On behalf of the MVC Coordinating Center, let me first start this end-of-year blog by thanking you all for your partnership and continued support throughout 2025. In case you blinked and its now December – don’t worry, you’re not alone! The last year has flown by with plenty of twists and turns along the way. Before we get caught up in the holidays and planning for 2026, we wanted to step back and celebrate the successes we achieved together over the last 12 months.
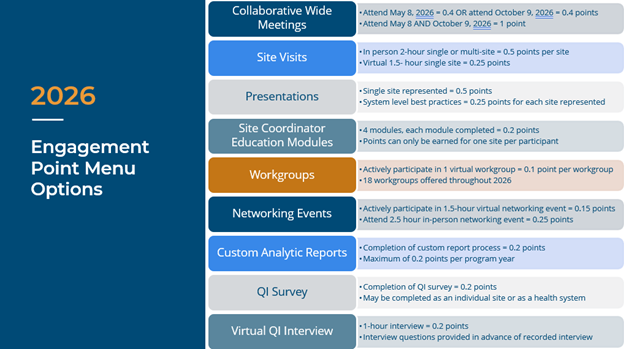
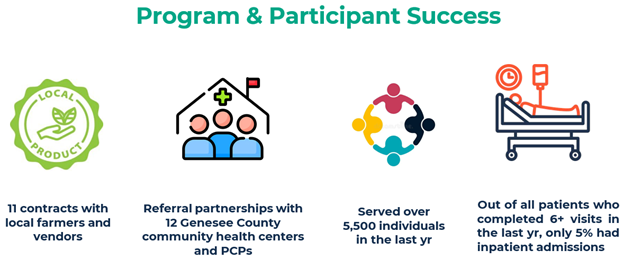
In writing my reflection piece last year, I highlighted that both our engagement participation and analytics utilization were far above previous years. While this gave us a hard act to follow, we are delighted to share that this trend continued upwards in 2025. Over the last year, we welcomed two new hospital members to the collaborative, delivered 23 virtual workgroups with an average attendance of 41, facilitated 24 different member presentations, completed 9 site visits, delivered 14 custom analytic requests, and supported 106 new users in gaining access to our online registry. On top of all of this, we held two collaborative wide meetings in Midland and Livonia, with 197 member representatives joining us to share stories, spotlight successes, and support one another in navigating all of the challenges which 2025 decided to bring.
These flagship numbers only tell one part of the story; the true value of each of the activities detailed above comes from the relationships and partnerships developed as a result of the time spent together. We hope you all have taken as much benefit from these collaborations as our group has during this time. Which brings me to another highlight…the MVC Coordinating Center. Let’s take a moment to celebrate the people who not only help make all of the above possible but that make this such a great place to work. Thank you to the entire MVC team for your hard work and commitment to supporting our members throughout 2025. I’m excited for what the next year will hold. Speaking of which, here’s a sneak peek of a few things that will be taking place in 2026.
Collaborative Wide Meetings, Networking Events, and Virtual Workgroups
MVC’s 2026 engagement events calendar is now live. Our spring collaborative wide meeting will take place on Friday, May 8 in Traverse City and we will be returning to Livonia for our fall meeting on Friday, October 9. These forums continue to be supported by virtual and in-person networking activities and dinners throughout the year, and dates for our regular suite of virtual workgroups can also be found on the 2026 calendar. Save the dates - we look forward to seeing you at each of these events!
