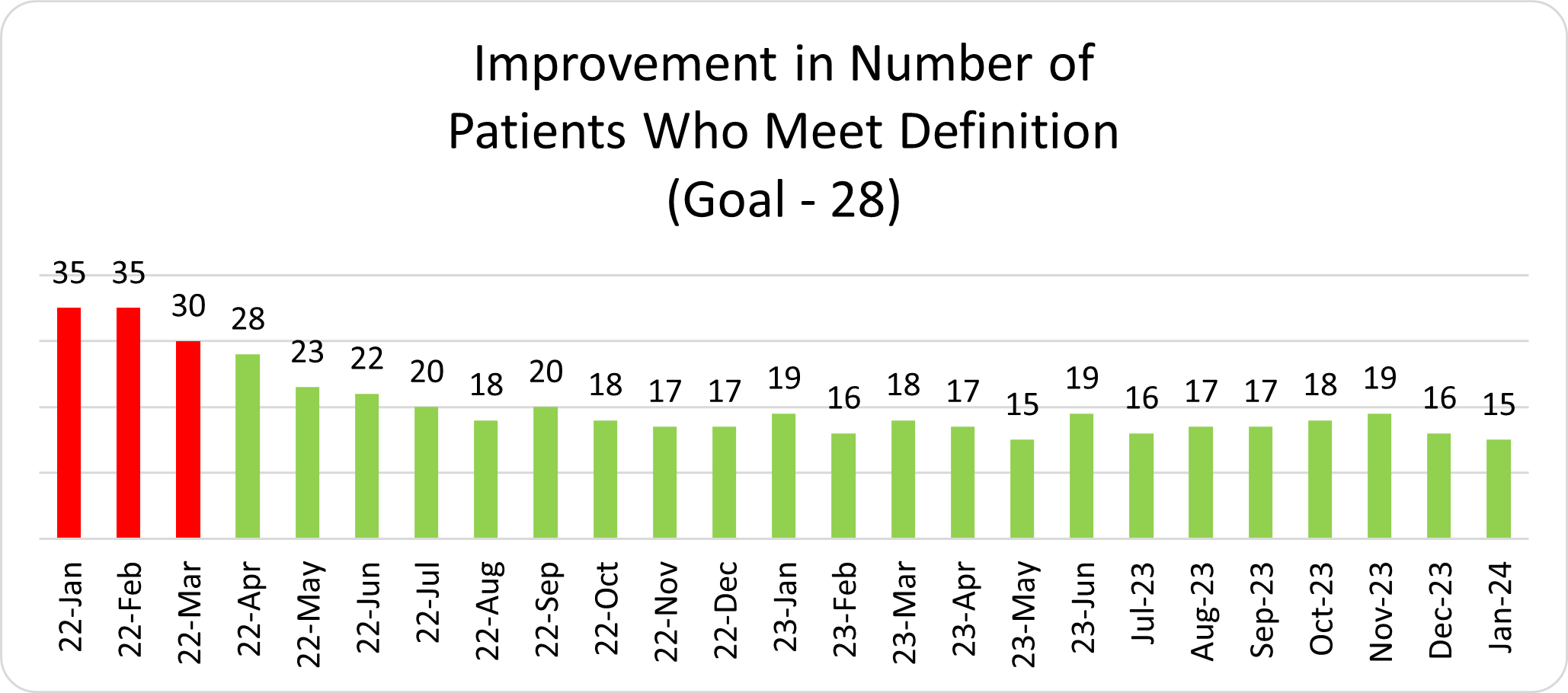
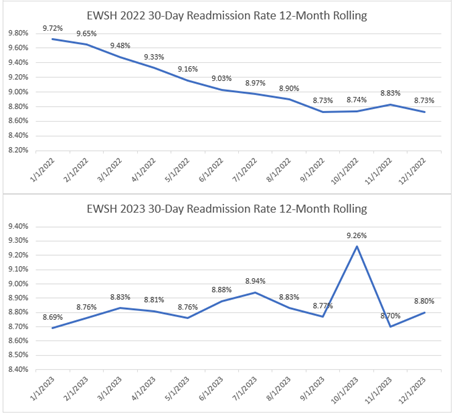
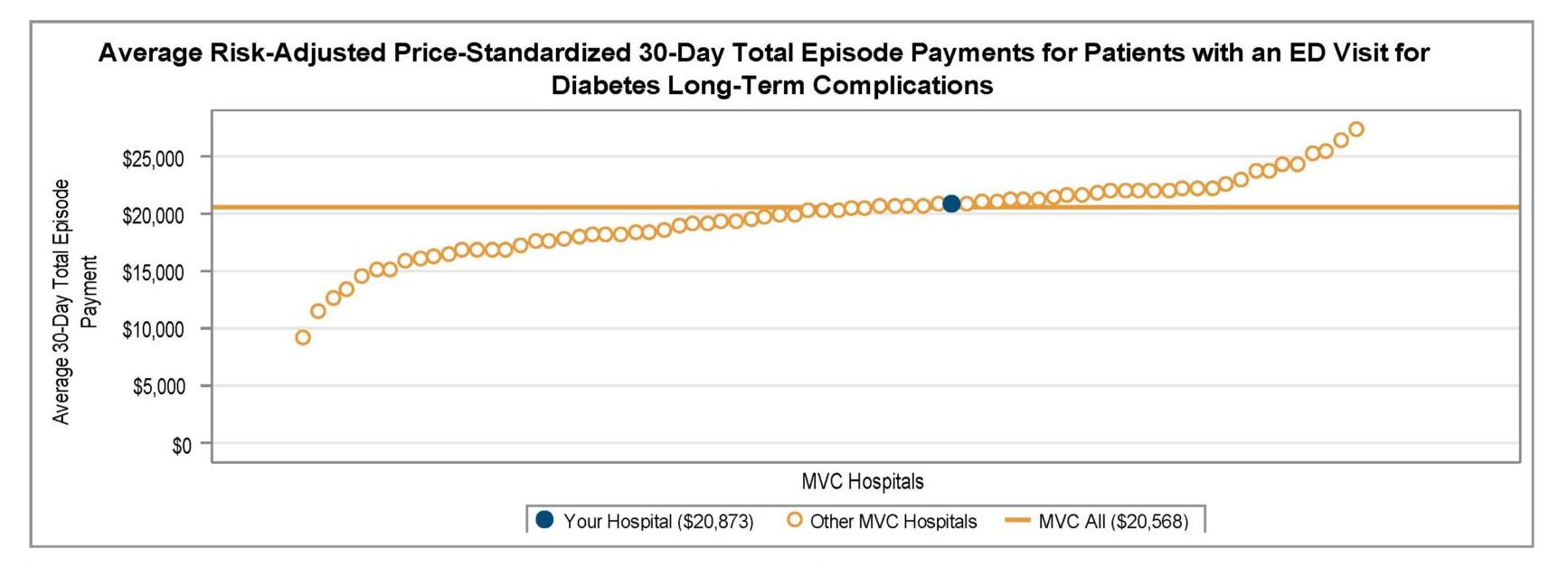
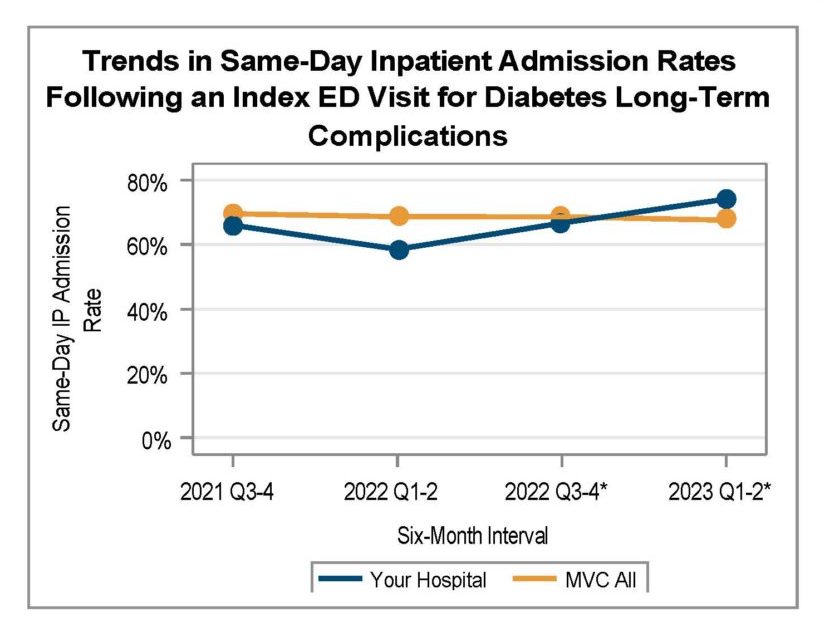
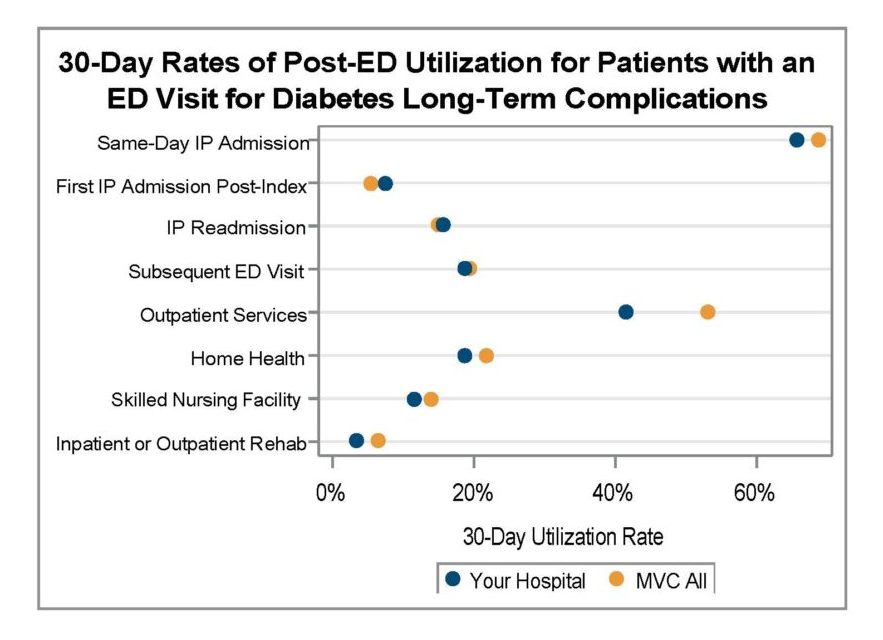
Ms. Fox detailed how this recent custom report investigated total episode payments, post-discharge care utilization, and specialist participation for patients admitted for a congestive heart failure (CHF) or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) event. After a detailed walk-through of the report components, focusing on patients with CHF, Ms. Fox introduced Beth Wendt, DO, Vice President of Clinical Operations and Medical Director of Quality and Accreditation at McLaren Macomb, who shared how McLaren Macomb has leveraged it’s custom MVC report to inform quality improvement efforts for their patients (Figure 3).
