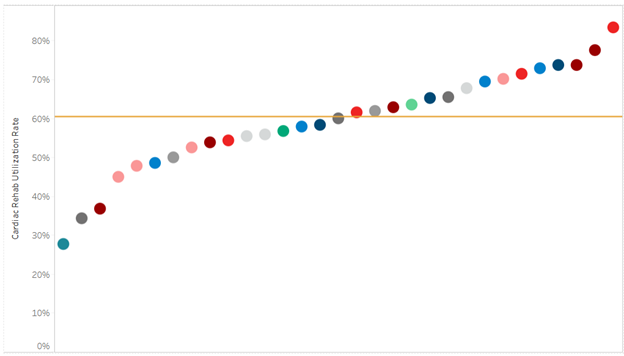In November, MVC hosted two virtual workgroup presentations – the first, a rural health workgroup, featured Hillsdale Hospital’s mobile health unit initiative. The second, a post-discharge follow-up workgroup, continued a presentation started at MVC’s February 2025 health in action workgroup on patient journey mapping and introduced a joint patient storytelling project by Healthy Behavior Optimization for Michigan (HBOM) and Michigan Cardiac Rehab Network (MiCR). The MVC Coordinating Center hosts workgroup presentations twice per month covering a variety of topics including post-discharge follow-up, sepsis, cardiac rehab, rural health, preoperative testing and health in action.
Rural Health Workgroup – Hillsdale Hospital
The first workgroup of the month provided a review of Hillsdale Hospital’s mobile health unit, which aims to deliver essential health services to patients living in rural communities who may otherwise struggle physically or financially to reach traditional care settings.
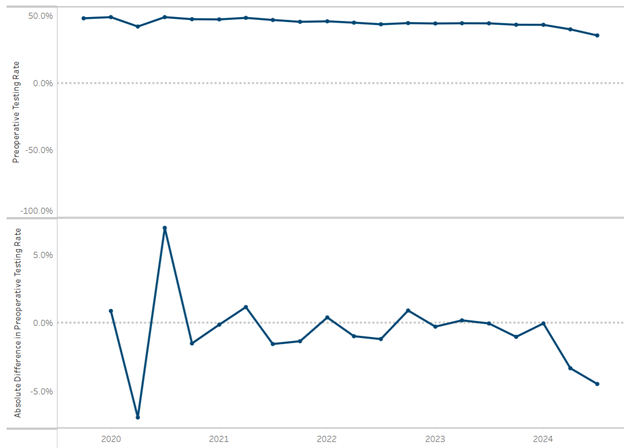
As Lindsey Crouch, Director of Outpatient Clinics, Home Care, and Durable Medical Equipment for Hillsdale Hospital explained, rural communities face higher health outcome variation, transportation issues, limited accessibility to primary care providers, and high unnecessary emergency department (ED) utilization (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Hillsdale County Community Health Needs Assessment (CHNA) Survey Data: Difficulty Finding or Getting Transportation to a Doctor in 2024, 2022, 2019, and 2016

During the Covid-19 pandemic, Hillsdale County’s health department purchased a mobile health unit in an effort to close the gap in healthcare access for their community. However, despite continued need, utilization of the mobile unit has waned in recent years.
Hillsdale Hospital aimed to revitalize the mobile health unit to:
- Bridge access gaps in rural areas. For many rural residents, distance to hospitals or clinics, limited transportation, and infrastructure challenges can hinder timely access to care. A mobile health unit can bring services to patients rather than requiring patients to travel long distances. This helps to reduce one significant non-medical barrier to care.
- Focus on preventive and ongoing care. The mobile unit’s design supports not just acute care, but preventive services — screenings, check-ups, chronic disease management — especially helpful for rural populations that may have higher chronic disease burden and less frequent access to routine care.
- Address gaps in health outcomes between communities. By delivering care directly to underserved communities, this model aligns with broader efforts to ensure that where a person lives does not determine whether they receive high-value, quality healthcare.
Throughout this program, Hillsdale Hospital aimed to improve health outcome variation with a goal to achieve a 15% improvement in selected chronic disease metrics (e.g., blood pressure control) while also establishing partnerships with local organizations for sustainability.
Throughout the presentation and follow-up discussion, participants addressed several key considerations related to implementing and operating the mobile health unit including:
- Logistical planning & scheduling. Which rural towns or areas will be served? How often do visits occur? How to communicate the schedule to residents to maximize utilization?
- Service offerings. What mix of services beyond basic triage should be included? Considerations may include screenings, chronic disease management, preventive care, and referrals when needed to ensure the mobile unit meaningfully supplements local rural healthcare capacity.
- Coordination with local providers. What existing local hospitals, clinics, and community health organizations should be involved to ensure continuity of care? Consider these, especially follow-up and referrals, for more advanced services.
- Addressing rural-specific challenges. What unique barriers impact your community? Consider transportation, limited staffing, and supply chain constraints.
Hillsdale Hospital’s mobile health unit embodies a vision for bringing high-value, high-quality care to rural Michigan. By lowering access barriers and delivering preventive and ongoing services directly to patients in their communities, this initiative can help improve health outcomes, reduce reliance on emergency services, and foster trust in healthcare among rural residents.
Insights from this workgroup have several practical implications for other rural hospitals and provider organizations across Michigan:
- Expansion is possible through mobile care. Rural hospitals can leverage mobile health units as an extension of their current clinical outreach, helping to connect with populations that may rarely visit brick-and-mortar facilities.
