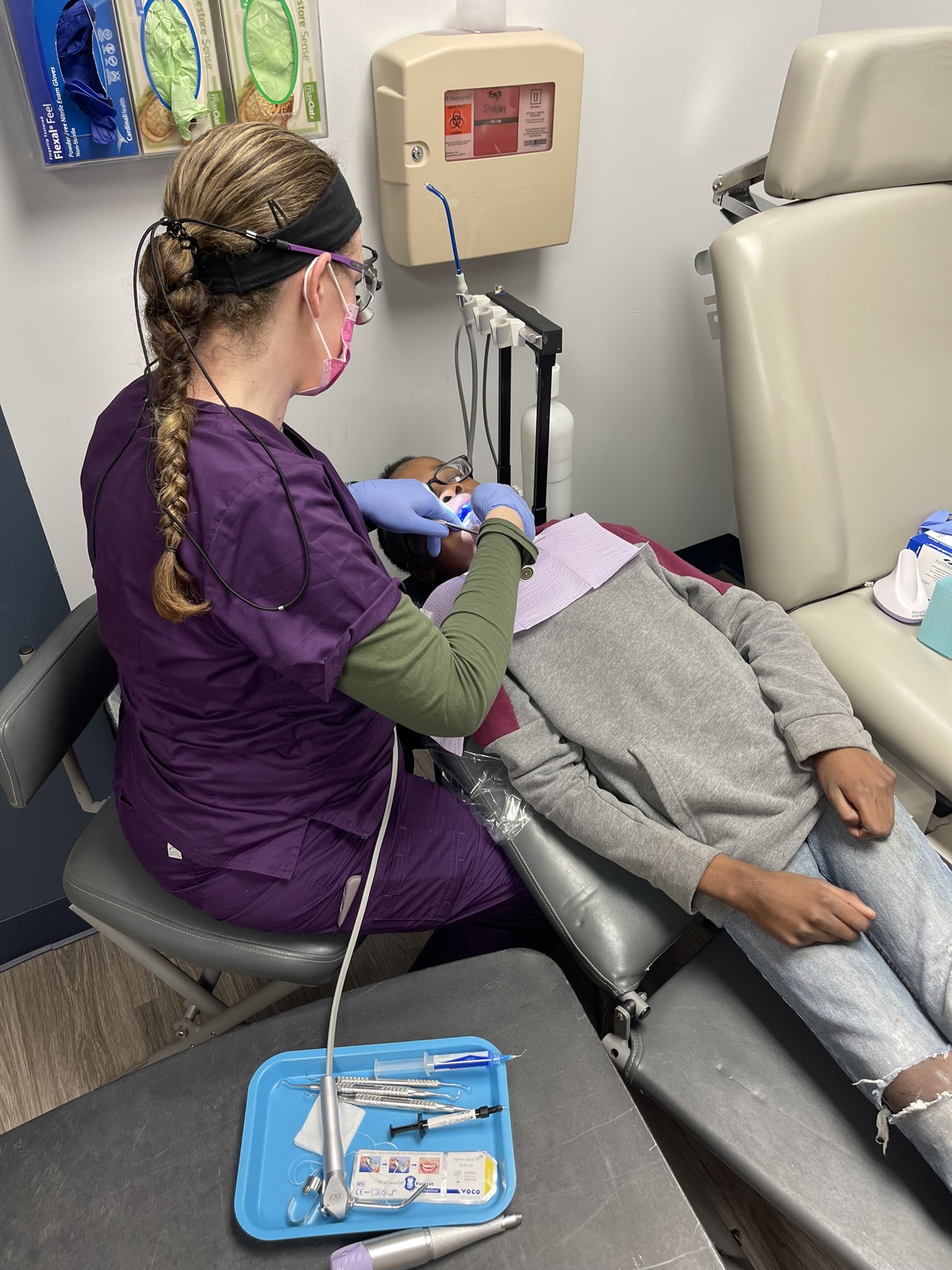
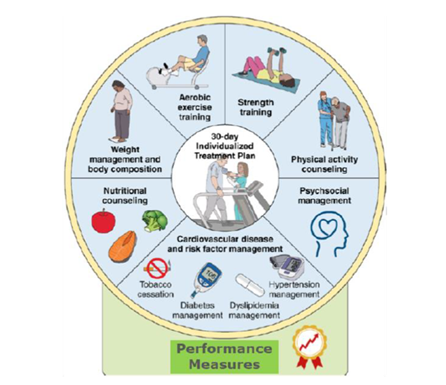
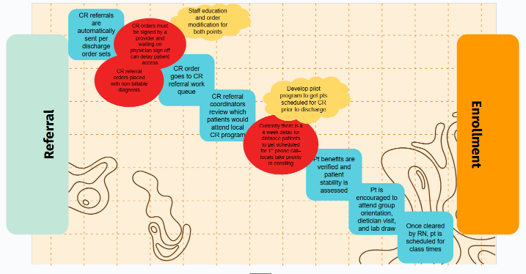
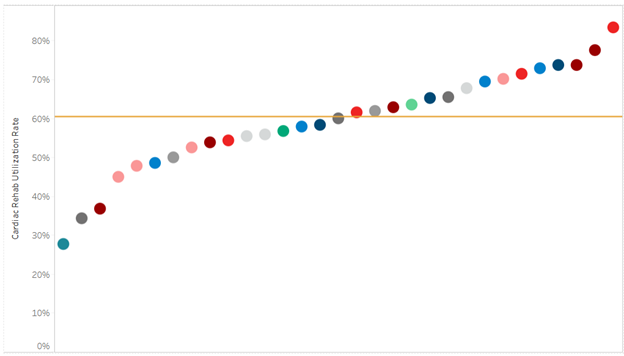In March, MVC hosted two virtual workgroup presentations – the first, a rural health workgroup focused on enhancing early detection of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in primary care and the second, a post-discharge follow-up workgroup focused on the impact of launching a population health program. MVC hosts two virtual workgroups per month with topics rotating between post-discharge follow-up, sepsis, cardiac rehabilitation, rural health, preoperative testing, and health in action (ad hoc focused topics). Each month, the MVC Coordinating Center publishes key highlights from the past month’s presentations to provide resources and support best practice sharing across the state.
Rural Health Workgroup March 11, 2025
In support of National Kidney Month, MVC’s first rural health workgroup of 2025 featured a presentation by Mary Wozniak, Program Manager for the National Kidney Foundation of Michigan (NKFM) and Jill Oesterle, Director of Provider Solutions for Michigan Center for Rural Health (MCRH). The joint presentation focused on the partnership between NKFM and MCRH on a 2024 Medicaid Impact and Expansion grant.
Low recognition of CKD is a chronic health problem. Nearly 35.5 million Americans are projected to have CKD but according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) up to 90% of patients are unaware of their CKD status. Additionally, among Medicaid beneficiaries with CKD, the average estimated healthcare costs per year is more than six times the average cost per person when compared to patients without CKD.
