As August is National Breastfeeding Month, many healthcare professionals and hospitals across the country are joining in to promote its benefits. Currently, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends exclusive breastfeeding of infants for the first six months of life and then alongside solids as long as mutually desired by mother and child for two years and beyond. This updated recommendation – the AAP previously recommended breastfeeding through age one and beyond – acknowledges its continued benefits for mother and child.
Many experts suggest that it is an investment in the health of current and future patients, not just a lifestyle choice. In updating its guidance, the AAP clarifies that breastfeeding beyond one year and up to two years has significant benefits to the mother in particular; lower rates of diabetes, high blood pressure, and breast and ovarian cancers are associated with long-term breastfeeding. In breastfeeding infants, some studies indicate there are fewer respiratory and gastrointestinal infections, incidents of severe respiratory disease or sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), development of chronic illnesses, doctor visits, hospitalizations, and prescriptions. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that an additional $3+ billion in medical costs per year can be attributed to low breastfeeding rates.
Breastfeeding is a personal choice – not everyone wants to or even can breastfeed their baby. For those who choose to, however, being successful is linked to the presence of interventions and support along the way. Evidence-based practices at the hospital level are a critical component for establishing breastfeeding.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) cited a systematic review of 38 randomized controlled trials that found short- and long-term increases in breastfeeding as a result of direct assistance and education across a variety of providers and settings in conjunction with structured training for health professionals. The AHRQ and the AAP also both cite increases in breastfeeding initiation and duration as a result of the Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative, which gives a special designation to facilities that successfully complete an assessment and implement the World Health Organization’s 10 Steps to Successful Breastfeeding.
Some of the evidence-based practices linked to higher breastfeeding rates include individualized support in the first few hours and days following birth, rooming-in, and education and support. Additionally, the CDC’s 2018 national survey of Maternity Practices in Infant Nutrition and Care (mPINC) identified institutional management as an area with the widest range of scores across all states, with 45 being the lowest state score and 95 the highest state score (see Figure 1). As this category is defined by activities such as nurse training and clinical competency, record keeping, and policy setting, it is clear that some important breastfeeding initiatives extend beyond the maternity ward.
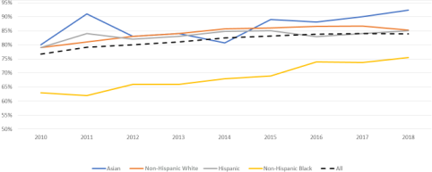
According to the AAP, there are also significant opportunities for more equitable gains in breastfeeding outcomes. The United States continues to see evidence of disparities in success rates – none of the Healthy People 2020 objectives for breastfeeding were met for non-Hispanic black mothers and infants. The rates for any breastfeeding are approximately 10% lower in non-Hispanic black mothers compared to the average for all races/ethnicities (see Figure 2). Similarly, there are disparities in mothers who are younger than 20, low income, or less educated. Hospitals interested in health equity initiatives likely have an opportunity in the realm of breastfeeding support that accounts for socioeconomic and cultural differences.
Figure 2. Rates of any breastfeeding in U.S. by race/ethnicity
A summary of recommendations, provider implementation tools, and other resources are summarized for healthcare providers in the AHRQ breastfeeding provider fact sheet. In addition, MVC would like to spotlight those members with ongoing or completed improvement efforts around breastfeeding. If your site has achieved the Baby-Friendly Hospital designation or has tools for addressing patient disparities in breastfeeding, please consider sharing your story with the Coordinating Center for the benefit of the larger collaborative.