MVC Site Visits
We visited a number of you in 2025, providing the opportunity to strengthen our understanding of member activities, priorities, and system-level practices. This effort will continue next year, and members can participate in these site visits in either a virtual or in-person capacity, with P4P engagement points on offer for taking part. If you are interested in getting on the calendar for 2026, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
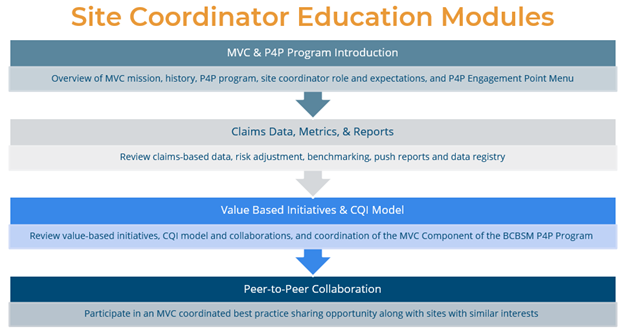
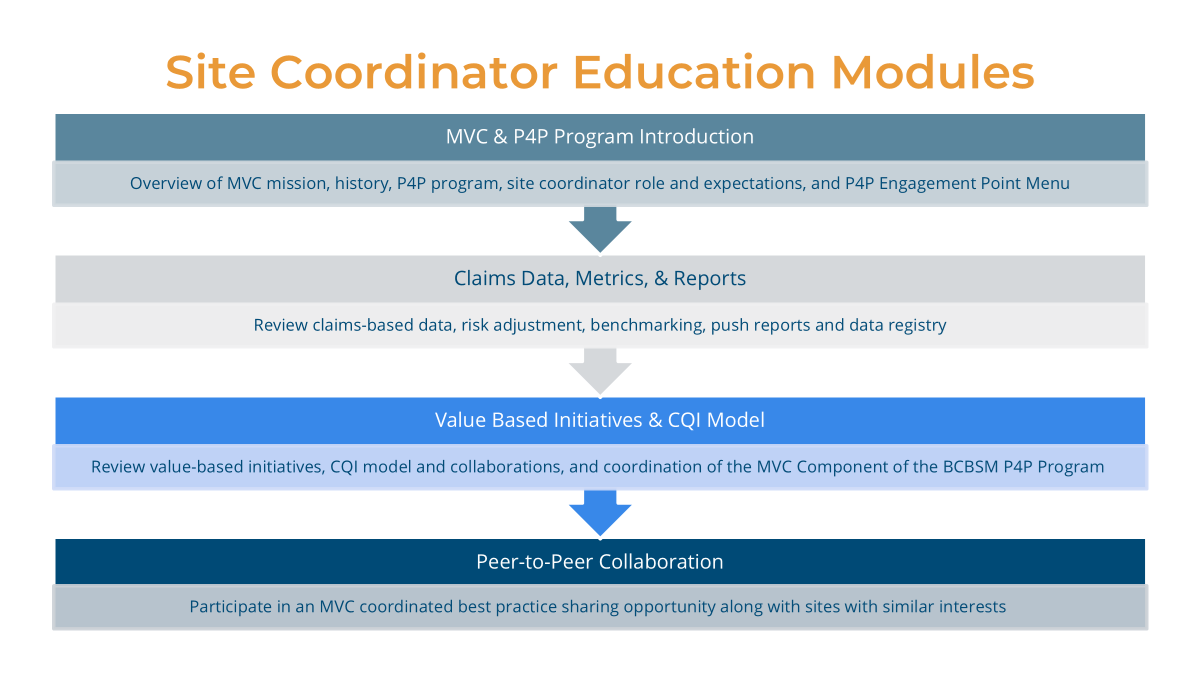
MVC Site Engagement Coordinator Education Program
In response to member feedback, MVC will be launching a new Site Coordinator Education Program in 2026, designed to offer a flexible, individualized, rolling training curriculum to provide members with a stronger understanding of MVC data, share