- Support chronic disease management. By delivery of routine care and screenings, mobile units can help stabilize chronic conditions earlier, reducing acute exacerbations and potentially reducing avoidable ED visits.
- Enhance care coordination. Partnering with mobile health teams and community resources can help coordinate follow-up appointments, testing, and specialty referrals to create a more continuous care experience for rural patients.
- Advance population health goals. Mobile services can function as a tool within a hospital’s broader population health strategy, align with value-based initiatives, community health needs assessments, and provide the opportunity for all people to achieve optimal health goals.
- Gather meaningful community insights. Regular presence in rural communities can help hospitals better understand local barriers, non-medical drivers of health, and other care gaps which may inform program planning, grant proposals, and collaborative partnerships.
MVC Rural Health Workgroup: Nov. 4, 2025
Post-Discharge Follow-Up Workgroup – MVC and HBOM
The second MVC workgroup of November featured a joint presentation by MVC’s Associate Program Manager, Jana Stewart, MPH and HBOM’s Informatics Design Lead, Noa Kim, MSI. The workgroup kicked off with an overview of the rationale behind placing a greater emphasis on post-discharge follow-up – particularly how timely and effective follow-up care can reduce readmissions, improve patient outcomes, and ease transitions from inpatient to outpatient or home settings.
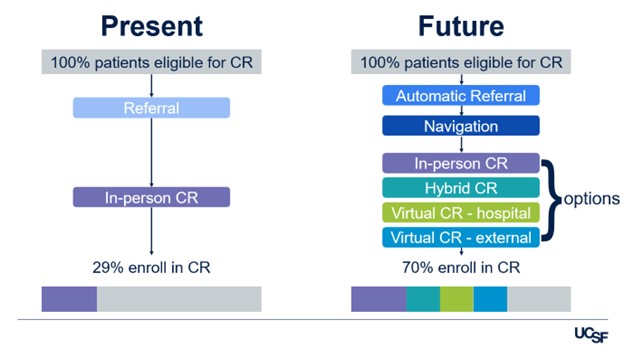
Next, as a continuation of the February 2025 health in action workgroup presentation on patient journey mapping, Stewart showed how mapping can be used to highlight key moments in a coronary heart failure (CHF) patient’s journey where there may be opportunities for post-discharge care coordination improvement – e.g., medication reconciliation, patient knowledge, frequent rehospitalization, low follow-up rates, and lack of social and community support.
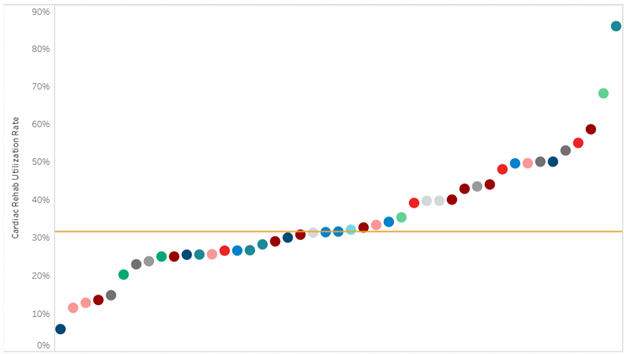
An important strategy for combating these challenges for CHF patients is engagement in cardiac rehabilitation. And yet, patients rarely optimize this opportunity. Patient storytelling can help patients recall details, model scenarios a patient may experience in the future, and reduce the burden of information provided during a visit and may be a strategy to optimize cardiac rehab enrollment.
Under the umbrella of Michigan Cardiac Rehab (MiCR), a collaboration between the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Cardiovascular Consortium (BMC2), MVC, and HBOM, several initiatives have been developed aimed at optimizing guideline-directed medical therapy including the development of NewBeat materials and now the Heart-to-Heart storytelling campaign (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Examples of MiCR Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy Campaigns

As Kim explained, the goals of the Heart-to-Heart project are to collect diverse first-person accounts of cardiac rehab in video, audio, and photo formats from patients and clinicians from across Michigan to produce a compelling, free, reusable story library for use by cardiac rehab advocates across Michigan and beyond.
For hospitals and health systems across Michigan seeking to improve post-discharge outcomes, insights from this workgroup offer the following next steps:
- Use journey mapping and storytelling in quality improvement. By mapping patient journeys and capturing patient experiences, providers can better identify and address systemic barriers to safe discharge and recovery.
- Adopt standardized discharge-to-follow-up workflows. Hospitals should ensure that discharge planning includes scheduling follow-up appointments, medication reconciliation, and clear communication of next steps before patients leave the hospital.
- Prioritize high-risk patients for post-discharge support. Patients with chronic illness, limited social support, or social determinants that might hinder recovery deserve extra attention during discharge planning and follow-up scheduling.
- Assign care coordinators or navigators. Especially for high-risk or complex patients, dedicated staff to oversee follow-up care – manage appointments, support communication, track adherence, and offer resources – may reduce readmissions and improve outcomes.
- Leverage post-discharge care as part of value-based care strategy. Effective follow-up after discharge supports long-term patient health, reduces avoidable costs, and aligns with goals of high-value care frameworks.
MVC Post-Discharge Follow-Up Workgroup: Nov. 20, 2025
If you are interested in pursuing a healthcare quality improvement project, MVC has data specialists available to help you navigate our data resources and create custom analytics reports to support your efforts. Please reach out to us by email [LINK] if you would like to learn more about MVC data or engagement offerings!