Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) affects over 1 in 9 adults in Michigan and increases the risk of kidney and cardiovascular disease, hypertension, nerve and eye damage. Although newer interventions have demonstrated effectiveness in treating and preventing T2D, barriers to widespread dissemination and implementation remain a challenge. Delivering evidence-based diabetes care to all T2D patients in Michigan is essential for creating a future where diabetes is no longer a chronic progressive disease.
With this vision in mind, the Michigan Collaborative for Type 2 Diabetes (MCT2D) launched in 2021 and aims to accelerate implementation of guideline-concordant care, through supporting its participating practices with quality improvement efforts. MTC2D is currently focused on three evidence-based strategies: dietary and lifestyle changes based on the use of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), guideline-directed antihyperglycemic medications, and low-carbohydrate eating patterns. MCT2D recognizes the importance of utilizing these strategies to reduce T2D incidence and to slow disease progression to improve health in Michigan and lower health care costs.
In three short years, MCT2D’s quality improvement efforts have already resulted in major achievements. As MCT2D Program Director and Associate Professor of Family Medicine at the University of Michigan Lauren Oshman, MD, MPH, stated,

So far, MCT2D has recruited more than 400 primary care, endocrinology, and nephrology practices across the state. Their efforts have resulted in a 12% relative reduction in patients with an A1c greater than 8% from 2021 to 2023, as well as an increase in CGM prescribing from 17% to 31% for patients who were on insulin (2021-2023).
MCT2D’s recent successes stem from its commitment to placing patients at the heart of their efforts. The MCT2D patient advisory board meets six times a year to guide the activities of the collaborative, including reviewing medication handouts, low-carbohydrate meal plans and grocery lists, instructional videos on injectable medications, and guides for using continuous glucose monitoring devices (Figure 1). This ensures materials are accessible and patient friendly. Patients are also invited to attend collaborative-wide and regional meetings to share their stories alongside healthcare professionals, further emphasizing the central role of the patient in MCT2D’s quality improvement initiatives.
Figure 1. MCT2D Resources and Education Materials