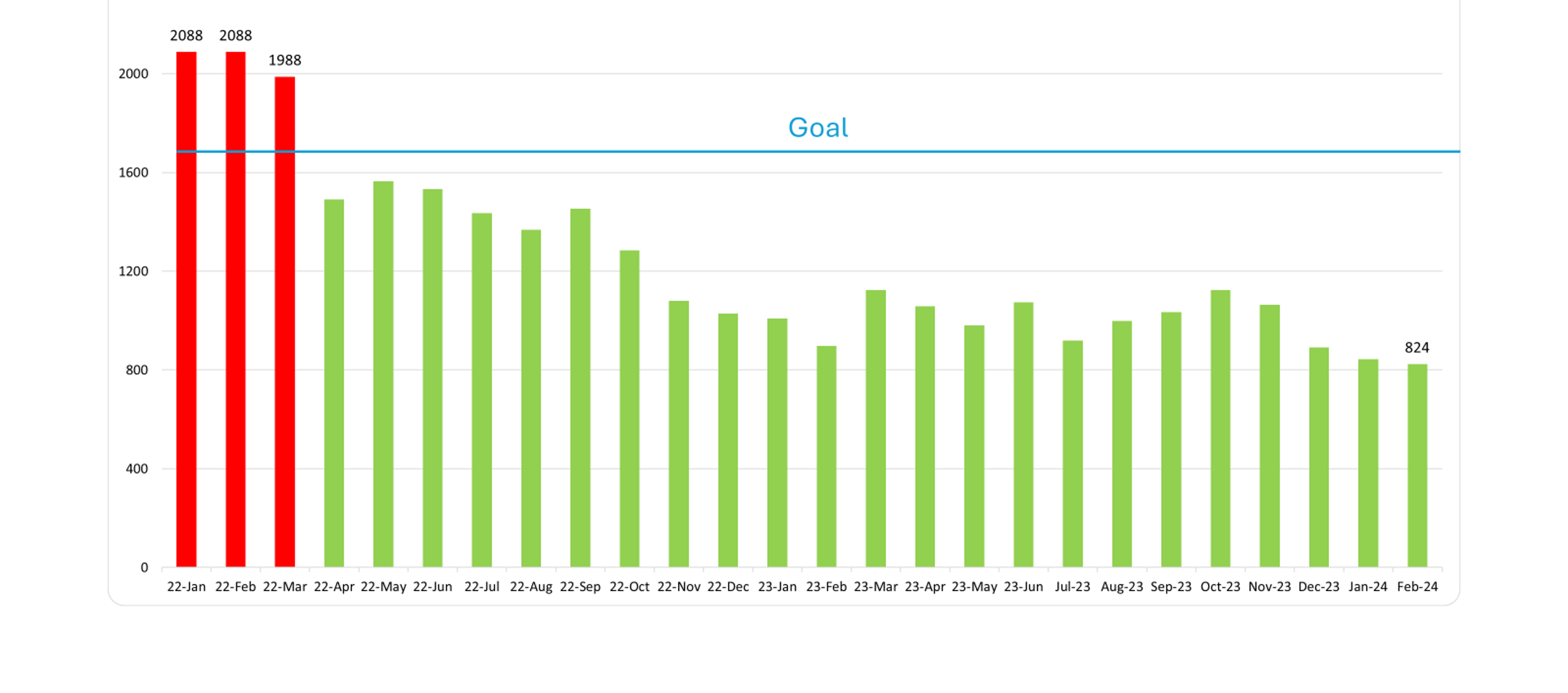
After Dr. Wendt’s presentation, Ms. Fox shared unblinded data from MVC hospitals for timing of first home health visit by patients following a CHF-related admission. If you are interested in a custom analytic report, please reach out to the MVC Coordinating Center to schedule a kick-off meeting.
