In May, MVC hosted two virtual workgroup presentations – the first, a sepsis workgroup focused on Covenant Health’s strategies and successes in improving sepsis bundle compliance under Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) reporting standards. The second, a health in action workgroup, focused on Michigan Medicine’s efforts to advance post-surgical recovery through early ambulation with the help of care path and command center supported real-time notifications. The MVC Coordinating Center hosts workgroup presentations twice per month covering a variety of topics including post-discharge follow-up, sepsis, cardiac rehab, rural health, preoperative testing, and health in action.
Sepsis Workgroup May 13, 2025
Improving CMS sepsis compliance is a national priority; hospitals that succeed not only avoid penalties but – more importantly – save patient lives. In her presentation, Amy Lorenz, RN, BAS, MPA, Lead QI Specialist and Sepsis Team Leader for Covenant Healthcare pointed out that a CMS compliance score review in January 2021 of just 64% predicated their site’s interest in pursuing methods to improve sepsis compliance.
To start, Covenant Healthcare reviewed the number of sepsis Best Practices Advisory (BPA) alerts (or OurPractice Advisory or OPAs) firing in the background of their Electronic Medical Records (EMR) based on Modified Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) Criteria. The numerous alerts lead to interruptions in workflow, alert fatigue, and frustration.
With the help of their EMR and IT teams, Covenant Health decided to research and validate the use of a predictive model available through EPIC called BPA Level 8. The predictive model is a ruled based, logical scoring system that relies on various criteria such as patient medication orders, lab values, age, and comorbidities to assess the risk of sepsis development for any patient. The predictive model also incorporates non-specific SIRS criteria and additional exclusion criteria (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Covenant Healthcare Base Sepsis Care Path Level 8 Criterion for Exclusion
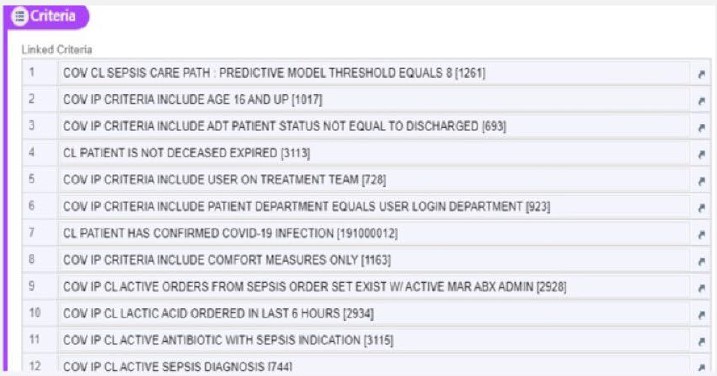
With the replacement of the SIRS Criteria with the Predictive Model in Q3 of 2023, Covenant Health saw the number of interruptive alerts drop from 90-100,000 to just 30,000 per month in 2024. Lorenz notes that this reduction in interruptive alerts alone was a relief to staff. However, they have additionally seen other positive outcomes including:
- A climbing RN action rate (10% to 24.5%),
- An increase in accuracy in sepsis diagnosis (9-18% to 50-60%), and
- A reduction in the number of sepsis flags missed by the model (only 1-2 per month)
These outcomes together suggest that in addition to reducing inefficient alerts, patients are increasingly receiving optimal and appropriate care. Additional outcomes of this initiative highlighted in the presentation included the development of a linked automatic blood culture and/or lactate level order set within the EMR. Additionally, with support from medical leadership, this order set can now be approved by RNs eliminating a common stopgap in care.
A multidisciplinary approach with regular staff feedback, education, and leadership support further drove engagement and compliance of staff. Another Covenant Healthcare team member on the call, Beth Turnbull, Lead Senior EMR Applications Analyst pointed out that nursing leadership was involved in the implementation of this predictive model from the beginning. Nursing also engaged in evaluating data dashboards, routine compliance audits, and collaborative huddles to monitor sepsis bundle adherence and maintain accountability.
While Covenant Healthcare’s predictive model is specific to their EMR program EPIC, attendees noted that there are other predictive model options available. Ultimately, the key takeaways from this presentation used to improve sepsis bundle compliance include:
- Identify and analyze fall outs: to prioritize and target education
- Deploy an easy-to-access knowledge base to support clinical decision-making: by creating a one-page resource or visual dashboards
- Promote transparency: by increasing access to real-time data and routine collaborative huddles to help keep teams accountable
- Secure leadership backing: but also empower front-line workers to make quality efforts stick
- Measure and validate interventions: based on data and compliance trends
MVC Sepsis Workgroup May 13, 2025
Health in Action Workgroup May 29, 2025
The health in action workgroup featured a joint presentation by Heidi O’Neill, MS, Project Manager Lead; Mary Nowlin, PA-C; and Niki Farquhar, MSE, Project Management Lead from Michigan Medicine. Their presentation centered on the power of interdisciplinary collaboration, data-driven processes, and scalable strategies to embed post-surgical real-time notifications for delayed post-operative ambulation into Michigan Medicine’s post-surgical clinical pathways.
