In 2020, the Michigan Value Collaborative (MVC) introduced the Preoperative Testing Value Coalition Campaign (VCC) with the aim of reducing the use of unnecessary preoperative testing for surgical procedures. Preoperative testing, especially in low-risk surgical procedures, often provides no clinical benefits to patients but is ordered regularly at hospitals across Michigan. As part of MVC’s campaign to eliminate unnecessary and potentially harmful preoperative testing, the Coordinating Center developed a related push report, the latest version of which was shared earlier this week to help members benchmark data for common preoperative tests. MVC and the Michigan Surgical Quality Collaborative (MSQC) partnered to distribute these reports more widely and to encourage clinical and quality personnel to work together in identifying patterns and exploring new strategies.
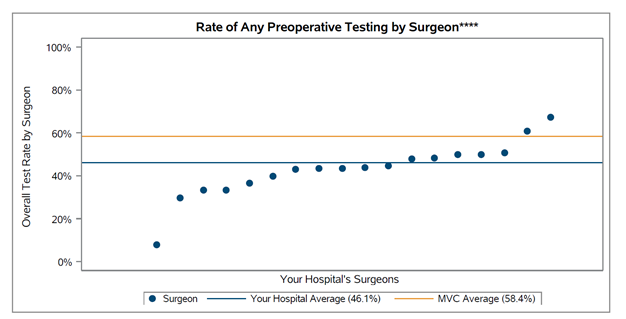
This iteration of the report is the first to include blinded surgeon-level reporting, which will allow for a more nuanced understanding of variation within a given hospital. To include this, the Coordinating Center attributed one surgeon per episode based on condition-specific BETOS codes and NPI specialty information, with the understanding that the attributed surgeon may not be the individual ordering the preoperative test for that procedure. If their MVC data indicates wide variation between specific providers, hospitals may choose to drill down into their own data to investigate further. For hospitals that have several surgeons with enough cases for these procedures, there was significant variation in testing rates (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. Rate of Any Preoperative Test by Surgeon (Blinded Report)
Included in the report were patients undergoing elective and outpatient laparoscopic cholecystectomy, laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair, and lumpectomy. It incorporated index admissions between 1/1/2018 – 12/31/2020 for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan (BCBSM) PPO Commercial, BCBSM Medicare Advantage, Blue Care Network (BCN) HMO Commercial, BCN Medicare Advantage, Medicare Fee-For-Service (FFS), and Michigan Medicaid. Hospitals only received a report if they had 11 or more cases in at least one of the three conditions and at least 11 cases per year in the three procedures combined. The analysis evaluated the use of the following tests using CPT codes: electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, cardiac stress test, complete blood count, basic metabolic panel, coagulation studies, urinalysis, chest x-ray, and pulmonary function.
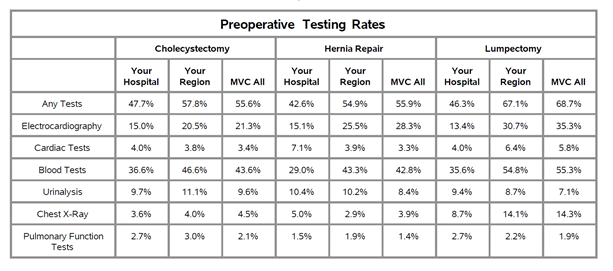
In general, the report demonstrated significant variation in testing rates between members, with some testing rates ranging from 20% to over 90%. Due to the amount of variation, MVC suspects that preoperative testing is overused at the state level such that even hospitals that are average or below average may still have significant opportunities to safely reduce preoperative testing. The report included a table with each hospitals’ rates for each procedure and test, with accompanying comparisons to the rates of regional peers and the collaborative as a whole (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. Preoperative Testing Rates Table (Blinded Report)
The report also included figures for preoperative testing rates by specific tests, by payer, and by procedure. The variety of figures is meant to help hospitals better understand its variability in utilization, since specific procedures or tests may be driving their overall testing rate. One figure, for example, presents a hospital's three procedure-specific testing rates alongside their overall or “combined procedures” rate. To more easily identify areas of opportunity to reduce their overall testing rate, a hospital can compare their procedure-specific rates to determine which is driving their average, as well as compare their average to those of their regional peers and the collaborative as a whole (see Figure 3).
Figure 3. Rate of Any Preoperative Test by Procedure (Blinded)
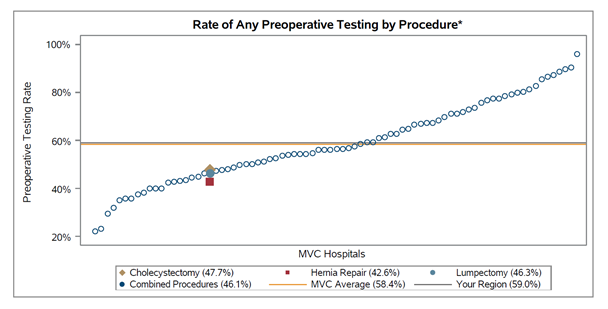
In the case of the blinded example above, this hospital is more frequently ordering preoperative testing in cholecystectomy patients but is ordering fewer tests on average than their peers for all procedures combined. This finding is atypical since lumpectomy was found to have a higher testing rate in general; cholecystectomy testing rates were generally lower. In addition, MVC found that electrocardiography and blood tests (complete blood count, basic metabolic panel, coagulation studies) had the highest testing rates across all procedures.
Helping MVC members to make internal and external data comparisons is core to MVC reporting and is critical to its efforts to reduce unnecessary testing. As part of MVC's continued efforts in this area, the Coordinating Center will share hospital-level preoperative testing data at its upcoming semi-annual meeting in order to foster continued awareness of wide practice variation and encourage best practice sharing between members.
MVC is eager to drive improvement in this area. For more information on how MVC is working to reduce unnecessary preoperative testing, visit its Value Coalition Campaign webpage here. If you are interested in a more customized report or would like information about MVC’s preop testing stakeholder working group, please contact the MVC Coordinating Center at michiganvaluecollaborative@gmail.com.