Following the MVC data presentation, an MVC member presentation was delivered by Steven Frazier, BA, RN, ACM, RN, Director of Quality and Patient Safety, Post-Acute Care with MyMichigan Health, and Allison Klimaszewski, RN, BSN, Nursing Supervisor at the Continuing Care Clinic Midland with MyMichigan Medical Group. They detailed how MyMichigan Health has implemented a continuing care clinic model (Figure 4) to support patients struggling to access primary care services in receiving post-discharge follow-up care after a hospitalization (see slides). Mr. Frazier and Ms. Klimaszewski shared that, while data is limited, the Continuing Care Clinic is making a difference for their patients. Patients receiving transition support care through the Continuing Care Clinic are showing lower all-cause readmission rates, pneumonia mortality rates are decreasing, and feedback is positive.
Following MyMichigan Health’s presentation, attendees were invited to participate in a poster session, featuring quality improvement initiatives from MVC hospital and physician organization members. The MVC Coordinating Center would like to thank all poster presenters for sharing their work. Electronic copies of the posters are available here: Posters 1-6, Posters 7-13.
After a networking lunch, attendees reconvened for roundtable discussions. During the session, attendees visited five tables of their choosing, where they learned about the work of the roundtable speaker, asked questions, and discussed the table topic with their peers. The MVC Coordinating Center would like to thank its roundtable presenters (Figure 5) for sharing their work and expertise.
Following the roundtable discussions, Jana Stewart, MS, MPH, Project Manager with MVC, presented results from MVC’s recent health equity member survey (see slides). After discussing the survey’s goals, use cases, and overarching questions, Ms. Stewart provided a high-level snapshot of the results, including the most common initiatives to reduce patient access challenges, common demographics of focus, the top barriers