November is Diabetes Awareness Month, a time to bring attention to the growing prevalence and impact of diabetes as well as the importance of early diagnosis, effective management, and prevention. According to the CDC, diabetes is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the United States, affecting vital organs such as the nervous system, kidneys, heart, and eyes. In 2021, it was estimated that 38.4 million people of all ages had diabetes—more than 1 in 9 adults in Michigan alone—a number that continues to rise globally. Additionally, recent studies show that 98 million American adults have prediabetes, putting them at high risk for developing Type 2 diabetes (T2D). The need for increased awareness and proactive care has never been more urgent.
Despite being one of the most prevalent chronic conditions worldwide, T2D is largely preventable. Given its chronic nature, it is essential to advocate for widespread access to patient resources, leverage data analytics to pinpoint areas for improvement, and ensure that all individuals across Michigan have the opportunity to access care that can prevent the disease from progressing.
MVC Offerings for T2D Care
MVC is committed to using claims-based data to improve the health of Michigan through sustainable, high-value healthcare. Recently, MVC expanded its focus to address T2D and its complications. In March 2024, MVC incorporated two high-volume emergency department (ED) conditions into its new ED-based episodes: diabetes with long-term complications (e.g., renal, eye, neurological, and circulatory issues) and short-term complications (e.g., ketoacidosis, hyperosmolarity, or coma). These ED-based episodes were developed in partnership with MEDIC and can be used to generate custom analytics for any MVC hospital or physician organization member.
MVC also has ongoing collaborations with the Michigan Collaborative for Type 2 Diabetes (MCT2D) to identify opportunities to improve care for T2D patients and evaluate the impact of CQI initiatives. Currently, both teams are partnering on a value exercise to assess whether practices participating in MCT2D reduced the use of certain diabetes medications compared to non-participating sites. This work will provide valuable insights into medication utilization.
More recently, MVC’s collaboration with MCT2D led to the creation of a new report on T2D in Michigan. It provided demographics and analyses for patients with T2D in Michigan insured by Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan (BCBSM), Blue Care Network (BCN), Medicare Fee-for-Service (FFS), and Michigan Medicaid between 2017 and 2023. The report also integrated pharmacy prescription claims. The report showcased several key trends, including:
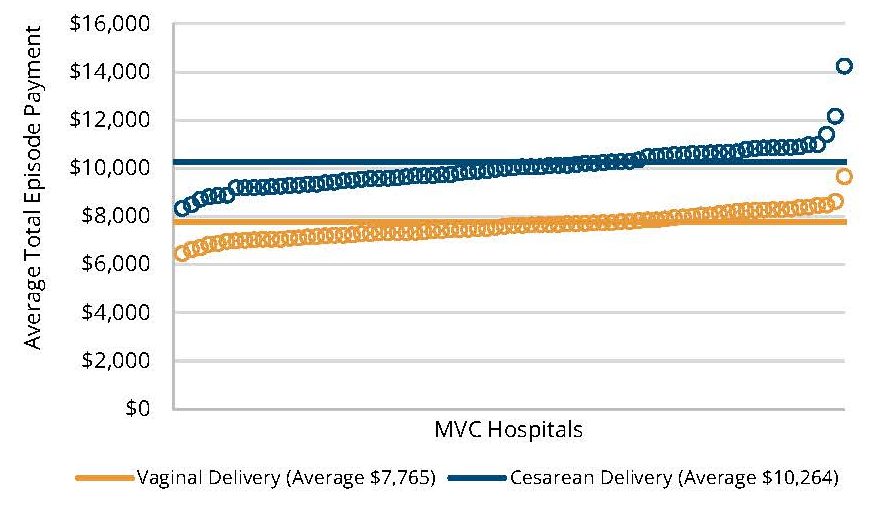
- A notable decrease in ED utilization and hospitalizations for T2D care from 2017-2023 (Figure 1).