tools to help evaluate metric progress, and facilitate peer collaborations. This program is in high demand with capacity already met for the first round of registration. Additional opportunities to participate in this new education program will open throughout the calendar year – more communications to follow!
New MVC Component of the BCBSM P4P Program PY26/27 Registry Pages & Webinars
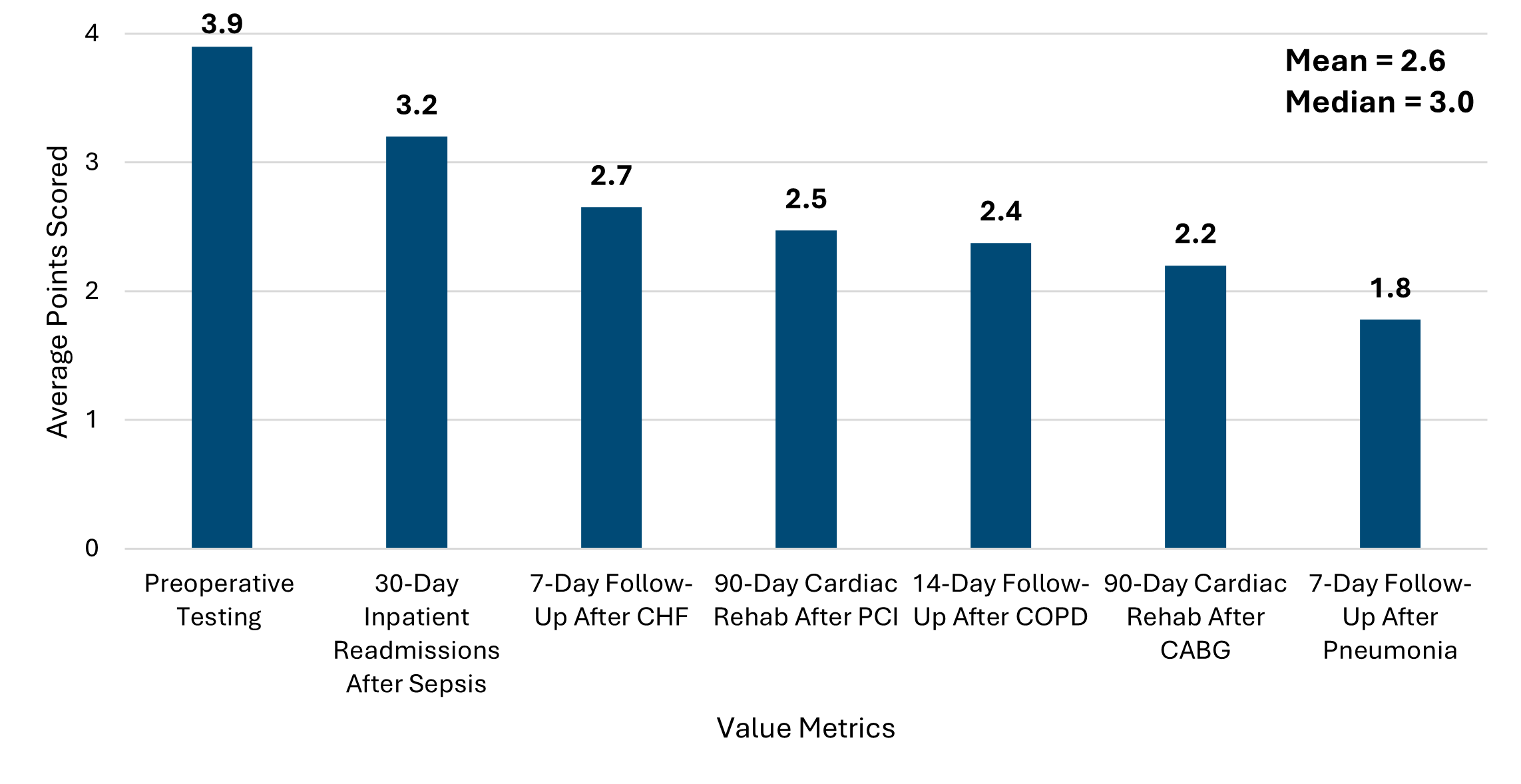
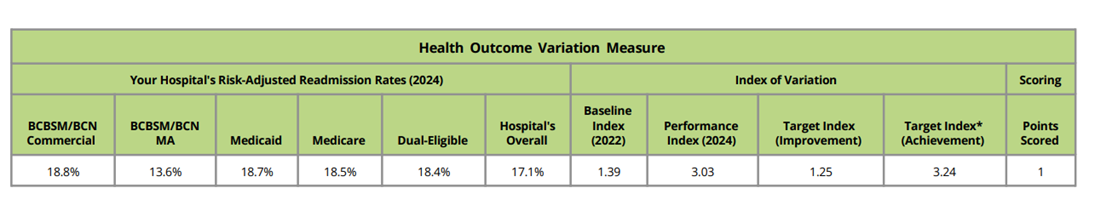
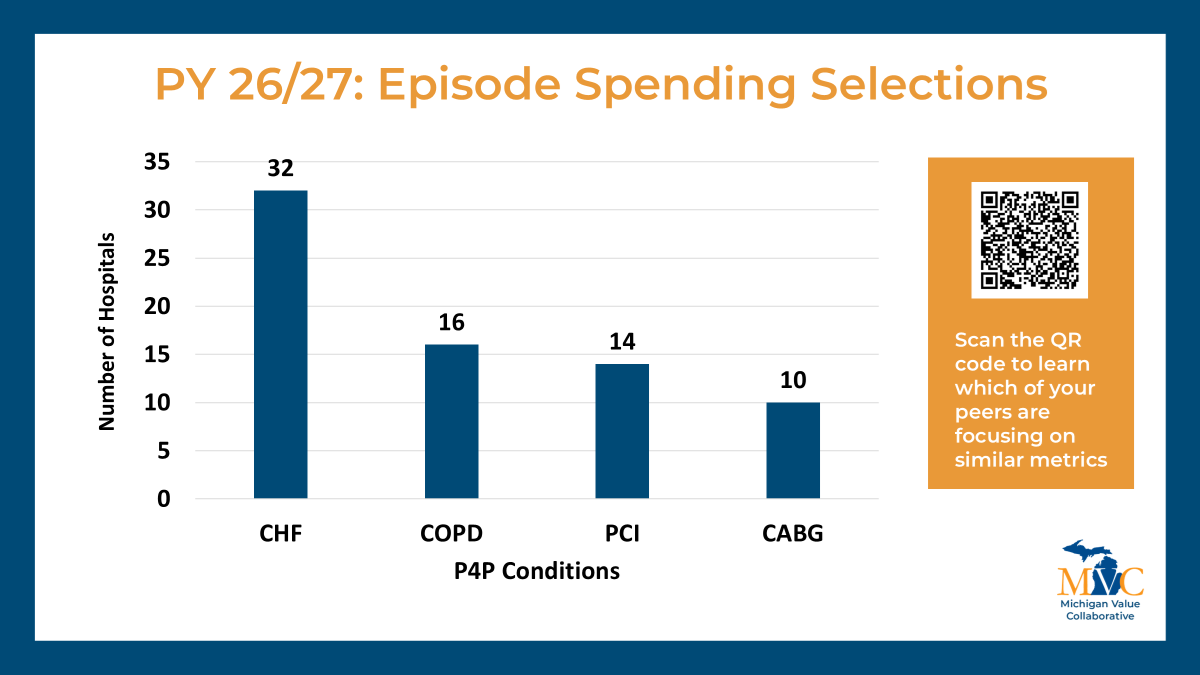
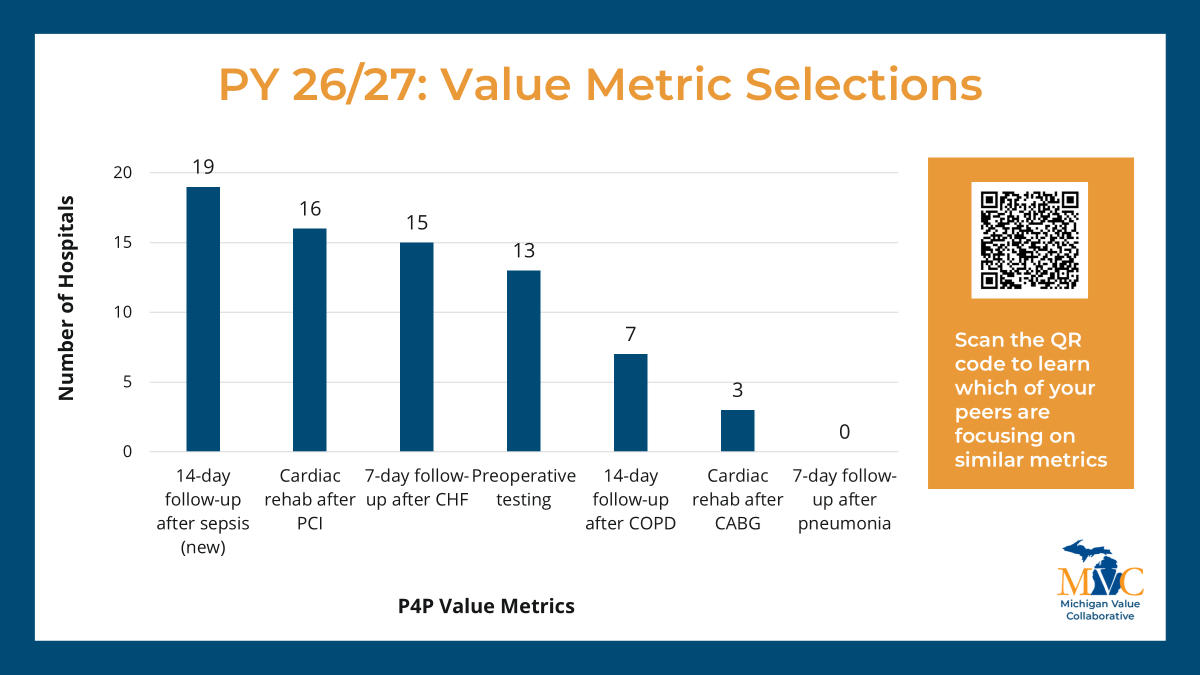
As with previous cycles, new P4P pages will be launched at the turn of the year to correspond with the changes implemented for PY26/27. These pages will look and feel similar to those currently available with a few important updates to reflect changes to our episode spending and value metric menu options and the introduction of MVC’s new Health Outcome Variation Measure. The latter reflects a new metric to the MVC Component, and to support members in navigating and utilizing these new registry pages, dedicated explainer webinars will be held in January.
MVC Push Reports and Custom Analytics
As highlighted above, MVC’s push reports and offer of custom analytics were well utilized by members in 2025, and to reflect member feedback, efforts will be spent strengthening this offering for member benefit in 2026. Remember, if you are interested in working with the Coordinating Center on a custom build, reach out to us by email. [LINK]
Thank you again for your continued partnership throughout the last year and we look forward to more successes in 2026. Have a great holiday and a happy new year when it rolls around.