preventing hospitals from developing and implementing health equity initiatives, and the most common data sources hospitals are using to identify or measure patient health disparities. Ms. Stewart also shared MVC’s equity strategy (Figure 6), detailing how MVC will support members in the health equity space.
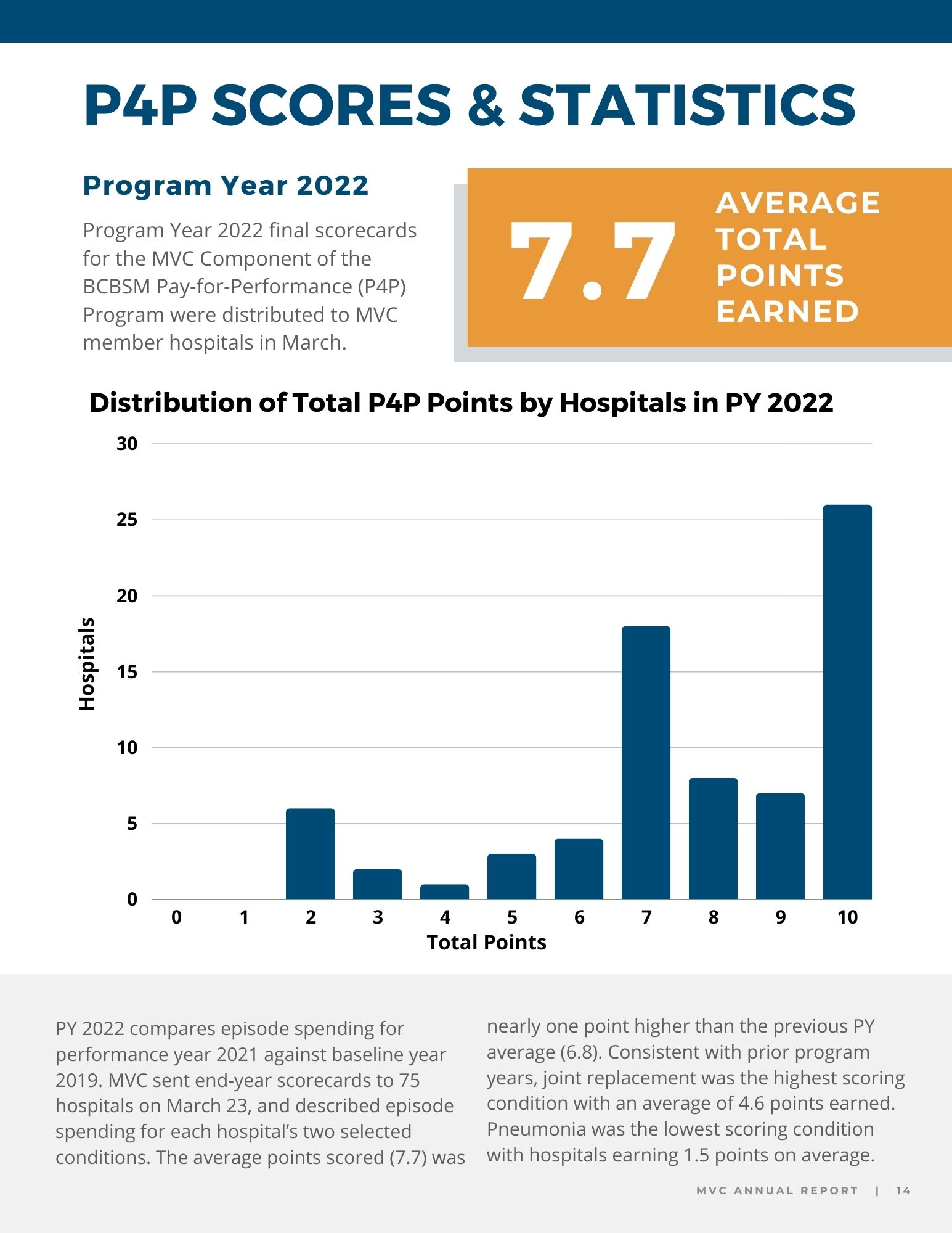
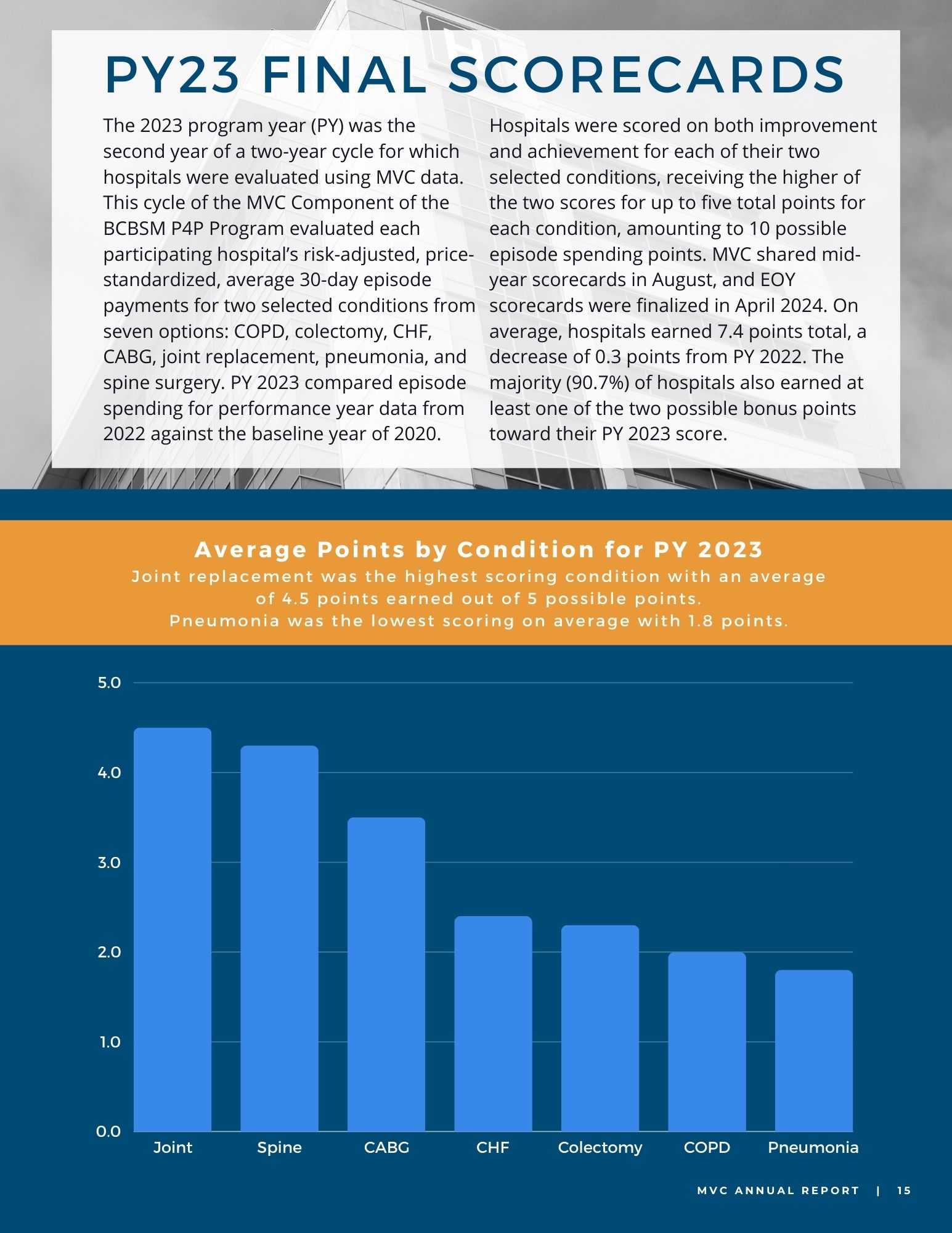
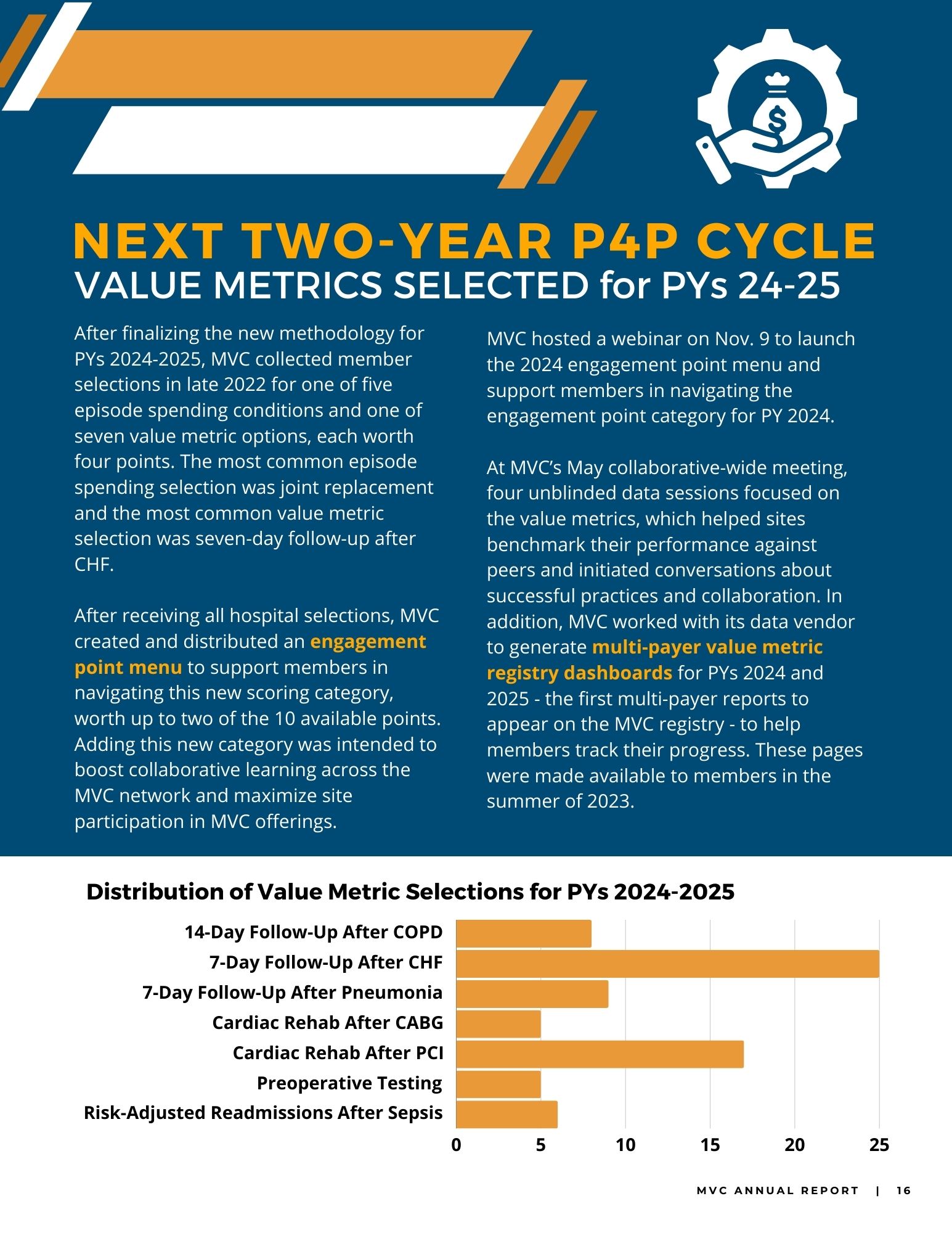
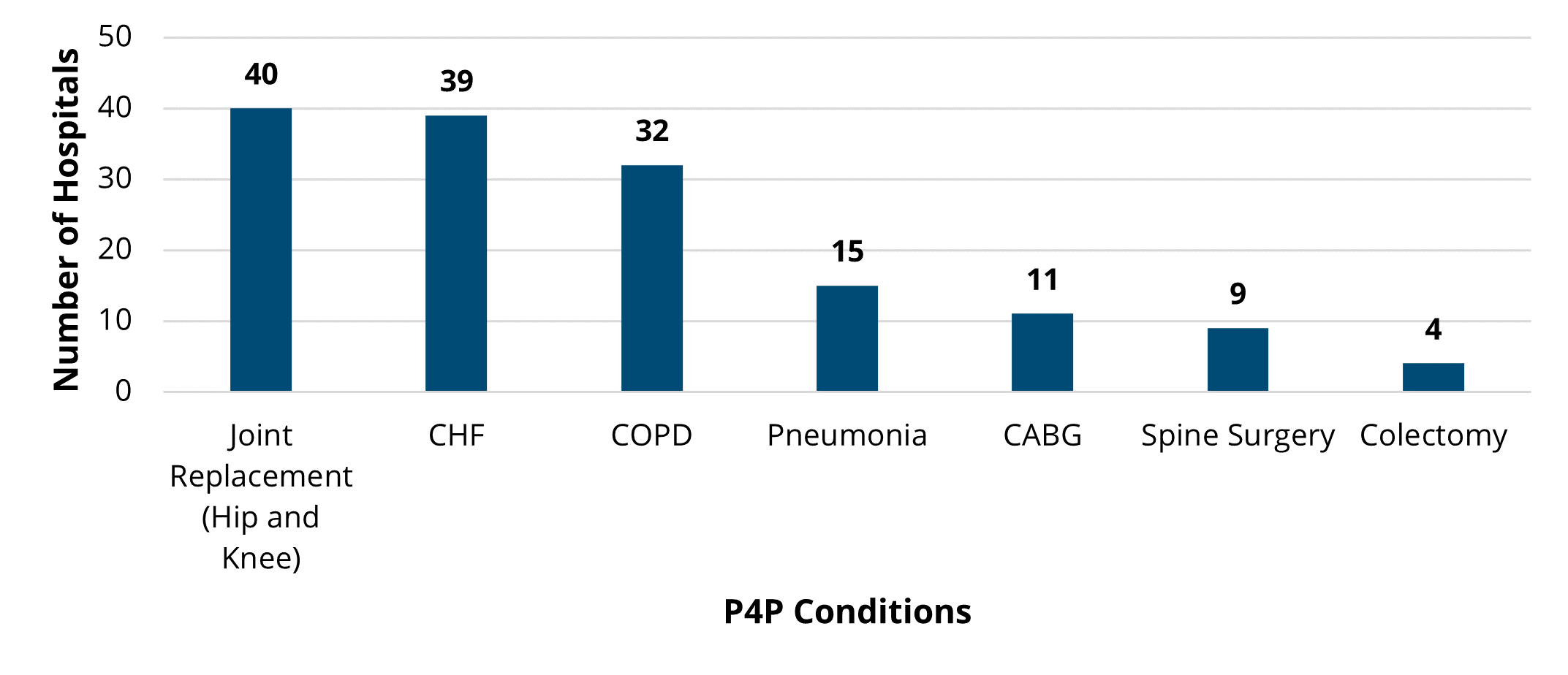
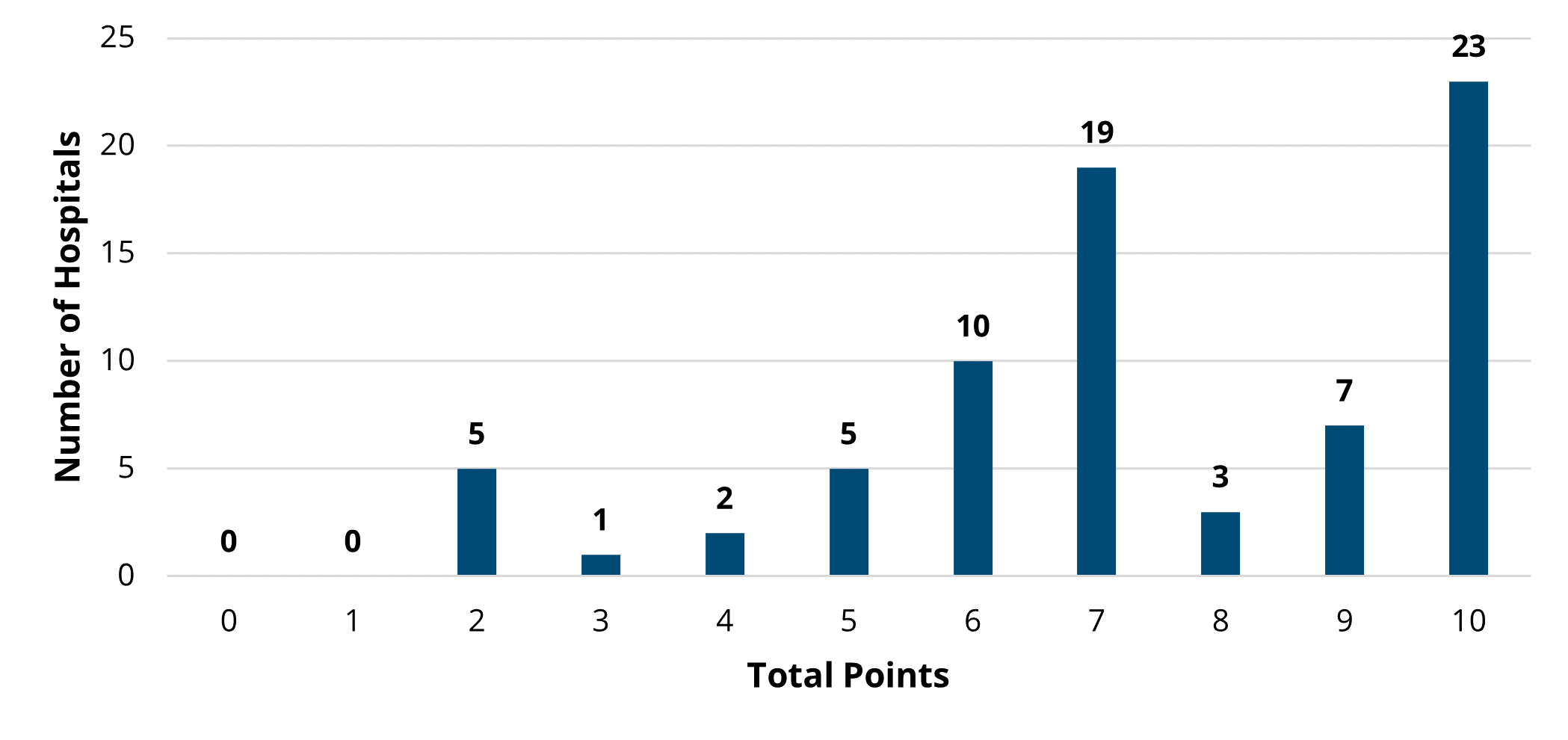
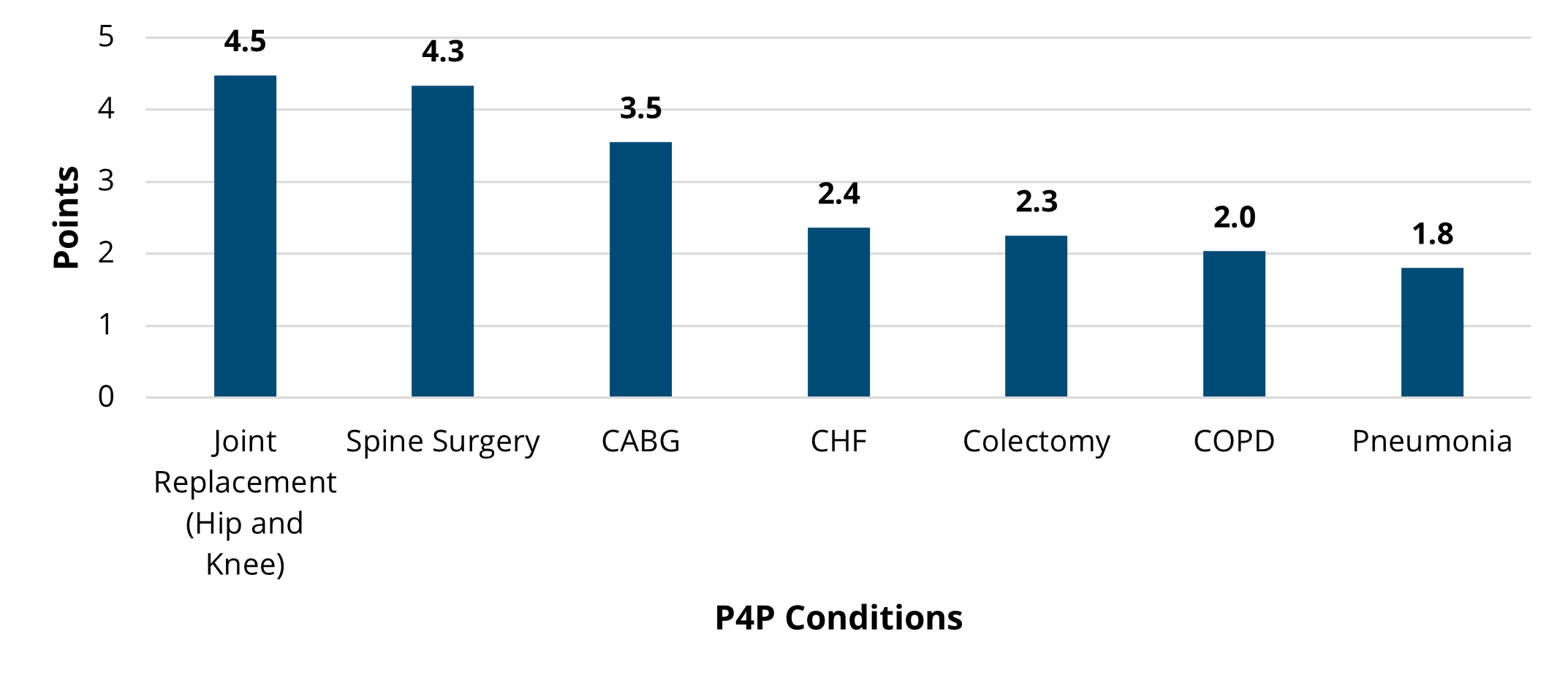
To close out the meeting, MVC Co-Director Mike Thompson, PhD, MPH, provided a review of Program Year (PY) 2023 of the MVC Component of the BCBSM P4P Program (see slides). After reviewing the program components, Dr. Thompson provided a summary of PY23 performance across the collaborative. It was also noted that PY 2024 mid-year scorecards will be distributed in the summer and current scores can be access by members on the MVC registry. If you or members of your team would like access to MVC’s registry, please contact the MVC Coordinating Center.
If you have questions about any of the topics discussed at MVC’s spring collaborative-wide meeting or are interested in following up for more details, contact the MVC Coordinating Center. MVC’s next collaborative-wide meeting will be in person on Friday, October 25, 2024, in Livonia.