In 2019, Michigan Medicine started a multidisciplinary quality initiative supporting teams across the site to improve outcomes called Advancing Care, Treatment Efficiency, Innovation, Value and Teamwork for Surgical Episodes (or ACTIVATE). O’Neill explained that ACTIVATE places emphasis on teamwork, innovation, and communication to drive patient experience and outcomes. By focusing on units/ services with high observed/expected (O/E) length of stay (LOS >1.0), high surgical volume, and positive leadership engagement; the ACTIVATE team ensured that each unit they invested in had room to improve and support to achieve their goals.
Post-surgical early ambulation, or getting patients up and walking as soon as possible after surgery, has been shown to decrease the length of hospital stay. Common ACTIVATE interventions to promote early ambulation include patient education videos, transport triggers for ambulation from stretcher to bed, documentation of ambulation within four hours, and the development of detailed clinical pathways (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. Common ACTIVATE Interventions to Promote Post-Surgical Early Ambulation
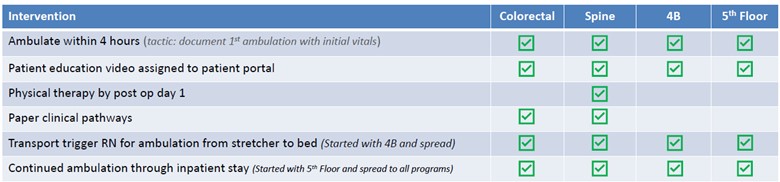
Additionally, Nowlin explained that as the ACTIVATE team spread their interventions across various services, from colorectal to spine then to more general surgical units (4B and the 5th floor) they noticed that there wasn’t a consistent order set for early or sustained ambulation. To ensure consistent documentation, the ACTIVATE team developed an early ambulation order set to be used across all units and started tracking their impact.
ACTIVATE’s efforts to outline post-surgical clinical pathways and optimization of documentation of ambulation eventually led to their collaboration with Michigan Medicine’s Capacity Operations Real Time Engagement Center (or M2C2), launched in November 2022. M2C2 is a state-of-the-art command center designed to act as the hub for Michigan Medicine operations and innovation by leveraging real-time visualization of patient milestone achievement based on EPIC data. Their goal is to not only improve LOS but to ultimately increase the percentage of patients who achieve post-surgical milestones (e.g., early ambulation) in a timely manner. Farquhar explained, M2C2’s integration of care paths and responsive actions when patients deviate from their expected progression are paving the way to reduced LOS, safe discharge, and increased bed capacity.
Figure 3. M2C2 Post-Surgical Procedure Care Path Framework
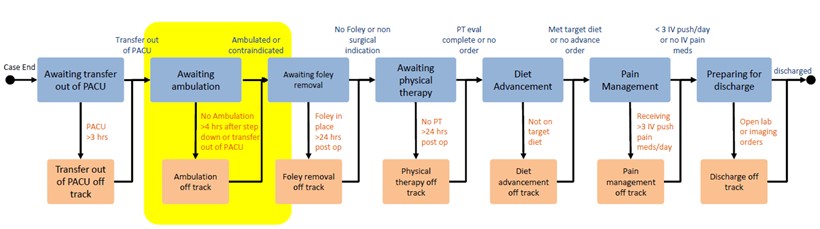
To develop the post-surgical care path framework (Figure 3), Nowlin and Farquhar met with other key stakeholders to ensure that ACTIVATE and M2C2 efforts to optimally progress patients through the early ambulation node of the post-surgical path were synced. Understanding the goal ACTIVATE had previously set for ambulation within four hours of exiting the OR, M2C2 set alerts for patients that had no documented ambulation by three hours post-surgery to allow for a one-hour intervention window. During this period, M2C2 clinical expeditors (CEs) conduct a patient chart review and then contact the nurse and medical provider to discuss barriers to ambulation.
Within the first quarter of the new M2C2 alert for ambulation going live, nearly 1280 alerts were logged: 559 resulting in contact with the care team to assess barriers to ambulation. When compared to baseline data, a 23.1% decrease in median time to first ambulation was observed for ICU post op patients. For non-ICU post-op patients, a 7.1% decrease was observed. Additionally, a 0.34 day decrease in average LOS was observed. These results indicate opportunities for enhanced patient recovery, shorter LOS, and better overall patient outcomes.
Lastly, Farquhar outlined opportunities to continue to progress with early ambulation including:
- Refine exclusions for patients that are not appropriate for early ambulation
- Improve visibility of ambulation status and timeline in EPIC
- Explore improved capture of ambulation in clinical notes
- Enhance alert communication to support nursing
- Continue to work on nurse-to-nurse APS consult orders for pain management control
MVC Health in Action Workgroup May 29, 2025
MVC’s May workgroups exemplify efforts from two different sites to place value on interdisciplinary teams, the importance of data visibility, and alignment across clinical, operational, and administrative units to ensure optimal quality improvement.
If you are interested in pursuing a healthcare improvement program, MVC has data specialists available to help navigate and create custom analytics reports. Please reach out to us by email if you would like to learn more about MVC data or engagement offerings!