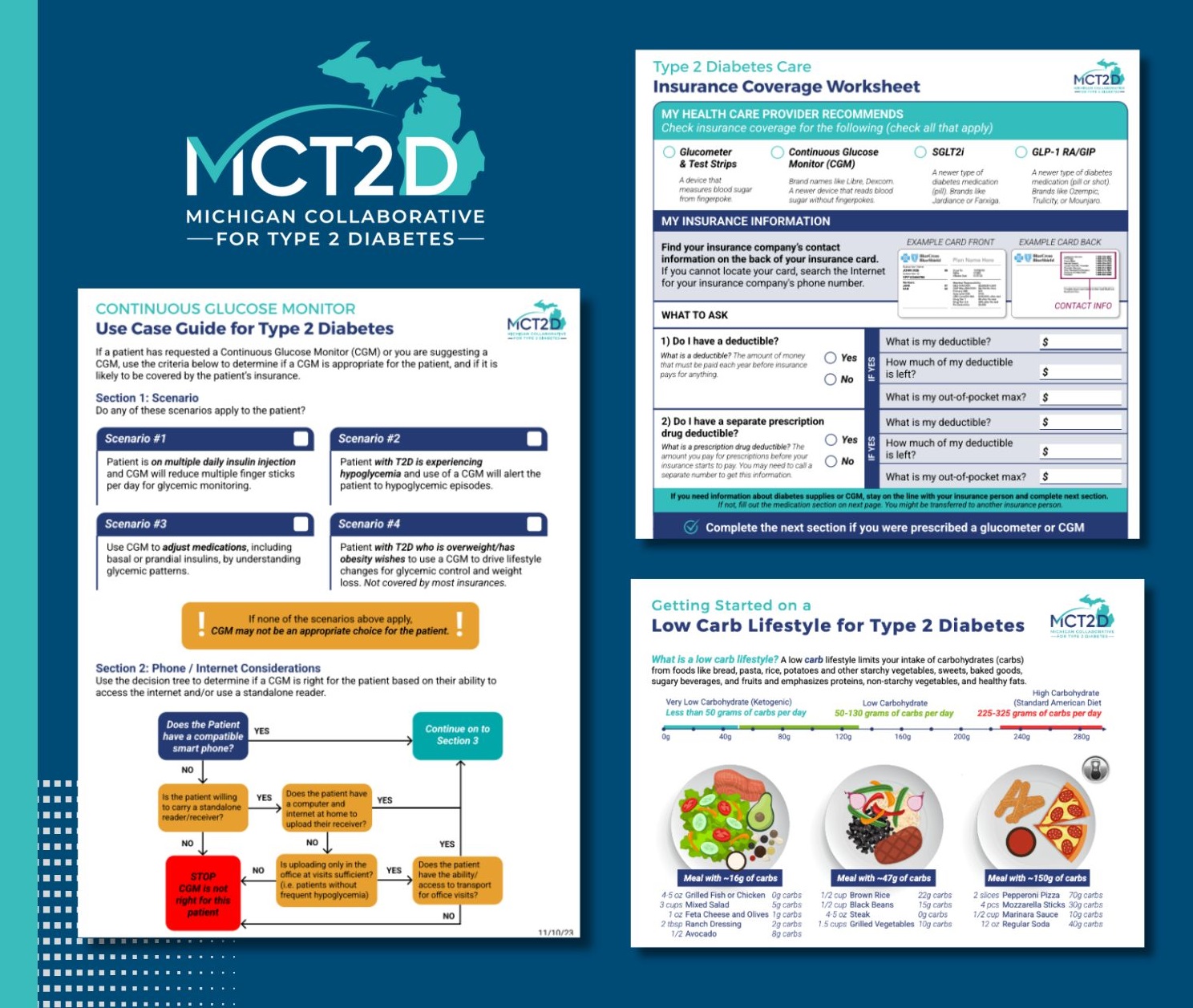
In addition to supporting patients, MCT2D addresses the needs of clinicians by offering guidance on clinical best practices, as well as insurance coverage and cost-related issues. MCT2D also hosts regional meetings twice a year and monthly educational webinars where guest speakers deliver presentations on topics requested by collaborative members. Sessions have covered topics such as “Mental Health and Diabetes,” “Working with Specialists,” and “Metabolic Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes.”
MCT2D’s impact on the quality of T2D care is dependent on strong collaborative partnerships with its 23 participating physician organizations. While MCT2D brings together physician participants from primary care, endocrinology, and nephrology, it centers the crucial role of other members of the care team, including pharmacists, nurse practitioners and physician assistants, care managers, nurses, and dietitians. As Dr. Oshman explains, "Taking care of people with T2D is a team sport. The strength of our collaborative comes from our diversity."
Over the past year, MCT2D and MVC have collaborated in several ways. MVC provides claims-based data and analytic consultation to support MCT2D in establishing quality improvement benchmarks. MVC also collaborated with MCT2D in 2024 to develop a statewide report on T2D in Michigan. This report provided a comprehensive overview of the demographics, healthcare visits, and prescription utilization patterns of patients with T2D in Michigan. The report highlighted key trends in healthcare utilization within this patient population, including emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and consultations with primary care providers (PCPs) and specialists.
MVC is currently partnering with MCT2D on a value exercise to compare the use of guideline concordant medications and change in cost and outcomes among T2D patients in MCT2D practices compared to non-participating practices. This work significantly enhanced the MVC team's understanding of pharmacy claims data from BCBSM and BCN and provided valuable insights that will inform future projects and analyses using pharmacy claims data.
MVC is proud to partner with MCT2D in advancing T2D care across Michigan. The BCBSM-funded CQIs play a crucial role in driving healthcare quality improvement, and MVC is excited to continue showcasing the innovative contributions of individual CQIs and the ways in which MVC’s data analytics are supporting high-value care initiatives across the portfolio.