Despite the availability of diagnostic tests like estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and albumin: creatinine ratio (ACR), fewer than half of individuals with diabetes and less than 10% with hypertension receive annual CKD screenings, even though both groups face heightened CKD risk. For more information about testing, Wozniak recommended the guidelines for CKD screening and management from KDIGO and KDOQI.
Knowing that CKD can be diagnosed with two simple evidence-based laboratory tests, NKFM and MCRH teamed up to combat low CKD screening rates. To start, Wozniak and Oesterle explained that the partnership established a CKD Learning Collaborative Initiative made up of four rural health clinics: Cass City Family Practice, Cass City Medical Practice, St. Helen Mclaren Primary Care, and Clare McLaren Central. These sites were identified based on data indicating a high CKD prevalence or low CKD screening rates within their Medicaid patient populations.
The collaborative aimed to increase awareness of the importance of early detection and management of CKD among Medicaid eligible populations at Rural Health Clinics (RHCs) using a three-pronged approach:
- Increase provider and clinical education
- Promote referrals to evidence-based lifestyle change programming (through NKFM)
- Provide support and guidance to implement screening into clinical workflows
Each pilot site participated in an initial assessment including the collection of baseline data. NKFM then provided one-hour tailored clinical education sessions on various CKD topics from diagnosis and staging to lifestyle and nutrition approaches for prevention and management. Wozniak and Oesterle attribute the collaborative’s ability to adapt these trainings to each clinic based on their identified needs, capabilities, and goals to the successes observed in increased screening and diagnoses made at these pilot sites when compared to baseline data.