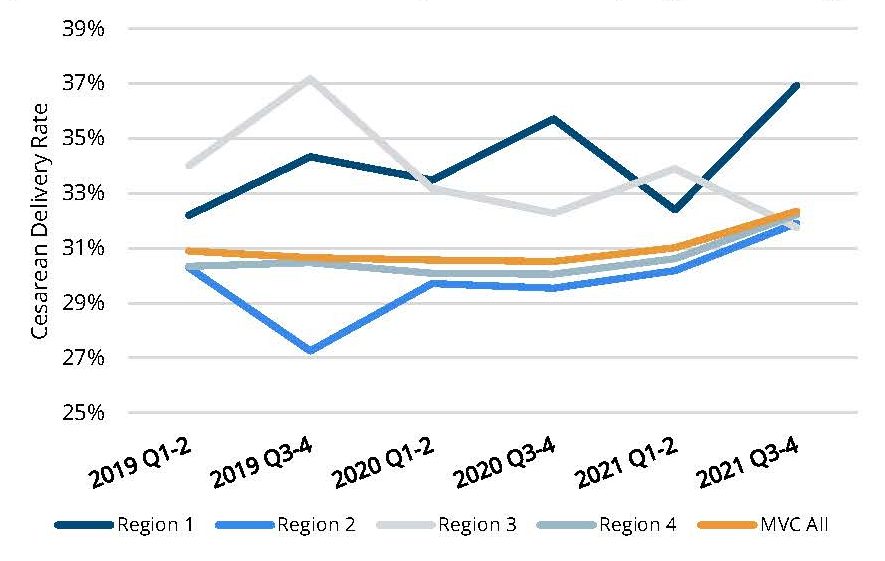
- An increase in visits with primary care providers (PCPs) and specialists, such as endocrinologists and nephrologists (Figure 2).
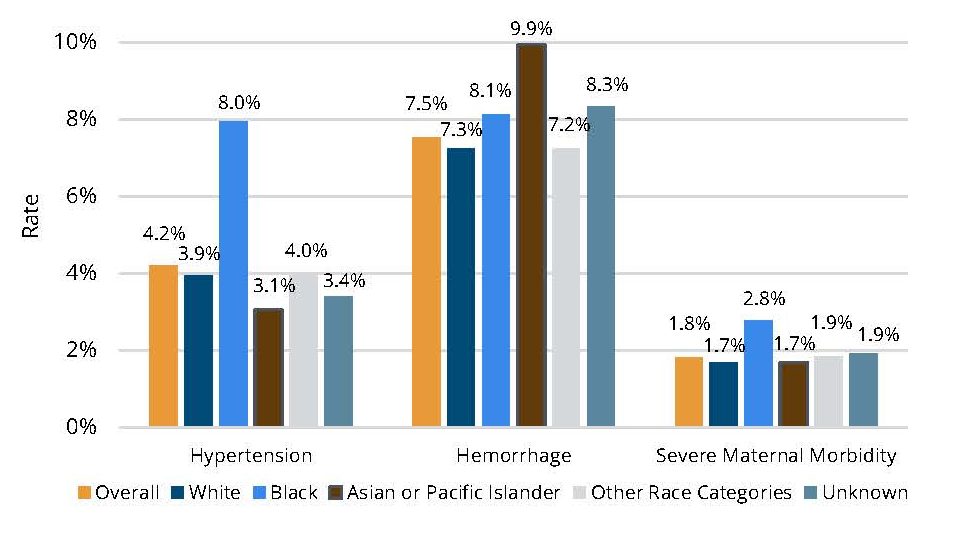
- A shift in prescription utilization, with increased use of newer medications like GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, while the use of older therapies such as insulin and sulfonylureas declined (Figure 3).
The report also highlighted important demographic trends, including that T2D patients in Michigan are, on average, older, more likely to be male, and more likely to be Black, with a higher prevalence of non-commercial insurance coverage. These insights are helping MVC and MCT2D to focus their future efforts.
Looking Towards the Future
Although the prevalence of diabetes is a significant challenge, the innovative efforts of groups such as MCT2D and the American Diabetes Association provide hope for the future. MVC is excited to complete and share its value exercise with MCT2D in 2025, as well as continue to build on its offerings to MVC member hospitals and physician organizations for diabetes-related improvement projects.
Diabetes Awareness Month offers an opportunity to reflect on the challenges faced by millions living with diabetes, while also recognizing the significant progress being made in the fight against the disease. With the continued support of healthcare professionals, organizations, and communities, MVC is committed to improving care, prevention, and education. Together, we can raise awareness, improve outcomes, and provide support for those affected by diabetes.