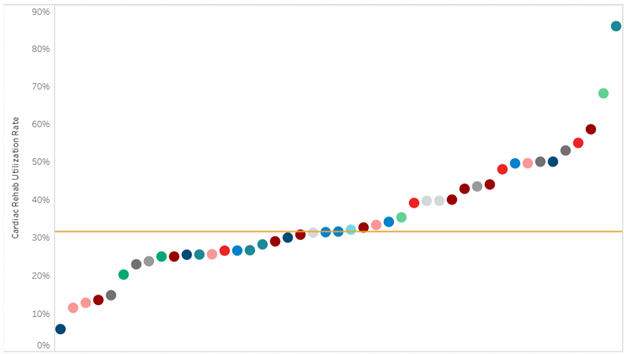
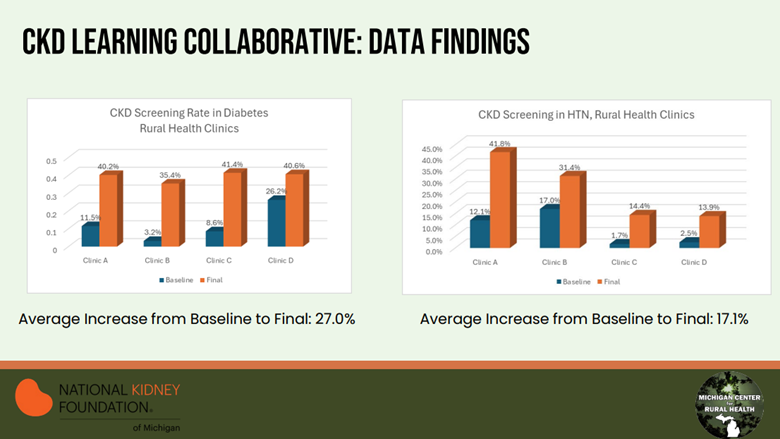
Amongst the four pilot sites, the collaborative found CKD screening rates in patients with diabetes increased on average by 27%, while in patients with hypertension (HTN) screening increased on average by 17% (Figure 1). Overall, CKD diagnosis increased by an average of 6.5% when compared to baseline.
Figure 1. CKD Learning Collaborative Data Findings
Empowering the healthcare team and patients with actionable recommendations was another strategy identified to be especially helpful in moving the needle on screening rates. Ensuring laboratory representation from the beginning of the project was especially helpful in overcoming challenges related to laboratory test ordering and reporting. Moving forward, the presenters note that the project timeline may need to be adjusted to build in enough time to identify clinic champions and develop buy-in with clinic staff.
Throughout the project, NKFM and MCRH met monthly with all the pilot sites together, as well as separately. This allowed them the opportunity to collaborate on shared successes and barriers while also offering an opportunity to cater education and guidance of interventions to each site’s needs. While each pilot site ended the project with different next steps, all will continue to receive support from NKFM and MCRH as they progress on their journeys to diligently increase CKD screening, diagnosis, and referrals to lifestyle management programs.
Using the remaining funds from this grant, NKFM and MCRH built on their successes by developing a CKD toolkit for rural providers. The toolkit allows them to broaden the reach of the CKD Learning Collaborative’s impact to more clinics across Michigan. While the toolkit does cater to a rural health clinic audience, any clinic interested in learning more about enhancing CKD care can access the suite of provider and patient education resources, workflows, and screening tools on MCRH’s website.
MVC Rural Health Workgroup Mar. 11, 2025
Post-Discharge Follow-Up Workgroup March 20, 2025
This month, MVC’s post-discharge follow-up workgroup featured a presentation by Morgan Albright, Director of Case/ Care Management and Population Health at Oaklawn Hospital and Zach Chapman, Executive Director of Oaklawn Medical Group. Their co-presentation centered on Oaklawn Hospital and Oaklawn Medical Group’s collaboration to integrate Medicare Annual Wellness Visits (MAWVs) into their population health program.
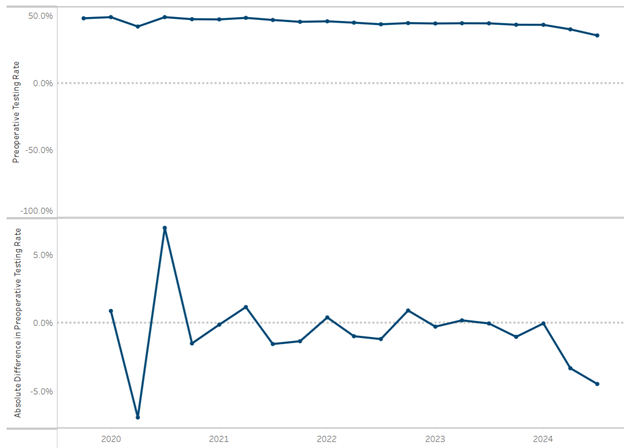
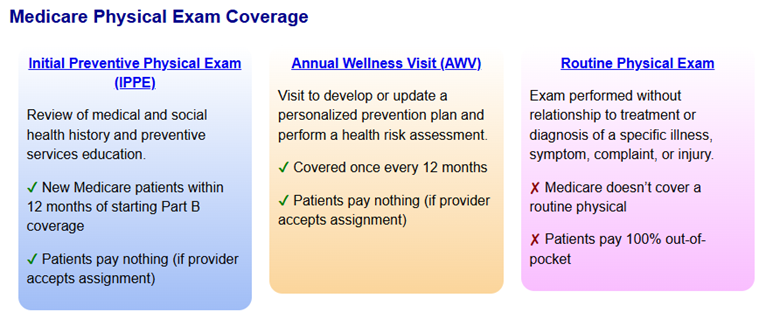
MAWVs focus on preventive care and health maintenance and include a health risk assessment, review of medical history, and development of a personalized prevention plan (Figure 2). Unlike a preventive physical exam (IPPE) or routine physical exam, MAWVs do not include a comprehensive physical exam. Albright explained that while MAWVs are a standard benefit for Medicare beneficiaries, these visits were infrequently completed due to the limited time available during a PCP visit. Additionally, since these visits are hands off assessments and previously stand-alone appointments, patient satisfaction following these visits was generally low.
Figure 2. Comparison of Medicare Physical Exam Coverage
In January of 2023, three population health nurses were integrated across Oaklawn’s outpatient offices with the goal of conducting dual and/or phone-prep MAWV appointments. Combining an MAWV with another regularly scheduled visit has helped to alleviate the barriers that existed for the Medicare patient population. Benefits of completing the MAWV include increased care planning, depression screening, and patient satisfaction.
An additional benefit to the integration of the population health nurses and MAWVs has been in the improvement of billing and revenue. Albright explained that while an initial MAWV does not necessarily generate revenue, any subsequent MAWVs, such as those focused on depression screening or social determinants of health (SDoH) concerns, are billable. Champman notes that in 2022, only 66 depression screenings were billed, compared to close to 4,000 in 2024. Similarly, billing for advanced care planning has increased from 94 cases in 2022 to 1,100 in 2024. Chapman estimates the return on investment is about 150% of the cost of a dedicated population health RN. He also noted the impact the introduction of population health support staff has had on reducing the primary care physician’s workload.
In addition to the MAWV assessments, Albright and Chapman note Oaklawn has initiated a chronic care management program. This program is a collaborative effort between Oaklawn’s care managers and a third-party chronic care management vendor. These check-ins take place between regularly scheduled appointments to ensure patients have the resources (access to medications, transportation, etc.) to be successful in management of their chronic conditions. The depth and breadth of the resources available between these two groups allows them to reach out to over 800 patients monthly. Identified downstream effects of this program have been reduced emergency department (ED) utilization and reduced length of stays (LOS).
Paired together, the addition of MAWVs and the chronic care management program have robustly increased Oaklawn Hospital and Medical Group’s ability to reach their aging Medicare patients. Overall, roughly 50% of Oaklawn’s eligible population completed MAWVs in 2024, compared to just 11% in 2021. This translates to about 1,800 wellness visits in 2021 versus 5,500 in 2024. Oaklawn’s next steps include intentionally working to engage with the remaining 50% of eligible Medicare patients to ensure they do not miss out on valuable healthcare resources.
To learn more about Medicare Wellness Visits including coding and billing requirements, visit the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services education website.
MVC Post-Discharge Follow-Up Workgroup Mar. 20, 2025
If you are interested in pursuing a healthcare improvement initiative, MVC has a robust registry of claims data that can be utilized, as well as site specialists who can help facilitate connections with peers doing similar work. Please reach out to us by email if you are interested to learn more about MVC data or engagement offerings. Please also join us for upcoming workgroups by registering on MVC’s website.